Watching helium gas lift balloons into the air is a lot of fun – or perhaps a tragedy if that balloon belonged to a small child who let it go. And, who hasn’t sipped the helium gas from a balloon and then quacked like Donald Duck? Although, that’s not the smartest thing to do since helium can displace the air in our lungs, or cause other problems with respiration.
Six Things About Opportunity's Recovery Efforts
NASA's Opportunity rover has been silent since June 10, when a planet-encircling dust storm cut off solar power for the nearly-15-year-old rover. Now that scientists think the global dust storm is "decaying" -- meaning more dust is falling out of the atmosphere than is being raised back into it -- skies might soon clear enough for the solar-powered rover to recharge and attempt to "phone home."
Hubble Paints Picture of the Evolving Universe
Astronomers using the ultraviolet vision of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope have captured one of the largest panoramic views of the fire and fury of star birth in the distant universe. The field features approximately 15,000 galaxies, about 12,000 of which are forming stars. Hubble’s ultraviolet vision opens a new window on the evolving universe, tracking the birth of stars over the last 11 billion years back to the cosmos’ busiest star-forming period, which happened about 3 billion years after the big bang.
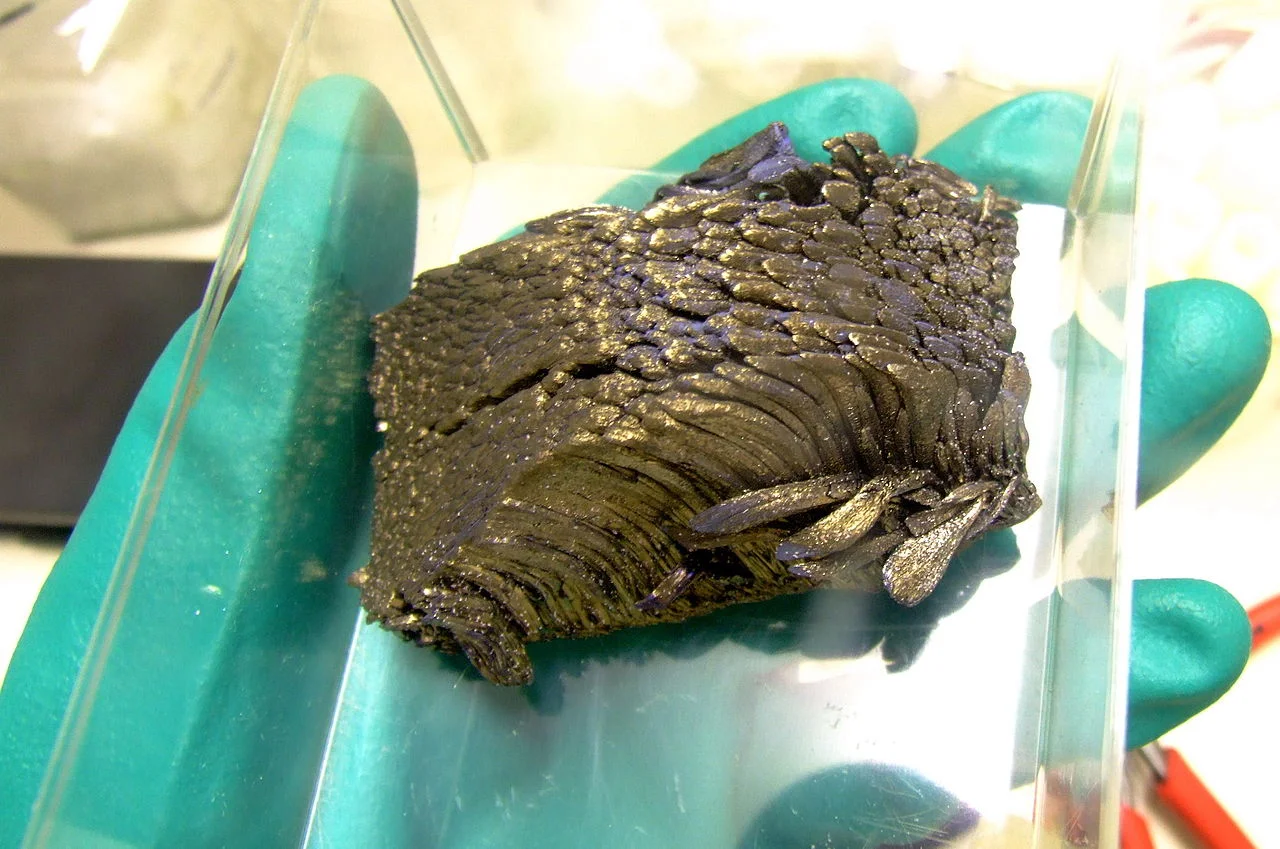
What are rare earths, crucial elements in modern technology? 4 questions answered
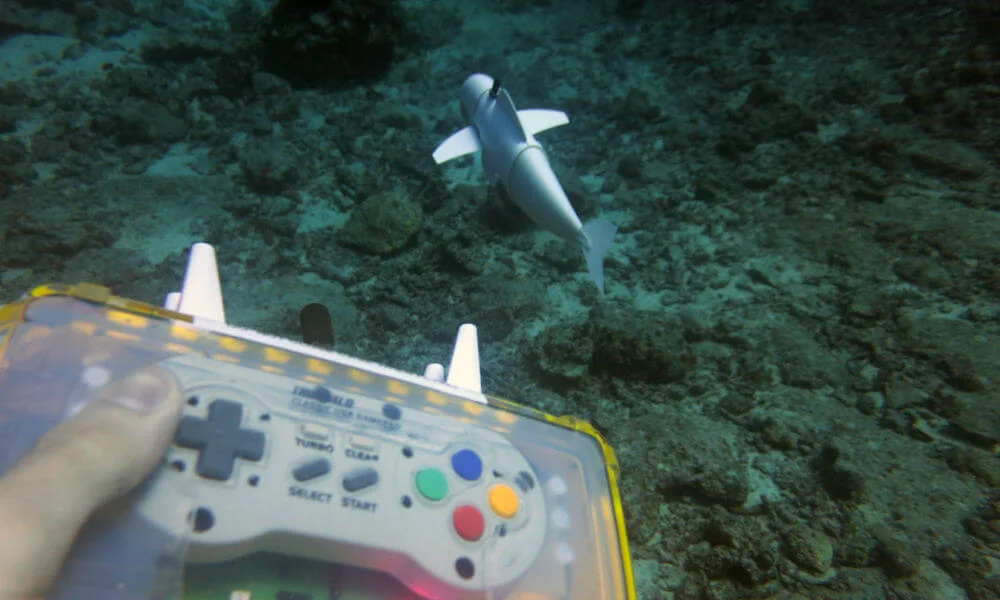
Watch This Lifelike Robot Fish Swim Through the Ocean
Hothouse Earth: our planet has been here before – here’s what it looked like
Even if carbon emissions are reduced to hold temperature rises at the 2°C guardrail of the Paris Agreement, changes already afoot in the environment such as melting permafrost and forest die-back could accelerate warming well into the future, potentially pushing our planet into what is being called a “Hothouse Earth” state.
