Telescopes have come a long way in the past few centuries. From the comparatively modest devices built by astronomers like Galileo Galilei and Johannes Kepler, telescopes have evolved to become massive instruments that require an entire facility to house them and a full crew and network of computers to run them. And in the coming years, much larger observatories will be constructed that can do even more.
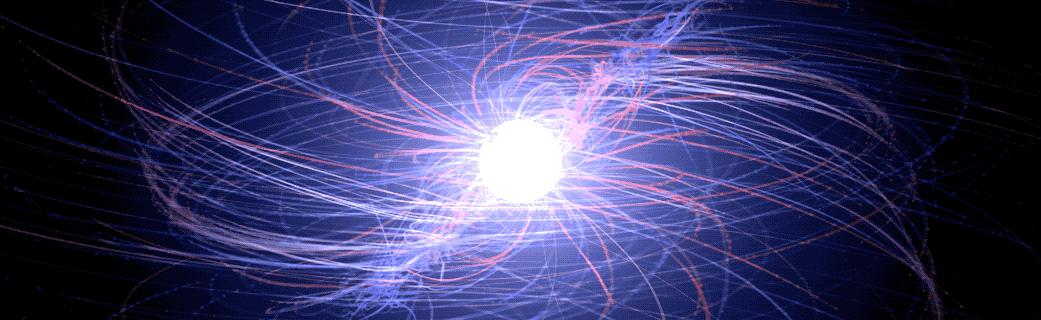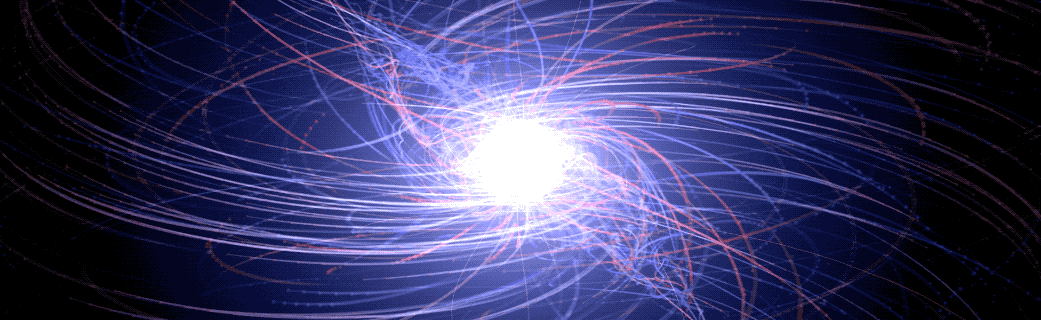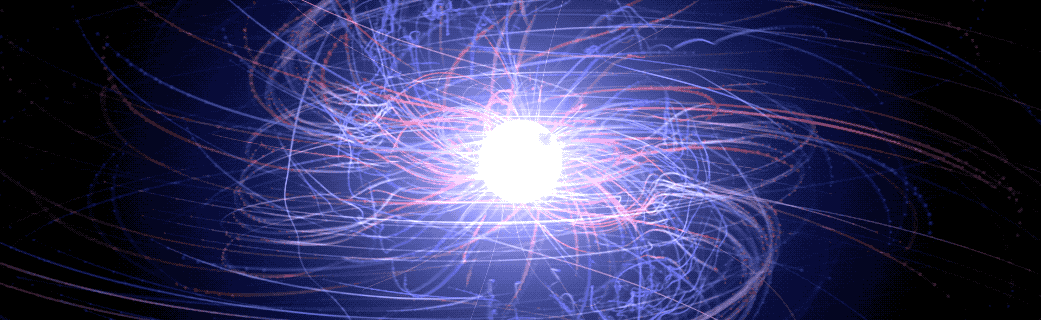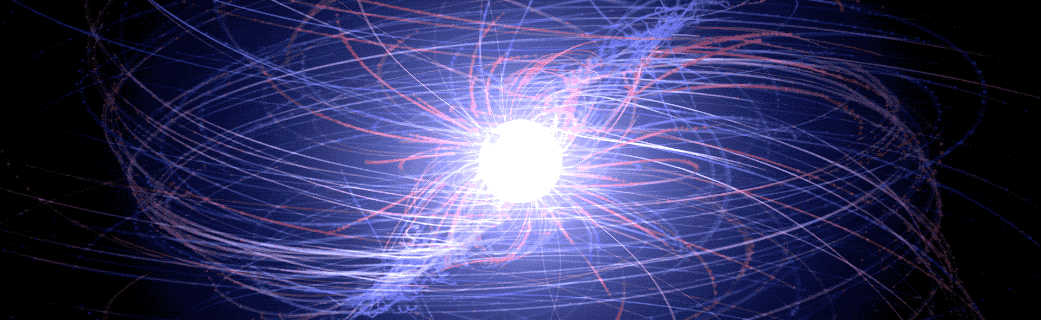
‘Pulsar in a Box’ Reveals Surprising Picture of a Neutron Star’s Surroundings
An international team of scientists studying what amounts to a computer-simulated “pulsar in a box” are gaining a more detailed understanding of the complex, high-energy environment around spinning neutron stars, also called pulsars. The model traces the paths of charged particles in magnetic and electric fields near the neutron star, revealing behaviors that may help explain how pulsars emit gamma-ray and radio pulses with ultra precise timing.
Meet the trillions of viruses that make up your virome
If you think you don’t have viruses, think again. It may be hard to fathom, but the human body is occupied by large collections of microorganisms, commonly referred to as our microbiome, that have evolved with us since the early days of man. Scientists have only recently begun to quantify the microbiome, and discovered it is inhabited by at least 38 trillion bacteria. More intriguing, perhaps, is that bacteria are not the most abundant microbes that live in and on our bodies. That award goes to viruses.
New materials are powering the battery revolution
