As the world's energy demands increase, scientists and engineers are turning their attention towards more sustainable, efficient, and innovative solutions. Solar Power Satellites offer a tantalizing possibility an endless supply of clean, green power, available day and night.
Image Credit: andrey_l via Shutterstock / HDR tune by Universal-Sci
Solar power from space
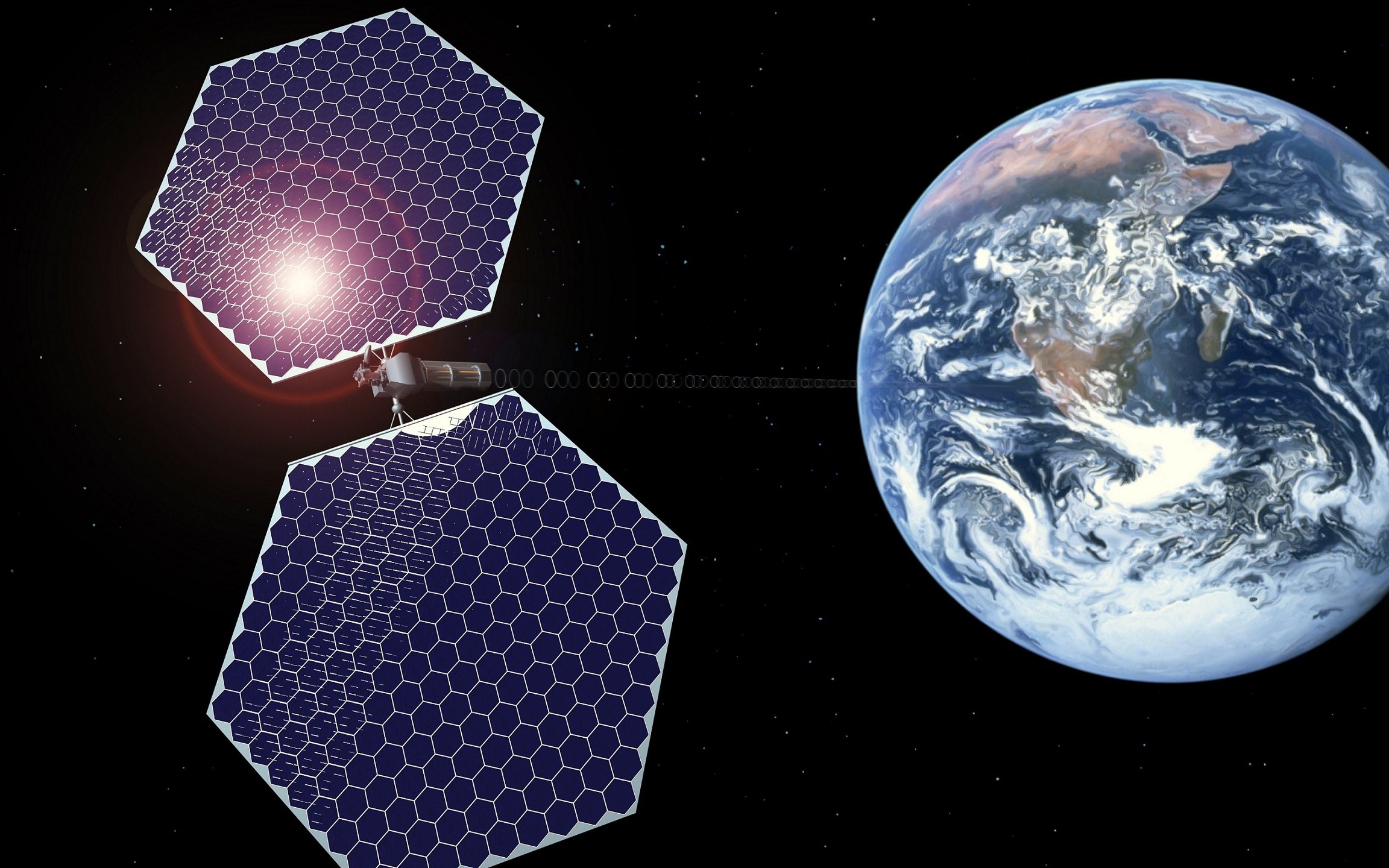
Among many innovative concepts exists the idea of solar power satellites - massive orbiting structures designed to harvest the sun's energy from space and transmit it to Earth in the form of microwave radiation.
Despite presenting various technical and logistical challenges, solar power satellites may revolutionize our approach to renewable energy, unlocking vast potential and moving us towards a sustainable future. In this article, we explore the intriguing concept of harnessing the sun's power from space.
Why would you go all the way to space for solar power?
The concept of Solar Power Satellites is rooted in the fact that space offers an environment with higher intensity and constancy of sunlight than the Earth's surface, unrestricted by atmospheric or weather-related impediments.
