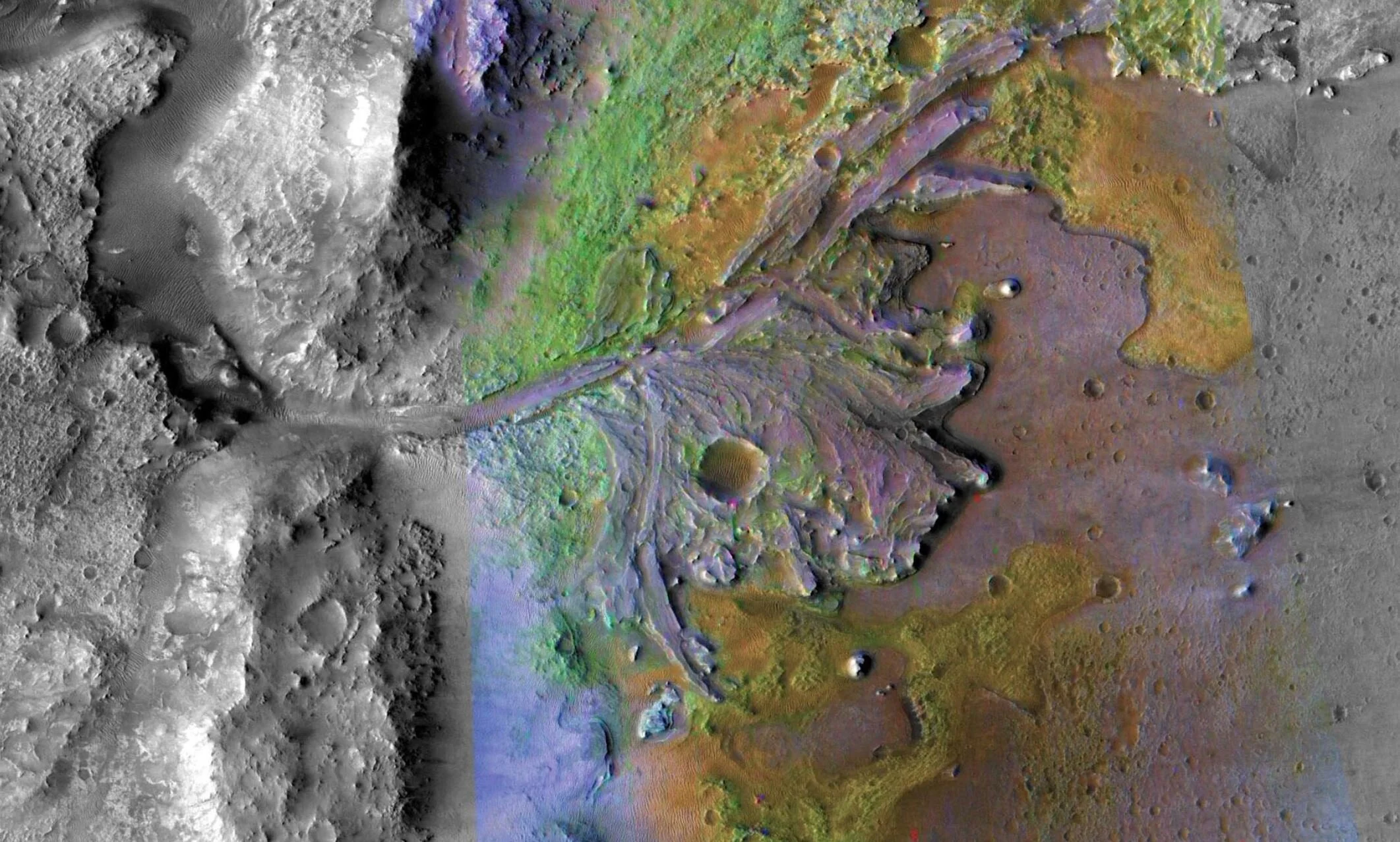
Scientists discovered hydrated silica in the Jezero crater on Mars, a spot where NASA plans to land its next Mars rover in 2020. The Rover is intended to search for signs of past life on the neighboring terrestrial planet.
How Do We Colonize Ceres?
Scientists recommend building a Martian settlement using bacteria
Astronomers detected actual water vapor on Europa for the first time!
Shape of the universe: could it be curved, not flat?