Frontal lobe paradox: where people have brain damage but don’t know it
Ageing in human cells successfully reversed in the lab
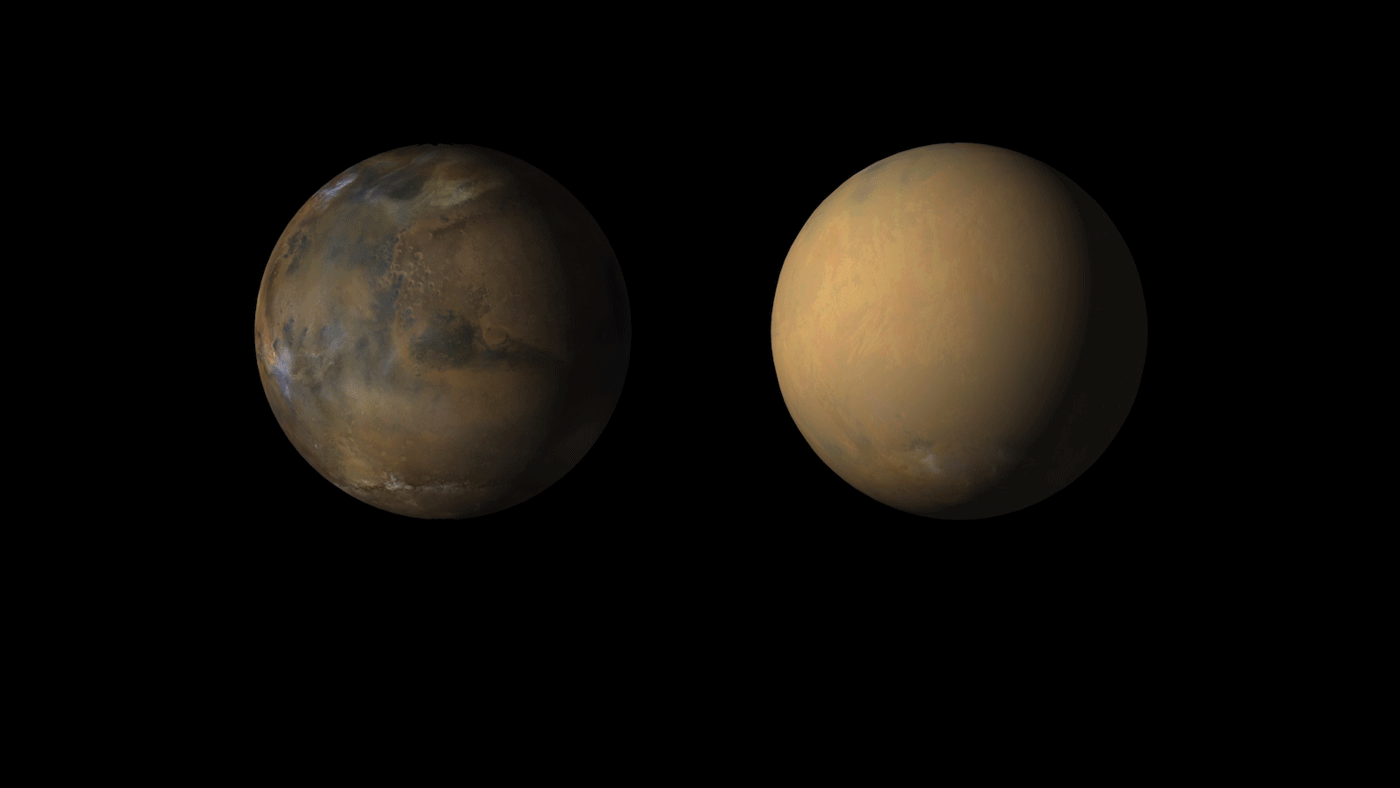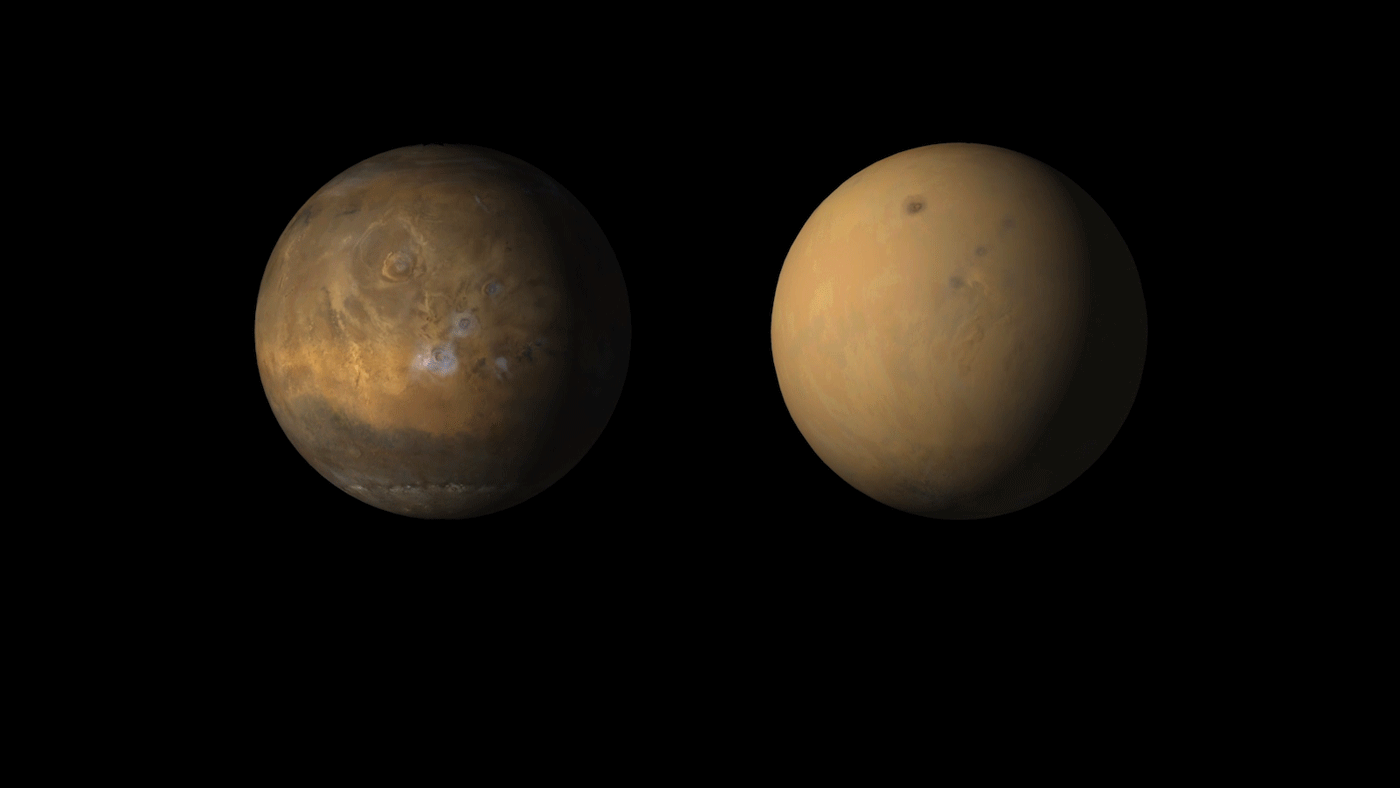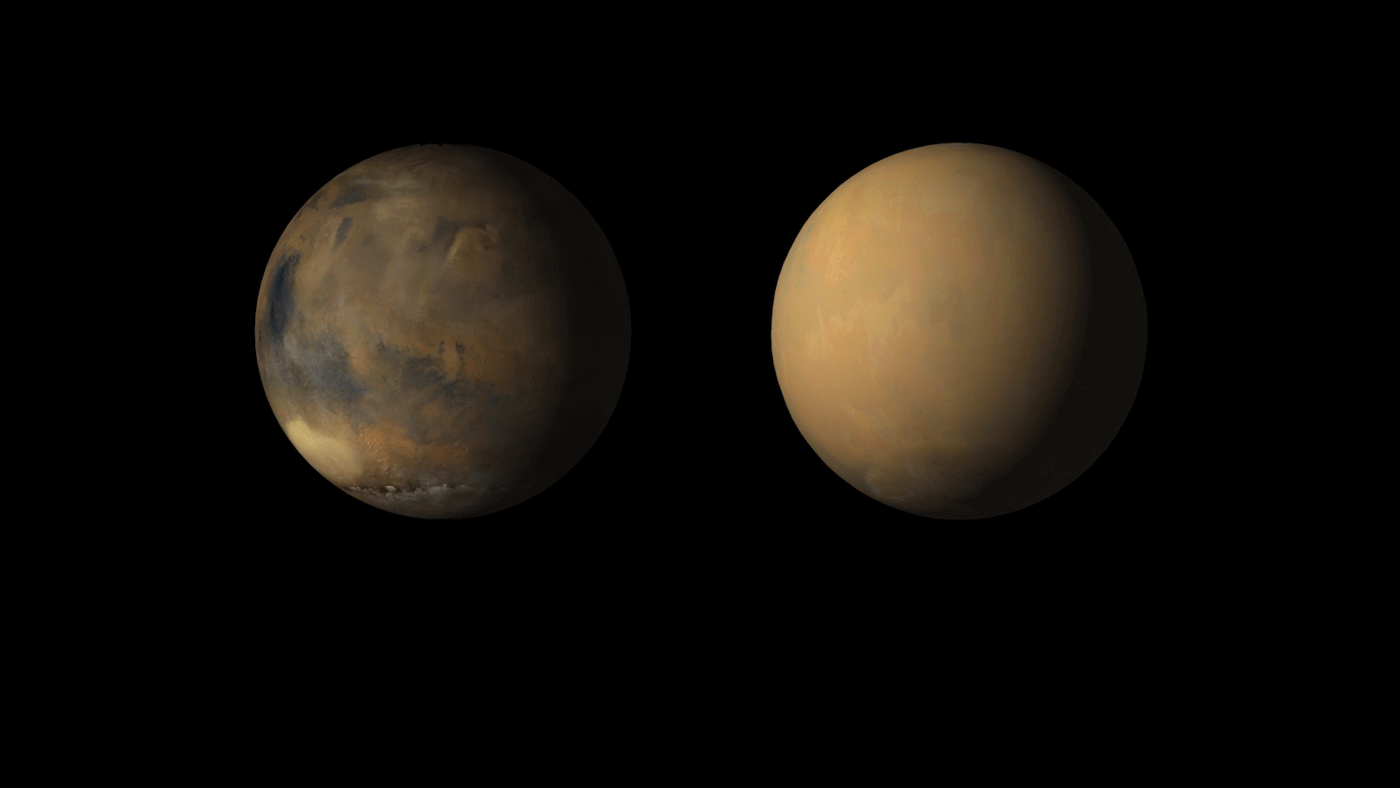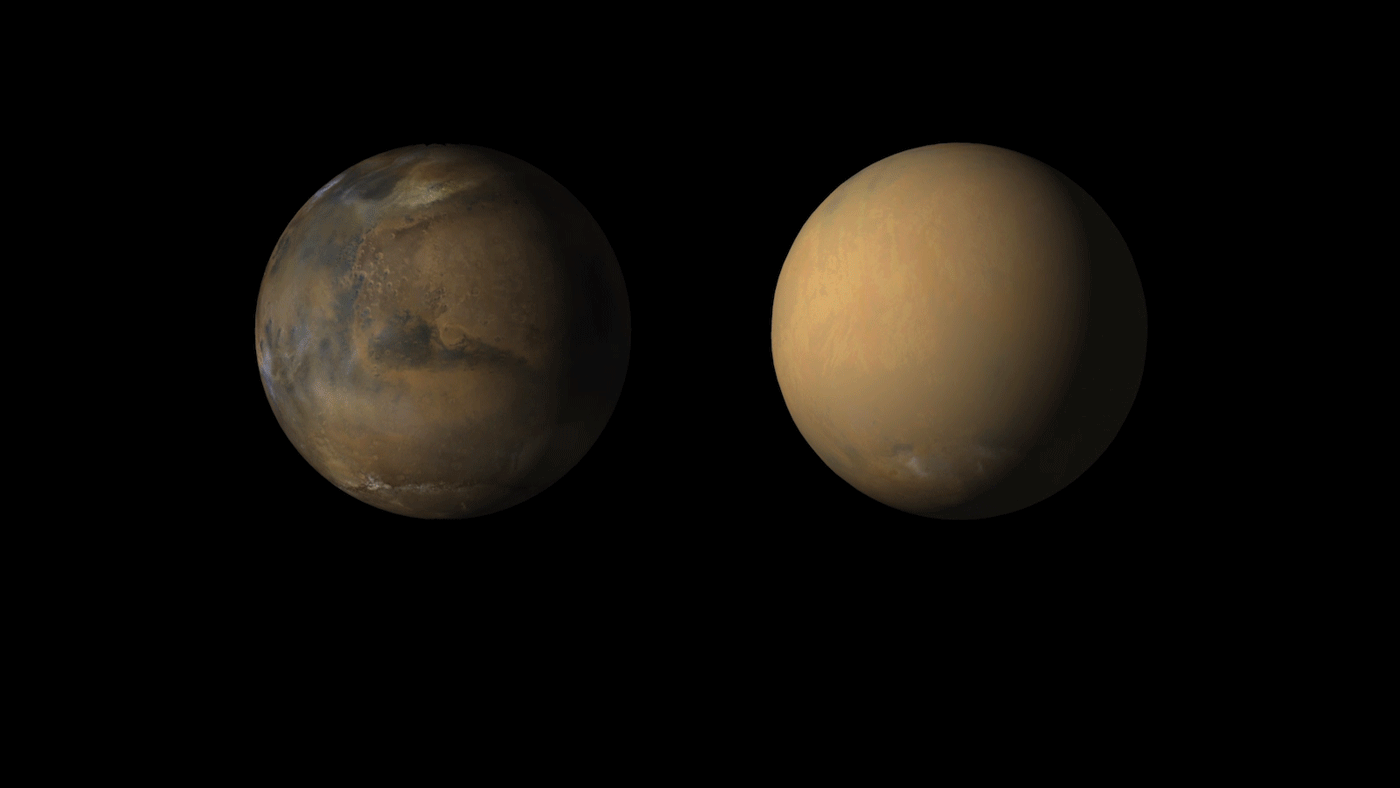
As the Martian dust storm subsides, there’s still no word from opportunity
Martian dust storms are a pretty common occurrence, and generally happen whenever the southern hemisphere is experiencing summer. Though they can begin quite suddenly, these storms typically stay contained to a local area and last only about a few weeks. However, on occasion, Martian dust storms can grow to become global phenomena, covering the entire planet.
Trees are made of human breath
