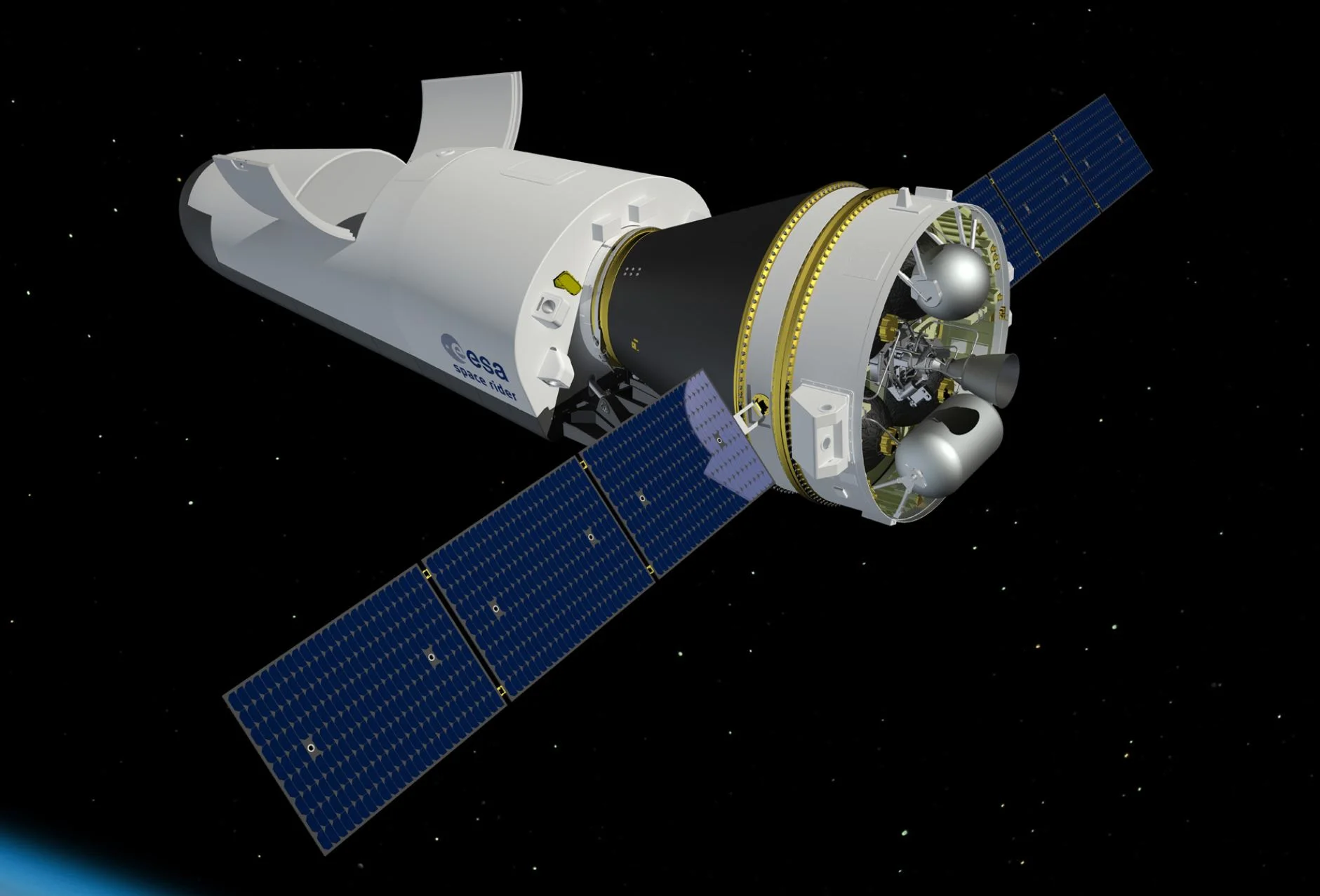
The ESA is developing its own spacecraft capable of re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere. The reusable spacecraft is called the Space RIDER (Reusable Integrated Demonstrator for Europe Return), and the ESA says that the Space Rider will be ready for launch by 2022. It’s being designed to launch on the Vega-C rocket from Europe’s spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana.