The central idea is to position extraordinarily large spacecraft in orbit around the Earth. These spacecraft would absorb solar energy, convert it into microwave energy, and transmit it to receiving stations, called rectennas, on Earth. The rectennas, in turn, convert this microwave energy into electricity, feeding it into the power grid for general use.
Two main designs
The design of Solar Power Satellites (SPS) is a complex affair involving advanced engineering and innovative technologies. Two primary design modules for SPS have been suggested, each offering unique advantages.
The first is the sandwich module design. This involves the transmitter and photovoltaic panels being placed in two layers, with the transmitter facing Earth. This compact design facilitates better energy transfer and requires fewer materials, thus potentially reducing construction and launch costs.
The second type is a disk-shaped design, where the photovoltaic panels and transmitter are placed on the same plane. The advantage of this design lies in its simplicity and the potential for more effective passive cooling due to the large surface area exposed to space.
There are also various configurations and architectural considerations for space-based solar power systems. The most common of which involves thousands of individual satellites, each in the range of 1-10 GW in power production, placed in geostationary orbit. Other concepts consider swarms of free-flying smaller satellites.
Each design offers its own set of advantages and challenges, making a choice between them dependent on future advancements in space technology and material science.
The Advantages of Solar Power Satellites
Space-based solar power is a revolutionary idea that comes with a broad array of benefits, potentially addressing some of the world's most pressing energy challenges.
Continuous power delivery
In space, solar power is available almost 24/7; this means that SPS can generate power more consistently than terrestrial solar power sources. Solar panels on Earth only produce power for less than 30% of the day on average.
Increased Efficiency
Not only can solar panels run 24 hours per day, but the amount of solar irradiance received in space is more significant than what is received on Earth due to atmospheric absorption and scattering.
Sunlight irradiance at geostationary orbit (for example) is about 1366 watts per square meter (W/m2). On Earth however, this value peaks at around 1000 W/m² a clear day at noon at sea level at the equator (so under ideal circumstances).
The average over the entire surface of the Earth (accounting for night and day and weather) is much less, about 164 W/m².
No Greenhouse Gas Emissions
After the initial investment and deployment, SPS would generate electricity without producing greenhouse gases. This clean energy production could play a pivotal role in reducing our carbon footprint and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Independence from Geographic Limitations
Unlike terrestrial power plants, the location of SPS in space makes it possible to transmit energy to any place on Earth, providing a unique solution for energy delivery to remote areas.
It is also relatively easy to redirect power to a different location if need be.
The Disadvantages of Solar Power Satellites
Of course, there are also many challenges that span various domains, from engineering and technology to economics. Below, we delve into some of the significant challenges that stand between the concept and the realization of space-based solar power.
Launch and Construction Costs
Building and deploying SPS requires advanced, expensive technologies. Despite the reduction in launch costs due to reusable rockets, the overall cost remains high.
Space Debris Management
The deployment of large structures like SPS in space could contribute to the existing problem of space debris. Designing these satellites to mitigate this risk would be essential.
Energy Transmission Safety
The use of microwave transmission of power presents challenges in terms of safety.
Ensuring that the power beaming process is safe for all life forms and does not interfere with existing telecommunications infrastructure is vital.
Safety Considerations
Safety in the operation of SPS is of critical importance. Concerns revolve around the microwave transmission of power from space to Earth. To ensure safety, the beam's intensity at its maximum at the Earth's surface should be less than a quarter of the solar irradiation constant, within the safe workplace limits as per existing regulations.
Several measures could be put in place to minimize potential exposure to the beam, such as controlling physical access and using aircraft's protective shells to intercept microwaves. Furthermore, the beam's design and structure should make it physically impossible to increase its intensity to unsafe levels.
Despite the safety measures and designs, research is ongoing to better understand the long-term impacts of beaming power via the ionosphere in the form of microwaves. Further studies are needed to ensure that there would be no unintended consequences of this revolutionary approach to energy production.
Immense potential
The concept of Solar Power Satellites presents an exciting, albeit challenging, avenue towards fulfilling the world's energy needs in a sustainable manner.
The potential advantages of such a system are immense, promising constant, efficient, and environmentally friendly energy production. However, significant challenges, both technical and logistical, need to be addressed. With these challenges in mind organisations like the European Space agency are already looking into the viability of space based solar power.
As we continue to innovate and advance in our technological capabilities, the dream of harnessing space for our energy needs might become a reality, marking a monumental leap forward in our pursuit of a sustainable future.
Sources and further reading:
Could solar panels in space supply Earth with clean energy? (nature)
Solar space power: an overview (International Journal of Ambient Energy)
How Satellites Might Fuel Europe's Future: A Revolutionary Take on Renewable Energy (Universal-Sci)
Too busy to follow science news during the week? - Consider subscribing to our (free) newsletter - (Universal-Sci Weekly) - and get the 5 most interesting science articles of the week in your inbox
FEATURED ARTICLES: