Recommendations usually include cutting out chocolate, other junk foods and dairy products. But is there evidence to actually support this?
NASA Hosts Live Discussion about Europa Findings, Potential for Life
NASA Spacecraft Discovers New Magnetic Process in Turbulent Space
Though close to home, the space immediately around Earth is full of hidden secrets and invisible processes. In a new discovery reported in the journal Nature, scientists working with NASA’s Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft — MMS — have uncovered a new type of magnetic event in our near-Earth environment by using an innovative technique to squeeze extra information out of the data.
Light could solve one of quantum computing’s big problems
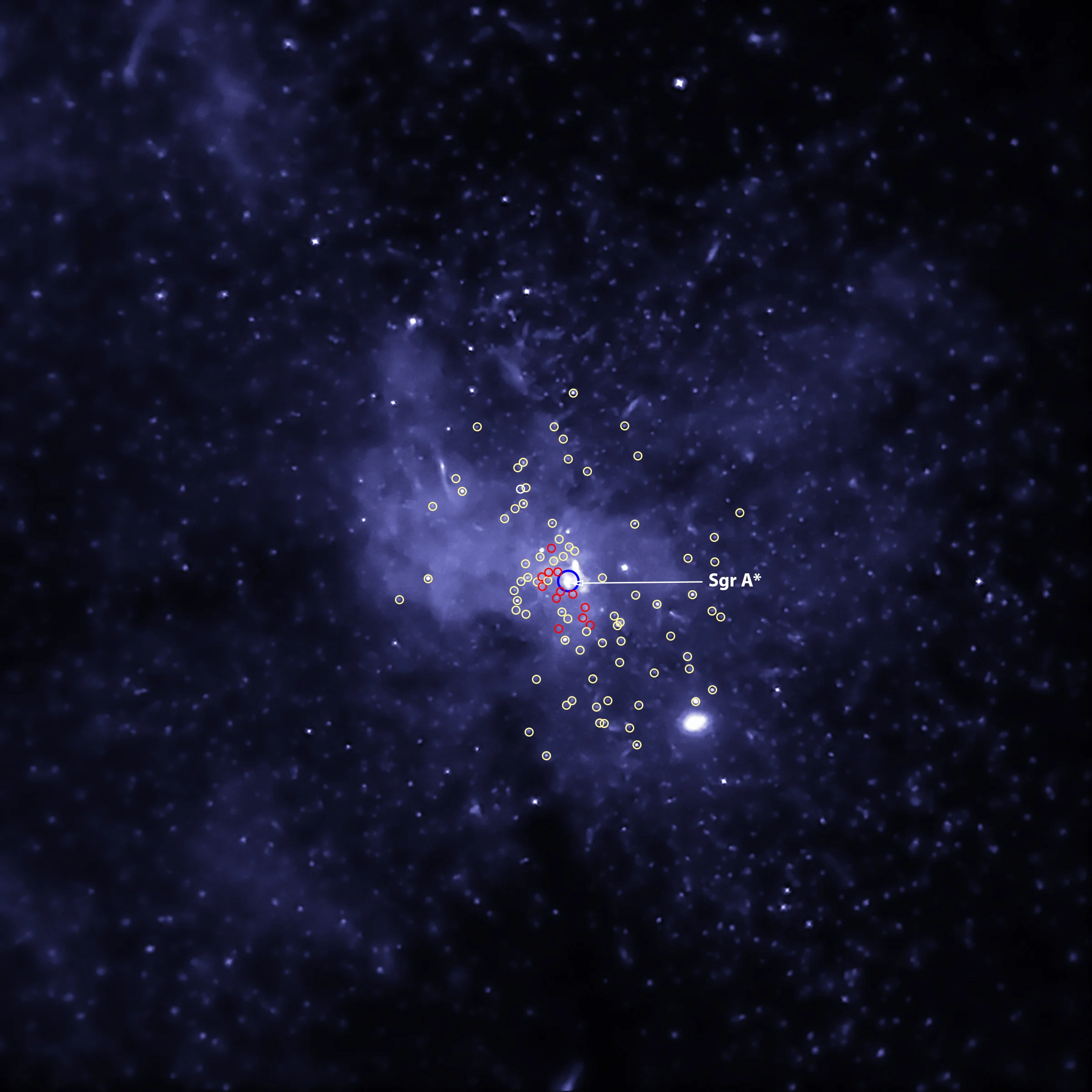
Black Hole Bounty Captured in the Milky Way Center
World’s most powerful camera can spot planets drowned by starlight
NASA’s NICER Mission Finds an X-ray Pulsar in a Record-fast Orbit
Scientists analyzing the first data from the Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) mission have found two stars that revolve around each other every 38 minutes — about the time it takes to stream a TV drama. One of the stars in the system, called IGR J17062–6143 (J17062 for short), is a rapidly spinning, superdense star called a pulsar. The discovery bestows the stellar pair with the record for the shortest-known orbital period for a certain class of pulsar binary system.