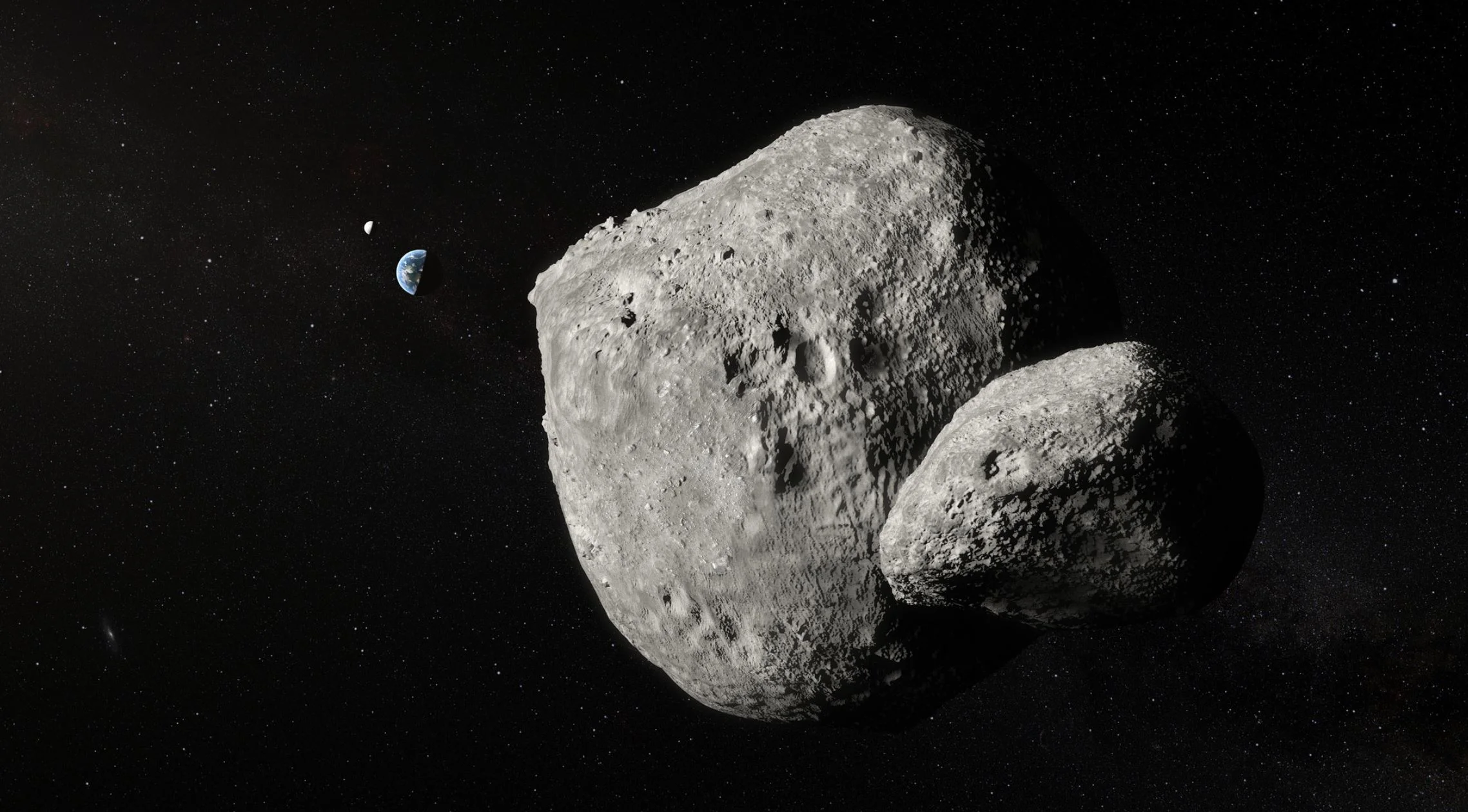
On the 25th of may a double asteroid came uncomfortably close to earth. Here’s what astronomers saw
On May 25th, 2019, a strange, double-asteroid (1999 KW4) flew past Earth at a distance and speed that is likely to make a lot of people nervous. As always, there was no danger, since the asteroid passed Earth at a minimum distance of 5.2 million km (3.23 million mi), over 15 times greater than the distance between Earth of the Moon, and its orbit is well-understood by scientists.
