Featured
Latest articles
For a long time, scientists believed this was how fish rested. Surprisingly, research reveals that this seemingly effortless behaviour actually uses almost twice as much energy as genuine rest.
Ice found in the vast reaches of space isn't as simple as previously thought.
A new study shows teenagers spend over 20% of their drive time looking at their phones, despite knowing the dangers. Experts say simple steps could help keep young drivers, and everyone on the road, safer.
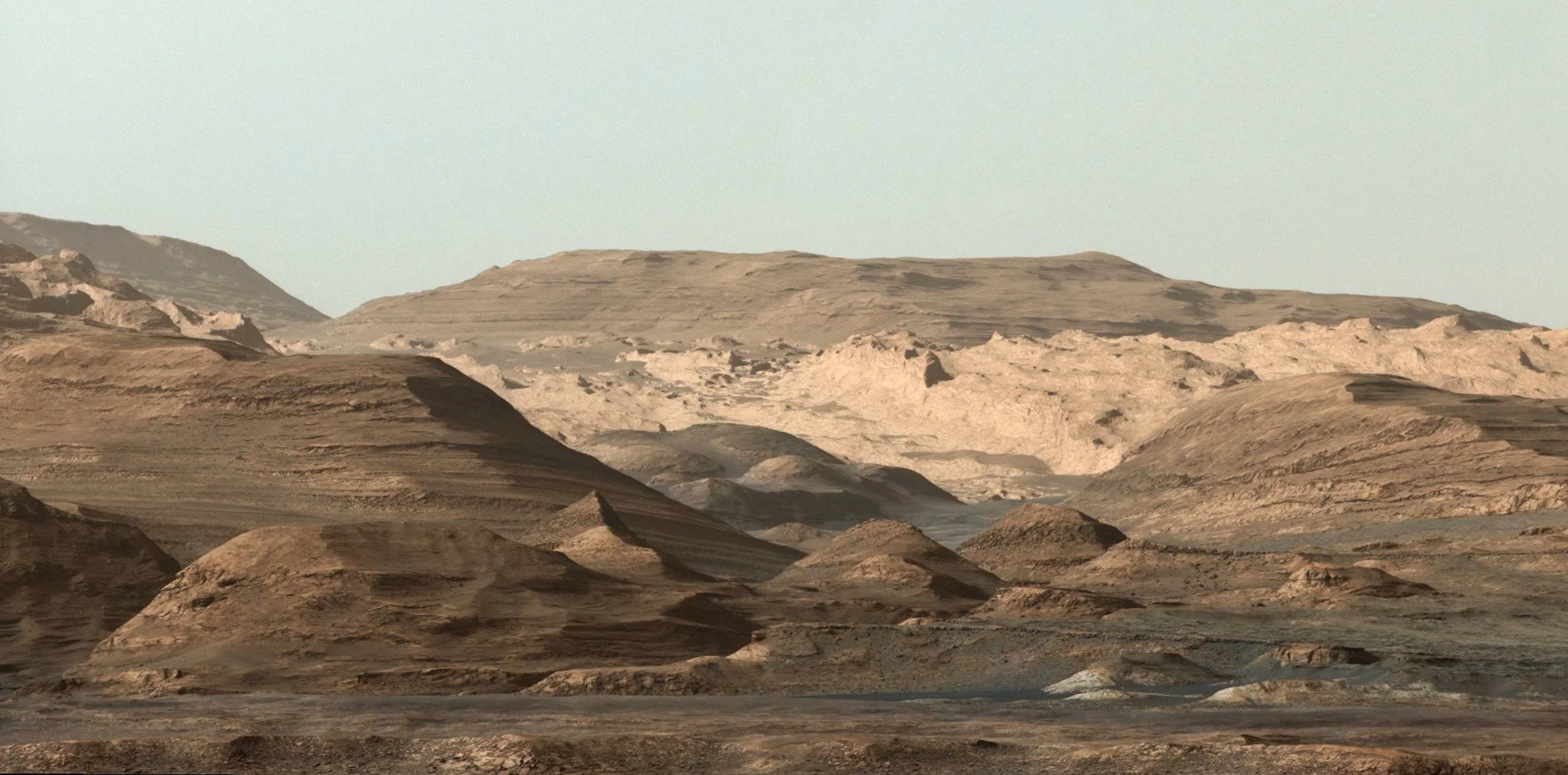
What changed Mars from a potentially habitable world into the barren planet we see today? Scientists at the University of Chicago have taken a significant step toward understanding this mystery.
Researchers have developed advanced materials capable of naturally cooling buildings, significantly reducing energy consumption and lowering utility bills.
Researchers have developed a 3D-printed sponge-like material that uses sunlight to turn seawater into drinkable water, no electricity required. This new aerogel could make clean water cheaper and more accessible for communities worldwide.
Four common causes and some helpful tips on what you can do to alleviate sleep problems according to science
Scientists at the University of Manchester and The Australian National University have created a new molecule that may soon enable ultra-compact hard drives about the size of a postage stamp by allowing data to be stored at 100 times the density of current technologies.