The giant planets in the solar system stunted the growth of mars
For centuries, astronomers and scientists have sought to understand how our Solar System came to be. Since that time, two theories have become commonly-accepted that explain how it formed and evolved over time. These are the Nebular Hypothesis and the Nice Model, respectively. Whereas the former contends that the Sun and planets formed from a large cloud of dust and gas, the latter maintains the giant planets have migrated since their formation.
How to understand one of Stephen Hawking’s final papers – according to an expert
The late physicist Stephen Hawking made a huge contribution to cosmology during his lifetime, but he didn’t quite manage to resolve all the mysteries of the universe. Now one of the last papers he ever worked on has been published – and it introduces some new ideas about the size and shape of the cosmos. But what does the research actually say and how important are the findings?
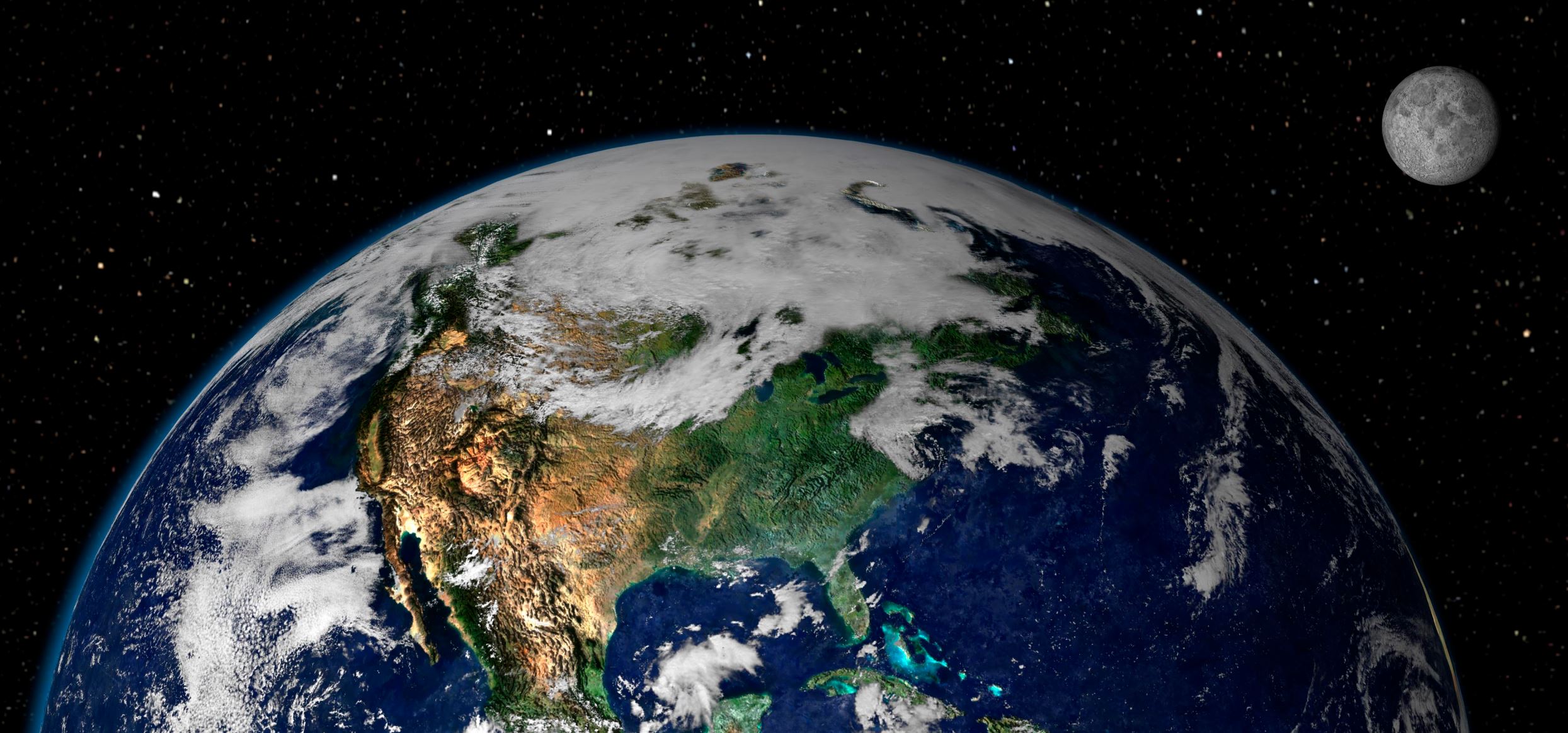
How many of earth’s moons crashed back into the planet?