There’s a Ring of Cool Gas Wrapped Around the Milky Way’s Supermassive Black Hole
There’s a lot going on at the center of our galaxy. A supermassive black hole named Sagittarius A-Star resides there, drawing material in with its inexorable gravitational attraction. In that mind-bending neighborhood, where the laws of physics are stretched beyond comprehension, astronomers have detected a ring of cool gas.
Astronomers See an Enormous Coronal Mass Ejection… On Another Star!
For the first time ever, astronomers have witnessed a coronal mass ejection (CME) on a star other than our very own Sun. The star, named HR 9024 (and also known as OU Andromeda,) is about 455 light years away, in the constellation Andromeda. It’s an active, variable star with a strong magnetic field, which astronomers say may cause CMEs.
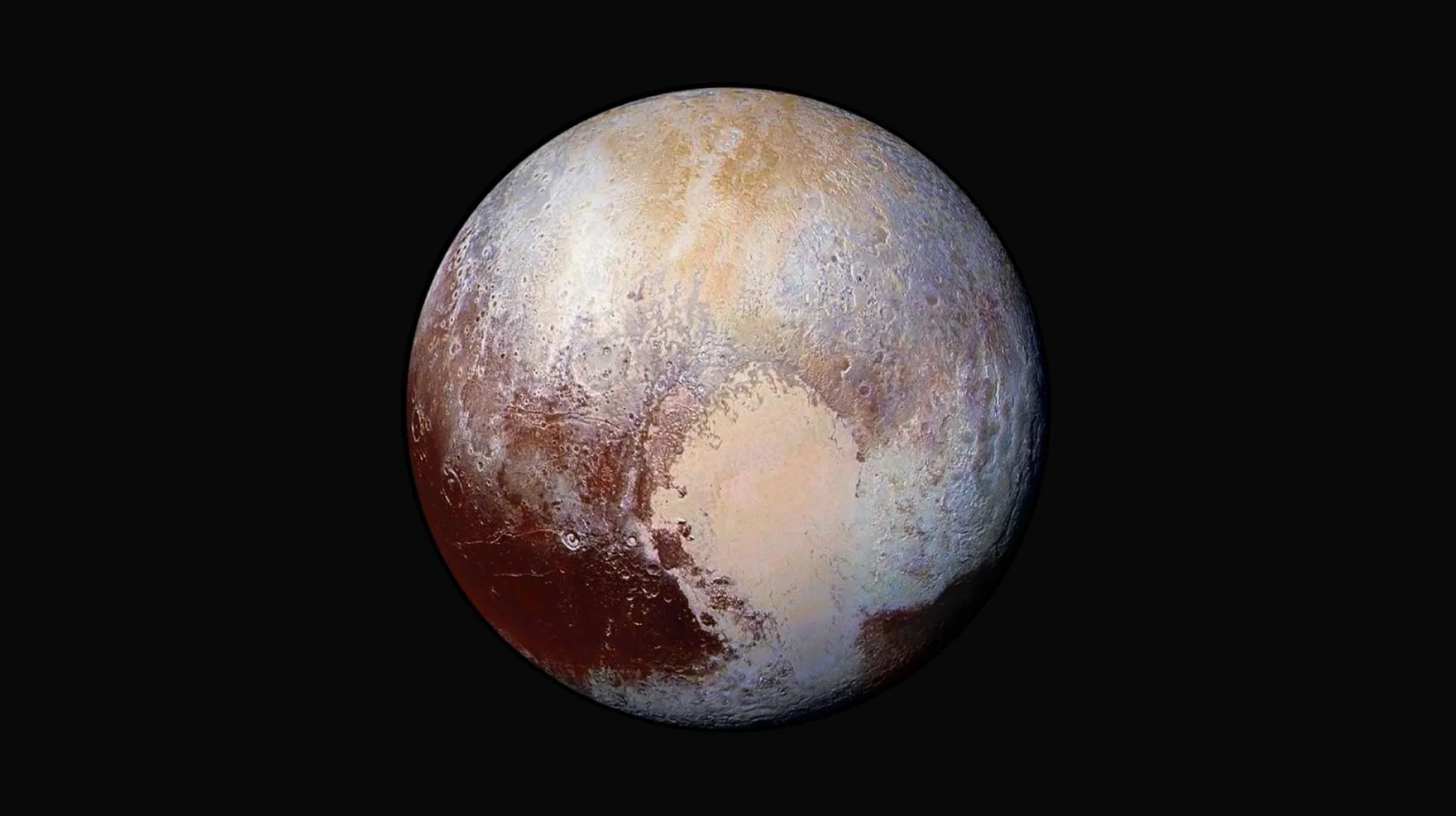
How Will NASA and ESA Handle Mars Samples When They Get Them Back to Earth?
ESO contributes to protecting Earth from dangerous asteroids
The unique capabilities of the SPHERE instrument on ESO’s Very Large Telescope have enabled it to obtain the sharpest images of a double asteroid as it flew by Earth on 25 May. While this double asteroid was not