Outside my office window, two skilled workers complete a hard and dirty job. They’re cutting the felled trunk of a tree into small enough pieces to be thrown into the back of a truck with the rest of the chipped remains. I know that this act was ultimately for my own safety. I, like tens of thousands of others over the past 50 years, regularly walked beneath the canopy of that tree.
Jupiter’s magnetic fields may stop its wind bands from going deep into the gas giant
Finding the Happy Medium of Black Holes
Why stretching is (still) important for weight loss and exercise
Fastest rotor ever made may shed light on quantum physics
Brains keep temporary molecular records before making a lasting memory
To uncover how the brain keeps track of an animal’s experience, we started by asking how the brain records its electrical activity. Every experience you have, from chatting with a friend to smelling french fries, corresponds to its own unique pattern of electrical activity in the nervous system and brain. These activity patterns are defined by which neurons are active and in what way they’re active.
Tess practices on a comet before starting on its science operations
On April 18th, 2018, NASA deployed the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), a next-generation exoplanet hunting telescope that is expected to find thousands of planets in the coming years. Alongside other next-generation telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), TESS will effectively pick up where space telescopes like Hubbleand Kepler left off.
Water Is Destroyed, Then Reborn in Ultrahot Jupiters
Imagine a place where the weather forecast is always the same: scorching temperatures, relentlessly sunny, and with absolutely zero chance of rain. This hellish scenario exists on the permanent daysides of a type of planet found outside our solar system dubbed an "ultrahot Jupiter." These worlds orbit extremely close to their stars, with one side of the planet permanently facing the star.
How clean is your desk? The unwelcome reality of office hygiene
The universe’s rate of expansion is in dispute – and we may need new physics to solve it
Next time you eat a blueberry (or chocolate chip) muffin consider what happened to the blueberries in the batter as it was baked. The blueberries started off all squished together, but as the muffin expanded they started to move away from each other. If you could sit on one blueberry you would see all the others moving away from you, but the same would be true for any blueberry you chose. In this sense galaxies are a lot like blueberries.