There are more mobile phones in the world than there are people. Nearly all of them are powered by rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, which are the single most important component enabling the portable electronics revolution of the past few decades. None of those devices would be attractive to users if they didn’t have enough power to last at least several hours, without being particularly heavy.
NASA Voyager 2 Could Be Nearing Interstellar Space
NASA's Voyager 2 probe, currently on a journey toward interstellar space, has detected an increase in cosmic rays that originate outside our solar system. Launched in 1977, Voyager 2 is a little less than 11 billion miles (about 17.7 billion kilometers) from Earth, or more than 118 times the distance from Earth to the Sun.
New Image Shows the Rugged Landscape of Comet 67P
In March of 2004, the European Space Agency’s Rosetta spacecraft blasted off from French Guiana aboard an Ariane 5 rocket. After ten years, by November of 2014, the spacecraft rendezvoused with its target – Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko (67P/C-G). Over the more than two years that followed, the spacecraft remained in orbit of this comet, gathering information on its surface, interior, and gas and dust environment.
Dark Matter Isn’t Made From Black Holes
In February of 2016, scientists working for the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) made history when they announced the first-ever detection of gravitational waves. Since that time, multiple detections have taken place and scientific collaborations between observatories – like Advanced LIGO and Advanced Virgo – are allowing for unprecedented levels of sensitivity and data sharing.