itself a threatening object, scientists used the opportunity to rehearse the response to a hazardous Near-Earth Object (NEO), proving that ESO’s front-line technology could be critical in planetary defense.
NASA is building up a map of the entire sky seen in X-rays, line by line with its NICER experiment
In June of 2017, NASA’s Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) was installed aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The purpose of this instrument is to provide high-precision measurements of neutron stars and other super-dense objects that are on the verge of collapsing into black holes. NICER is also be the first instrument designed to test technology that will use pulsars as navigation beacons.
Five ethical questions for how we choose to use the Moon
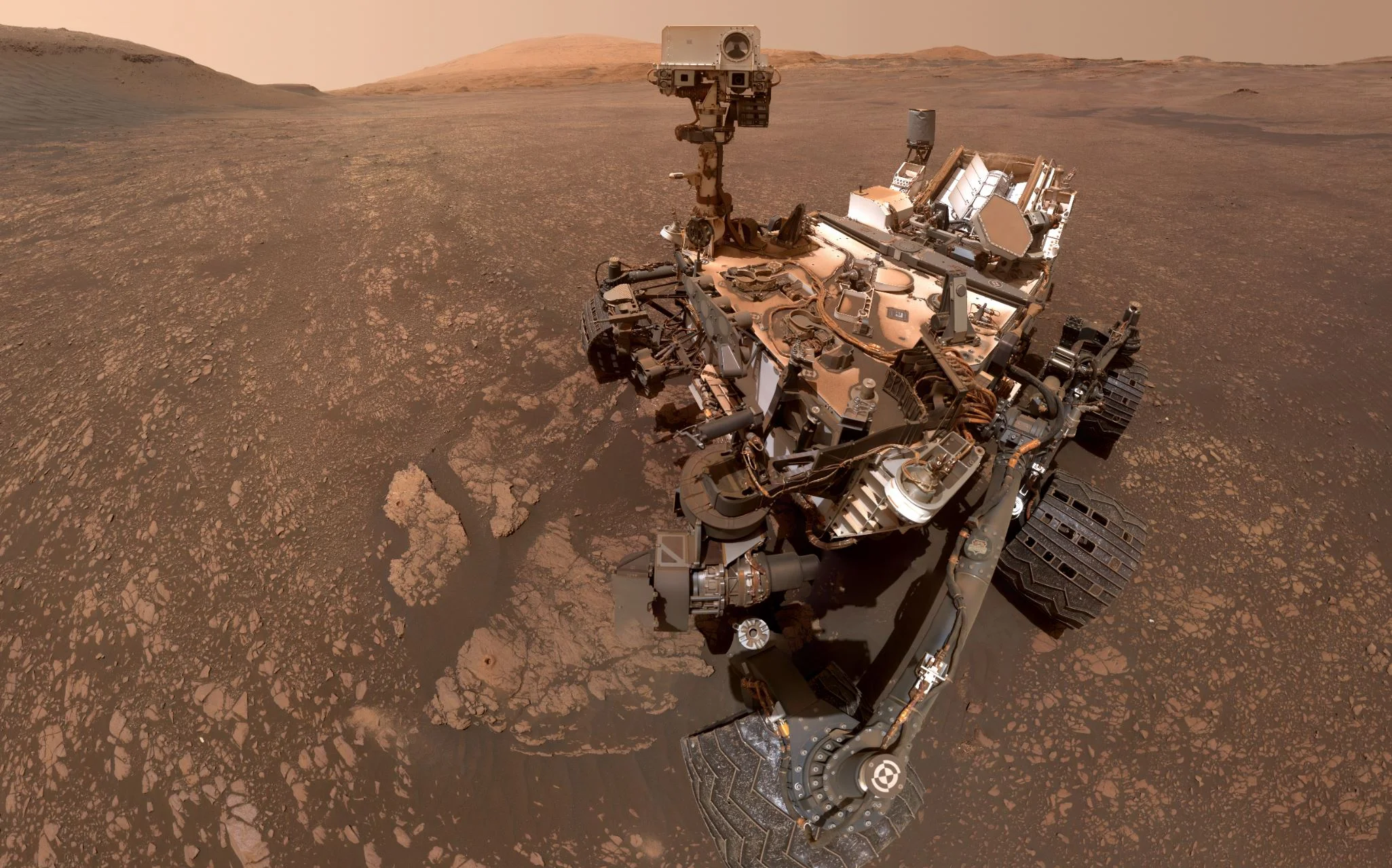
Curiosity has Found the Mother Lode of Clay on the Surface of Mars
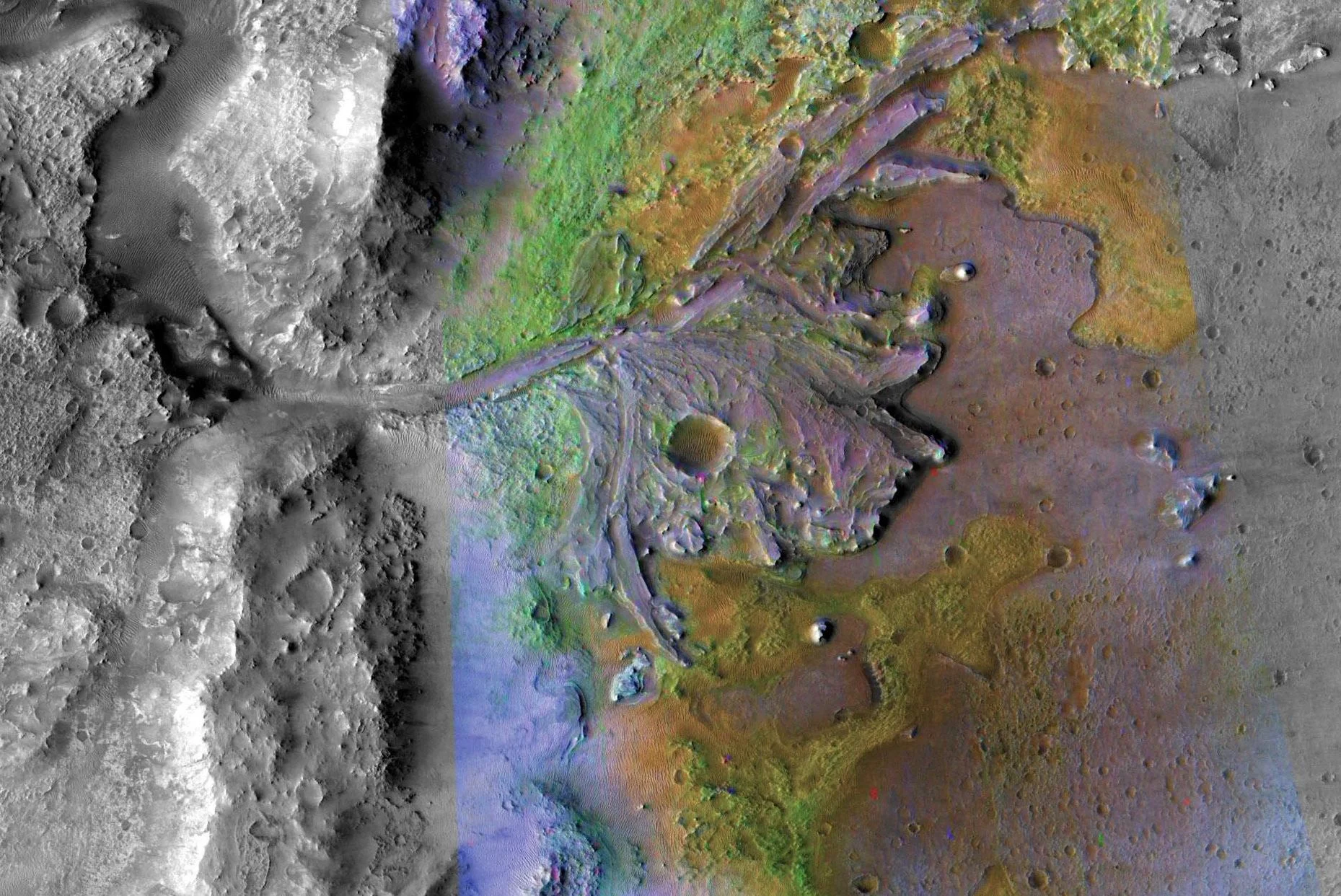
This is Where Mars 2020 Rover is Heading. From this Picture, I Think You Can Guess Why
NASA's Spitzer Captures Stellar Family Portrait
Why do Some Hubble Images Have That Chunk Taken Out of the Corner?
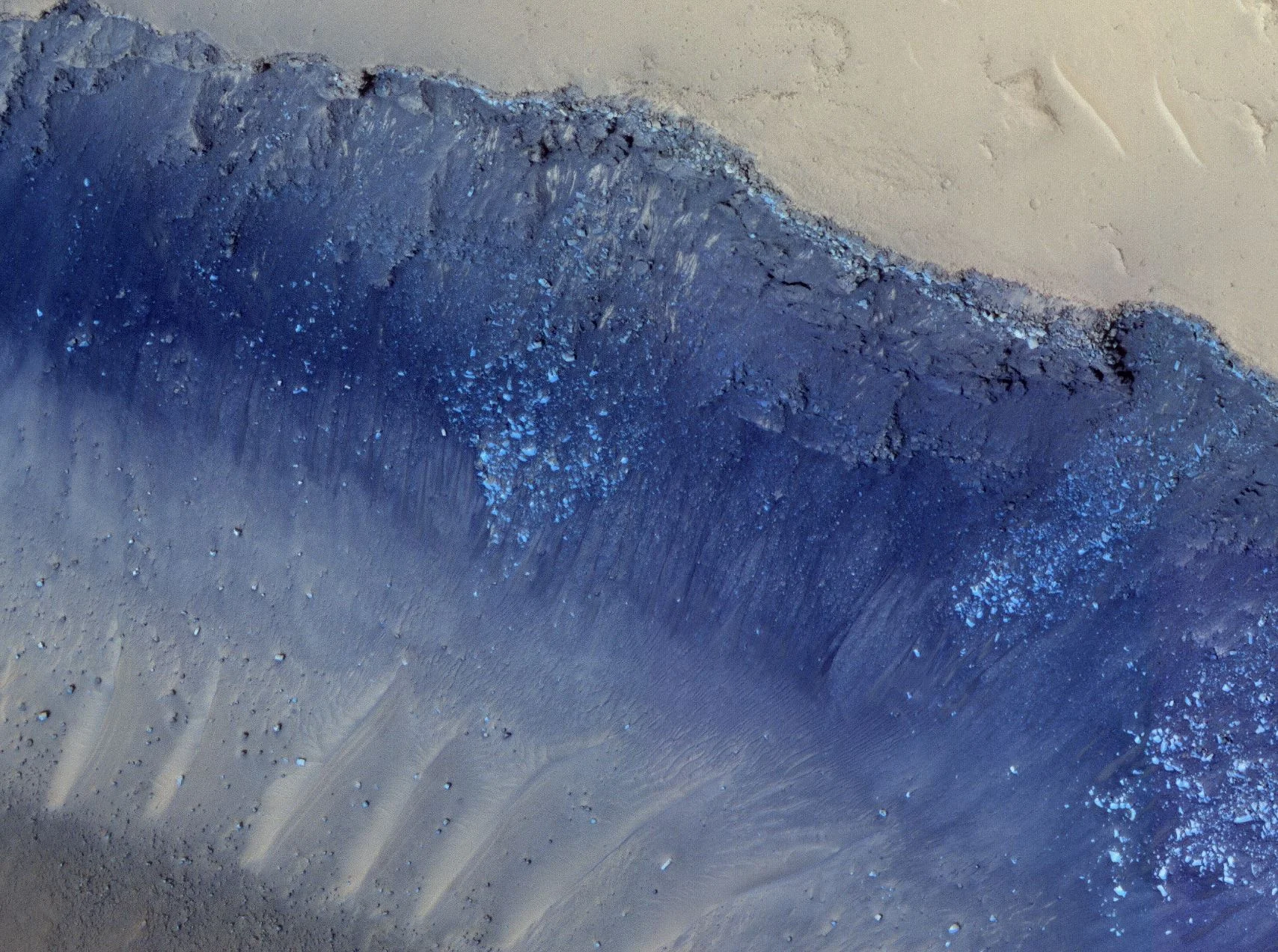
‘Unearthly’ factors move the sand on Mars
How long has gravity existed?
Three Ways to Travel at (Nearly) the Speed of Light
One hundred years ago today, on May 29, 1919, measurements of a solar eclipse offered verification for Einstein’s theory of general relativity. Even before that, Einstein had developed the theory of special relativity, which revolutionized the way we understand light. To this day, it provides guidance on understanding how particles move through space — a key area of research to keep spacecraft and astronauts safe from radiation.
18 (Yes, 18) New Earth-sized Exoplanets have been Found in Kepler’s Data!