Scientists discovered how to extract oxygen from the moon's 'soil'
Mysterious tiny black hole flashes like a strobe
An international team of astronomers filmed a small, flashing black hole in our Milky Way using unique, specialized high-speed cameras. The stellar black hole feeds on material from a nearby star and flashes hundreds of times per second. The researchers publish their findings in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Letters.
Scientists claim that planet 9 could actually be a primordial black hole with a diameter of just a few centimeters
Saturn becomes the planet with the most moons in the solar system after discovery of 20 new moons
Why microbes and not humans should be the first 'Earthly pioneers' to settle on Mars
Scientists predict a lot more interstellar objects coming our way
Six galaxies discovered that shouldn't exist due to their mysterious lack of dark matter
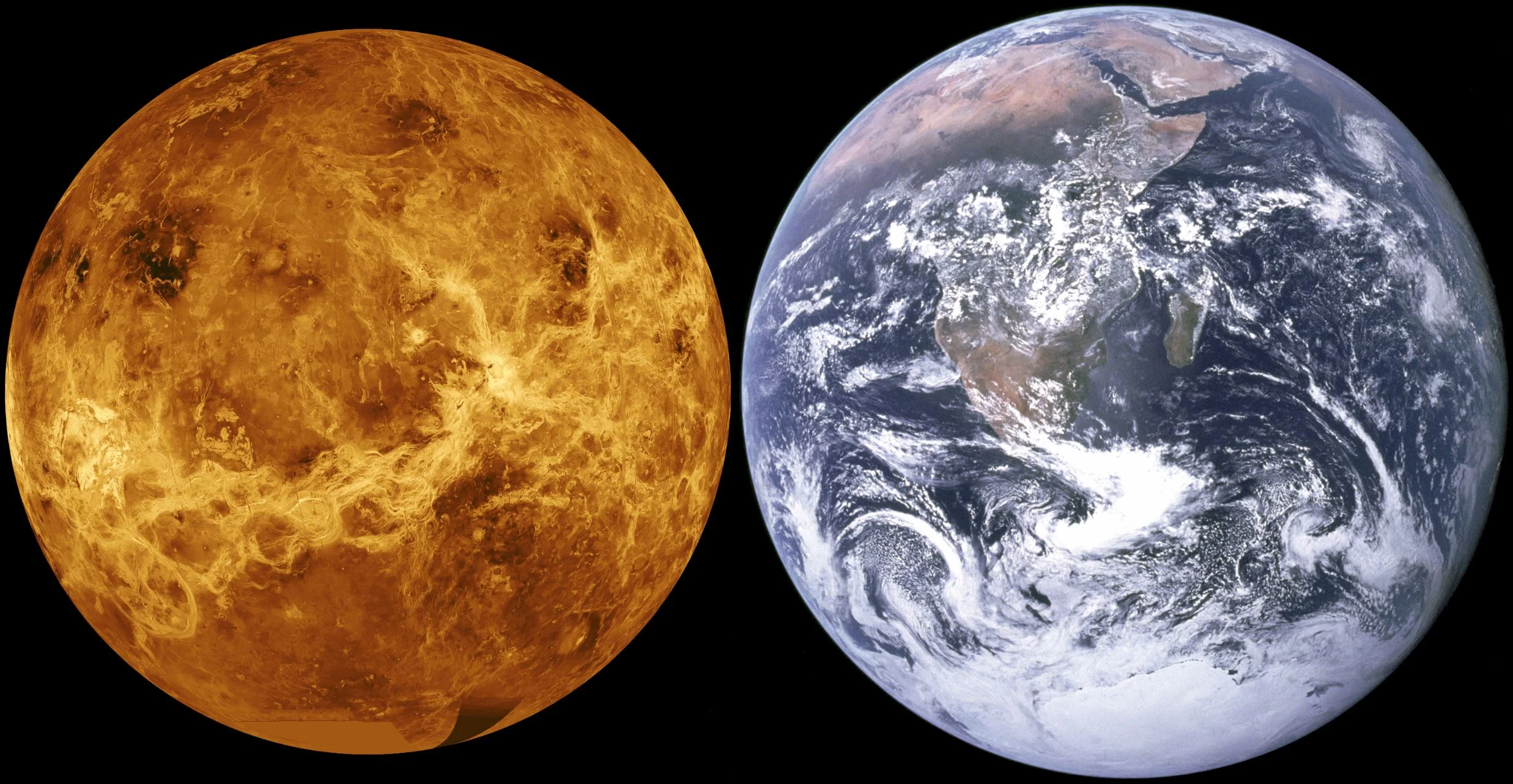
New simulations show that in a distant past, Venus might have been habitable for billions of years on end
Scientists successfully used self-learning neural networks to study dark matter
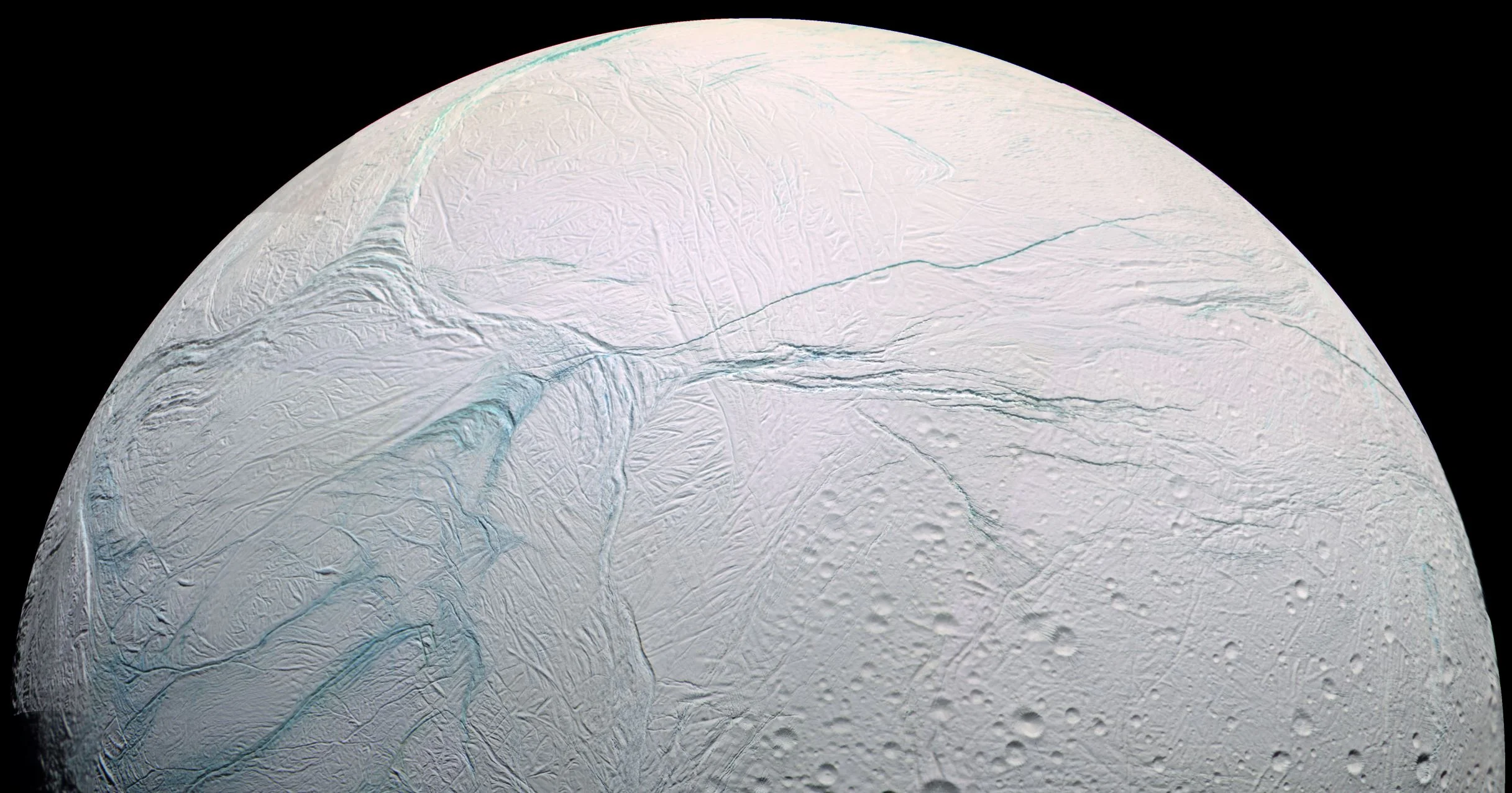
Enceladus Causes Snowfall On Other Moons of Saturn
Something is killing galaxies, and scientists are on the case
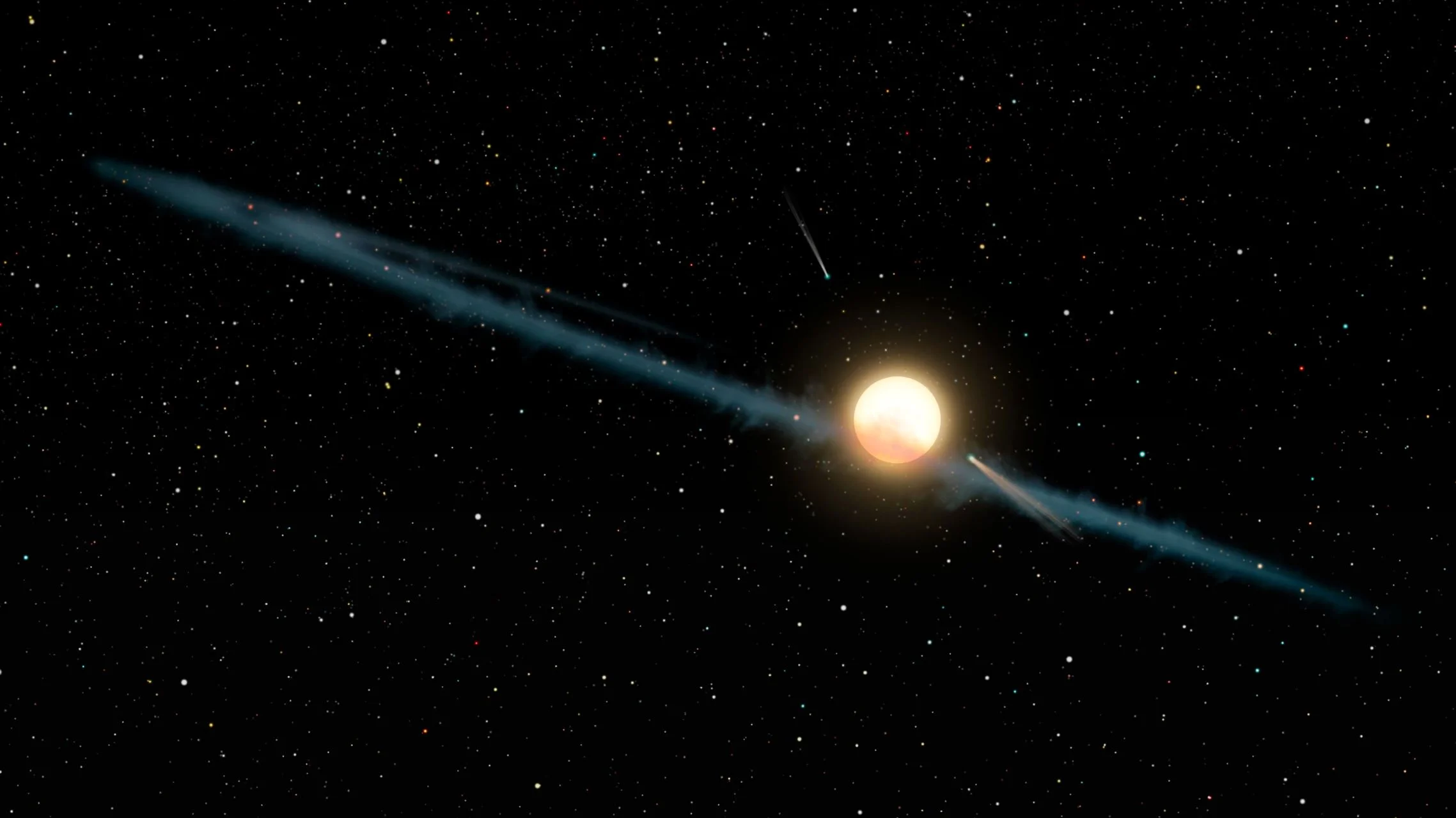
Scientists may finally have an explanation for the mysteriously dimming star that has captivated us for years
Scientists discovered the most massive neutron star ever, almost too enormous to exist!
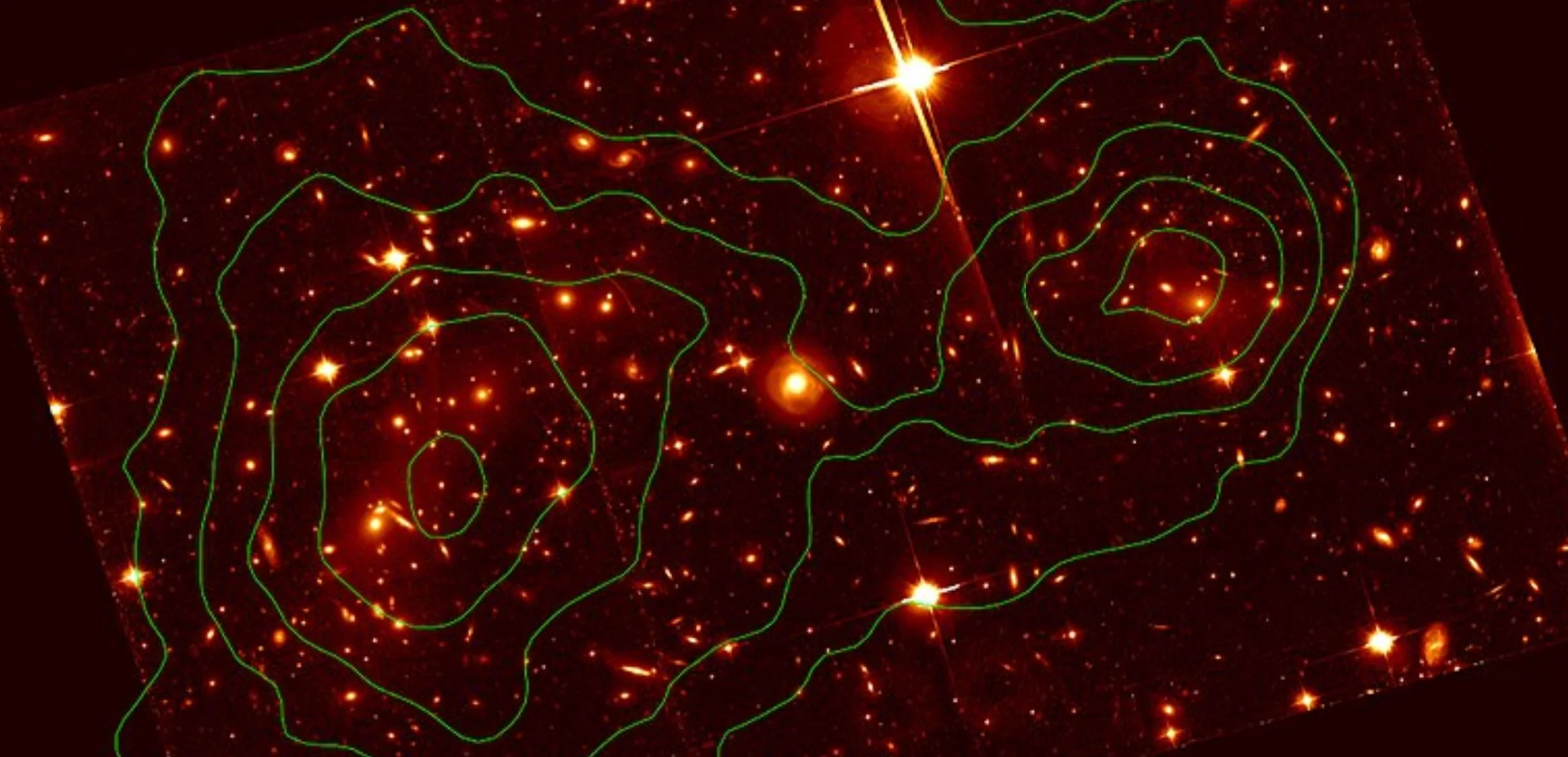
New measurements show that the universe is expanding faster than we thought
An international team of scientists has measured a new, higher value for the speed at which the universe expands. They used two massive galaxies as "gravitational lenses" to investigate the light from remote objects. The study was led by the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics in Garching in Germany.