A large-scale study suggests that women who regularly drink caffeinated coffee may experience healthier aging.
According to research, when it comes to protecting your heart, what you eat may be just as important as the type of diet you follow.
As people grow older they often seem to become less sociable. Is this actually the case, and if so, what causes this change?
Have you ever wondered how animals adapt to urban life, with its traffic jams and busy streets? A fascinating observation by researcher Dr. Vladimir Dinets sheds light on how some birds might not only survive but cleverly take advantage of human activities—particularly traffic.
A recent social media trend involving taping one's mouth shut at night to prevent mouth breathing has sparked considerable debate. But according to new research, this popular sleep hack may be less effective—and more risky—than people think.
Research reveals a concerning trend: America's largest cities are slowly sinking—some faster than others
Scientists have discovered just how little of the deep ocean we've actually seen.
Scientists have uncovered how a tiny molecular machine called the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier unlocks the gates to our cells’ powerhouses—an energy-boosting breakthrough that could pave the way for new treatments for cancer, diabetes, and more.
Astronomers have uncovered something unusual happening in our cosmic neighborhood—a small galaxy near the Milky Way is behaving strangely, and no one is quite sure why.
Researchers have successfully created solar cells using simulated lunar dirt, potentially offering astronauts a sustainable energy source without needing to bring heavy materials from Earth.
New research from Brown University reveals surprising insights into why Americans at every economic level have shorter lifespans compared to Europeans.
Have you ever eaten something that made you so sick you couldn't stomach the idea of eating it again? A team of neuroscientists has discovered exactly how the brain creates these strong food aversions after just one bad experience.
Scientists working in one of Earth's most extreme habitats, Antarctica, have made some surprising discoveries.
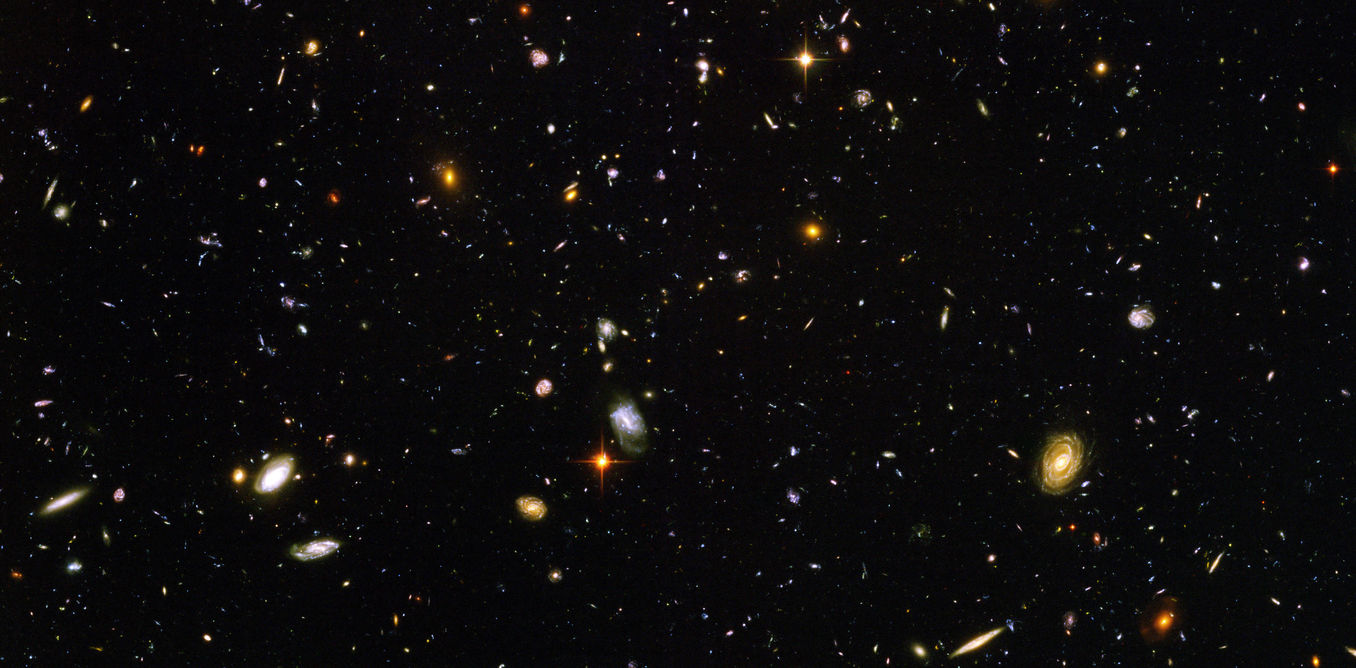
Scientists have long tried to explain the origin of a mysterious, large and anomalously cold region of the sky. In 2015, they came close to figuring it out as a study showed it to be a “supervoid” in which the density of galaxies is much lower than it is in the rest of the universe. However, other studies haven’t managed to replicate the result.
If you enjoy our selection of content please consider following Universal-Sci on social media:





















These are the world’s five deadliest volcanoes … and why they’re so dangerous