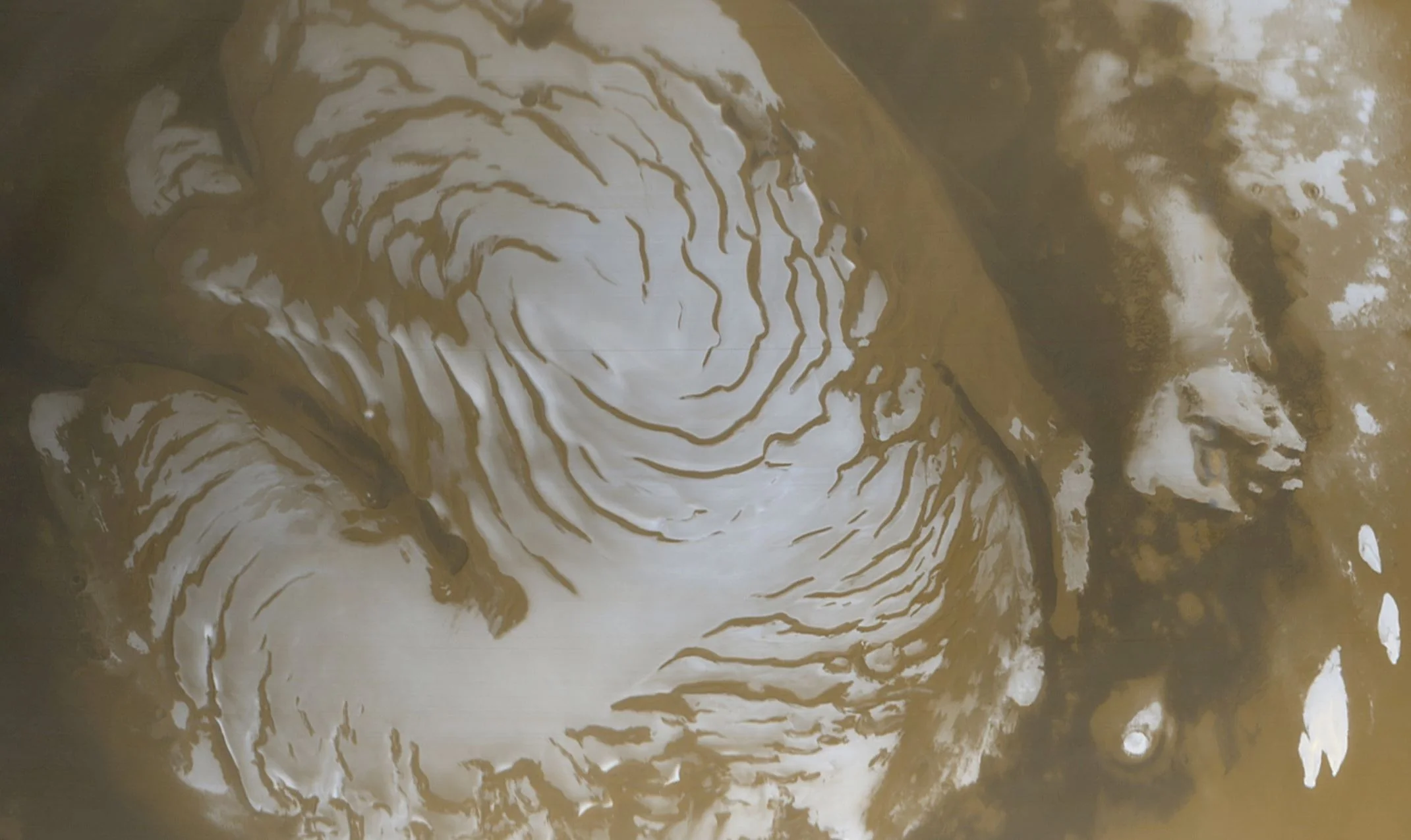
New layers of water ice have been found beneath Mars’ North Pole
One of the most profound similarities between Earth and Mars, one which makes it a popular target for research and exploration, is the presence of water ice on its surface (mainly in the form of its polar ice caps). But perhaps even more interesting is the presence of glaciers beneath the surface, which is something scientists have speculated about long before their presence was confirmed.
Theory proposes that Venus could have been habitable, but a large ocean slowed down its rotation, killing it
There’s no sense in sugar-coating it – Venus is a hellish place! It is the hottest planet in the Solar System, with atmospheric temperatures that are hot enough to melt lead. The air is also a toxic plume, composed predominantly of carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid rain clouds. And yet, scientists theorize that Venus was once a much different place, with a cooler atmosphere and liquid oceans on its surface.
Star formation in molecular clouds is fast but extremely inefficient
Star formation in molecular clouds occurs at a high pace but in an extremely inefficient manner. Most gas is quickly dispersed by the radiation from newborn stars. A team led by Dutch astronomer Diederik Kruijssen (University of Heidelberg, Germany) will publish this result tomorrow in the journal Nature.