For decades, scientists have pondered how Earth acquired its only satellite, the Moon. Whereas some have argued that it formed from material lost by Earth due to centrifugal force, or was captured by Earth’s gravity, the most widely accepted theory is that the Moon formed roughly 4.5 billion years ago when a Mars-sized object (named Theia) collided with a proto-Earth (aka. the Giant Impact Hypothesis).
The carbon footprint of tourism revealed (it’s bigger than we thought)
Breathing lunar dust could give astronauts bronchitis and even lung cancer
It’s been over forty years since the Apollo Program wrapped up and the last crewed mission to the Moon took place. But in the coming years and decades, multiple space agencies plan to conduct crewed missions to the lunar surface. These includes NASA’s desire to return to the Moon, the ESA’s proposal to create an international Moon village, and the Chinese and Russian plans to send their first astronauts to the Moon.
Other planets stretch out Earth’s orbit every 405,000 years
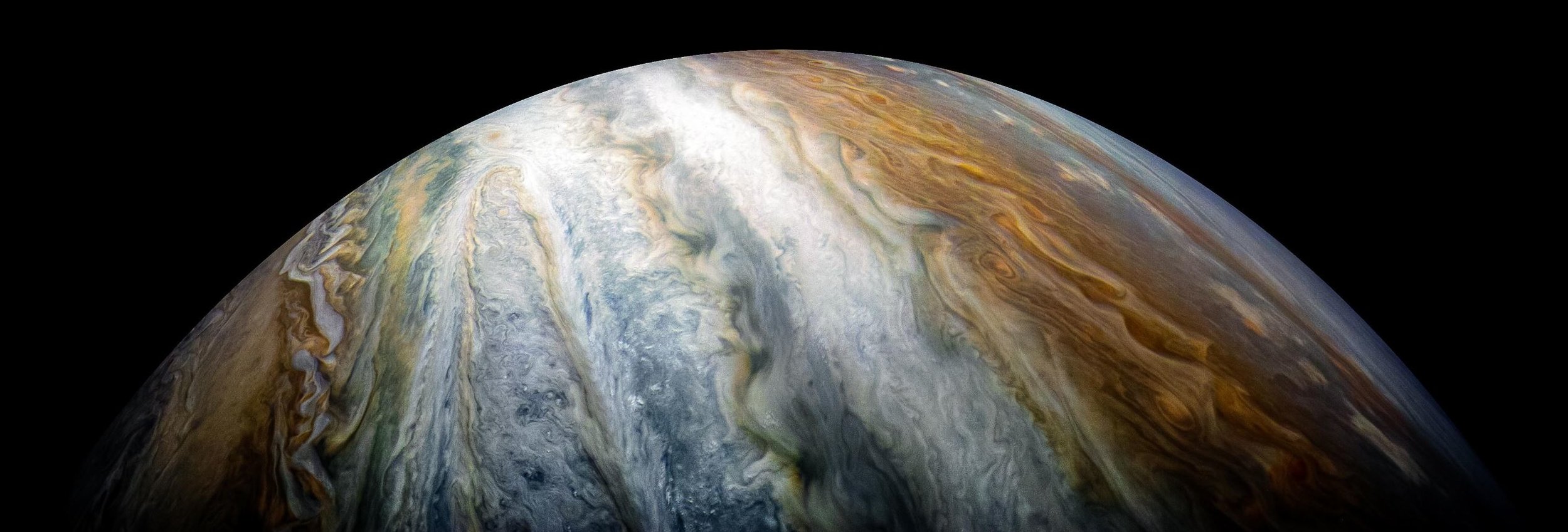
The latest from Juno as Jupiter appears bright in the night sky
NASA Satellite Images Show Fissures from Hawaii Volcano
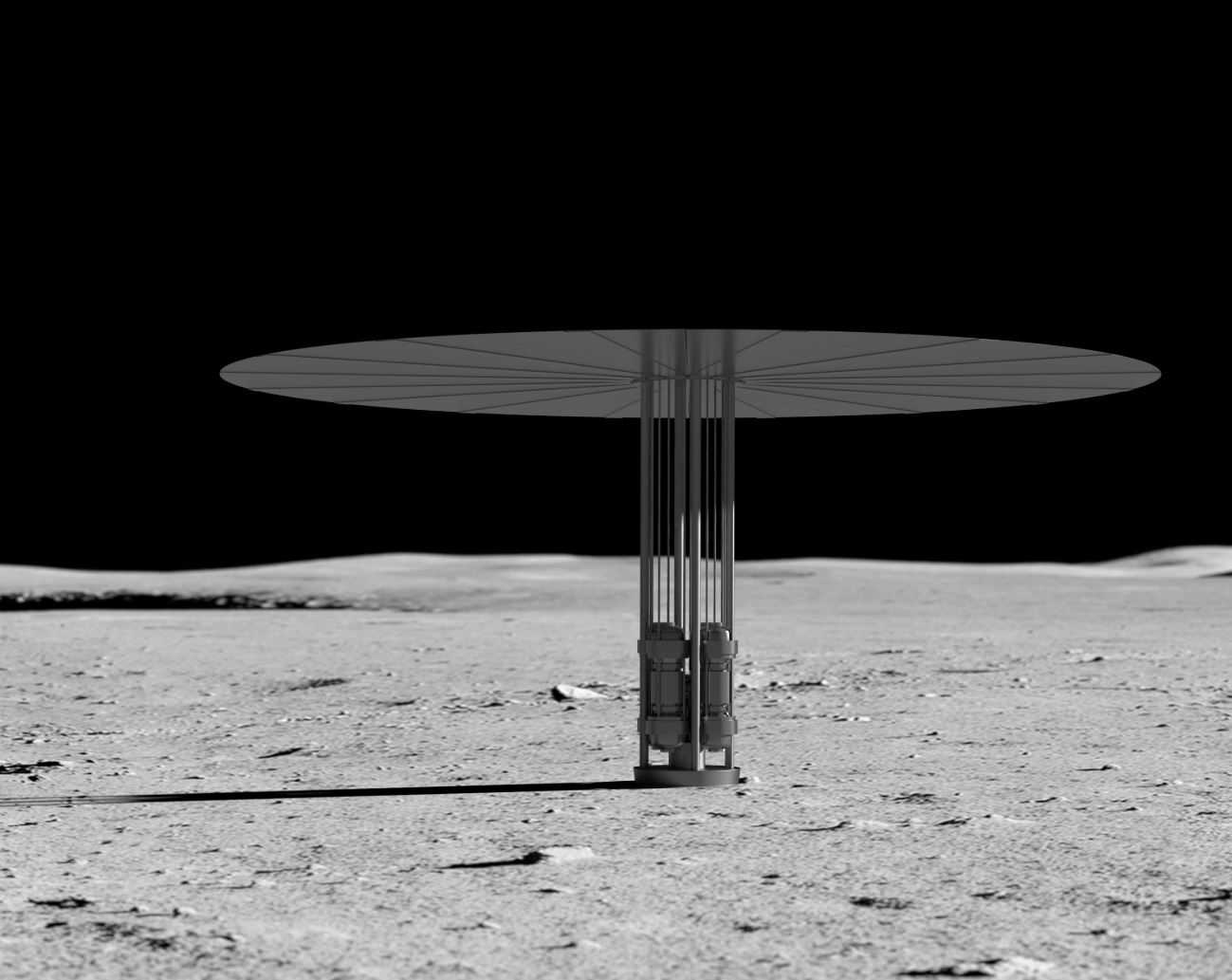
We Now Have A Working Nuclear Reactor for Other Planets — But No Plan For Its Waste
One of the TRAPPIST-1 planets has an iron core!
In February of 2017, a team of European astronomers announced the discovery of a seven-planet system orbiting the nearby star TRAPPIST-1. Aside from the fact that all seven planets were rocky, there was the added bonus of three of them orbiting within TRAPPIST-1’s habitable zone. Since that time, multiple studies have been conducted to determine whether or not any of these planets could be habitable.