Travelling overseas? What to do if a border agent demands access to your digital device
How the switchover to daylight saving time affects our health
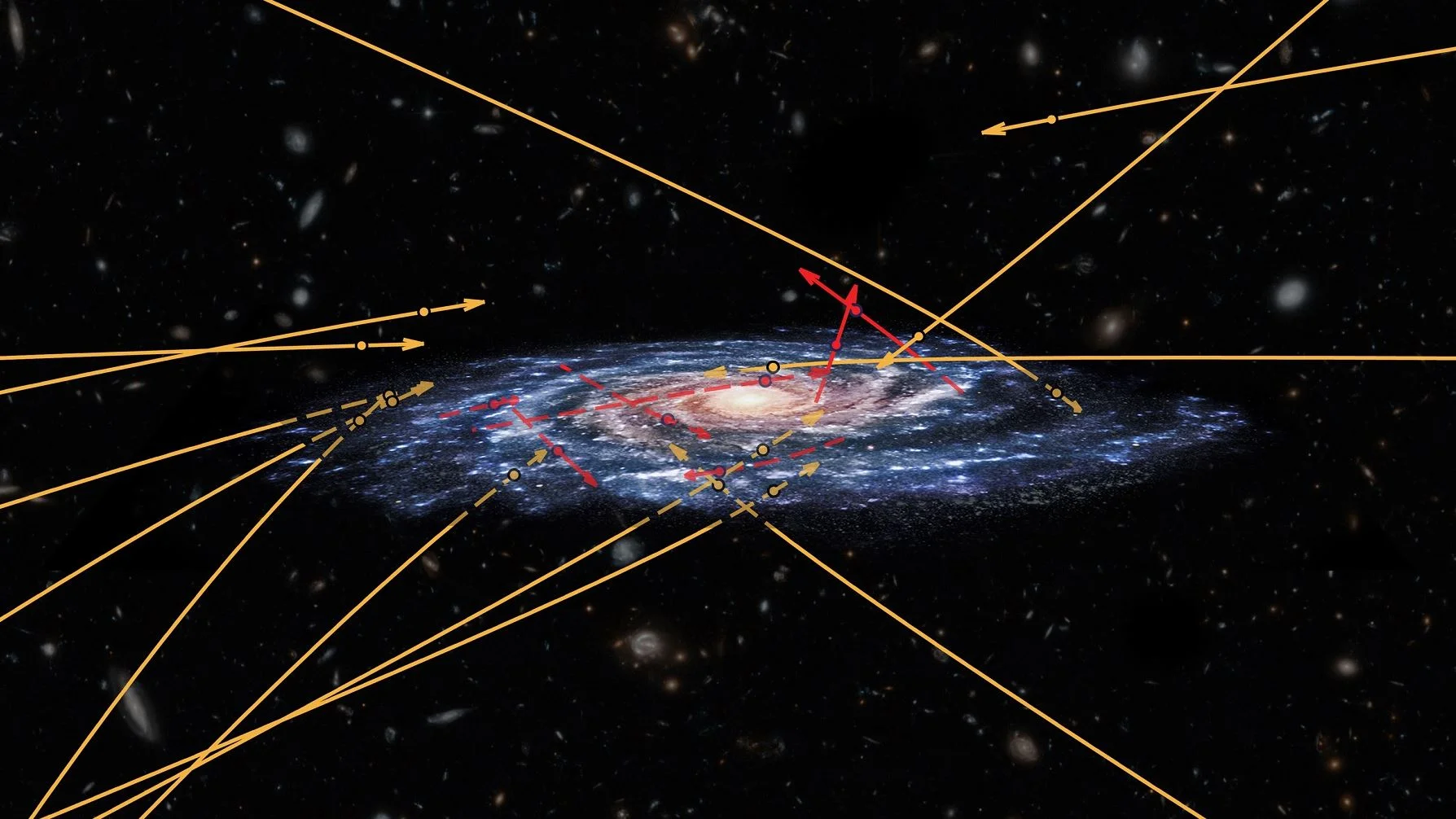
Gaia Sees Stars Out in Deep Space, Flying Between Galaxies
In December of 2013, the European Space Agency (ESA) launched the Gaia mission. Since that time, this space observatory has been busy observing over 1 billion astronomical objects in our galaxy and beyond – including stars, planets, comets, asteroids, quasars, etc. – all for the sake of creating the largest and most precise 3D space catalog ever made.
Explosive lies: how volcanoes can lie about their age, and what it means for us
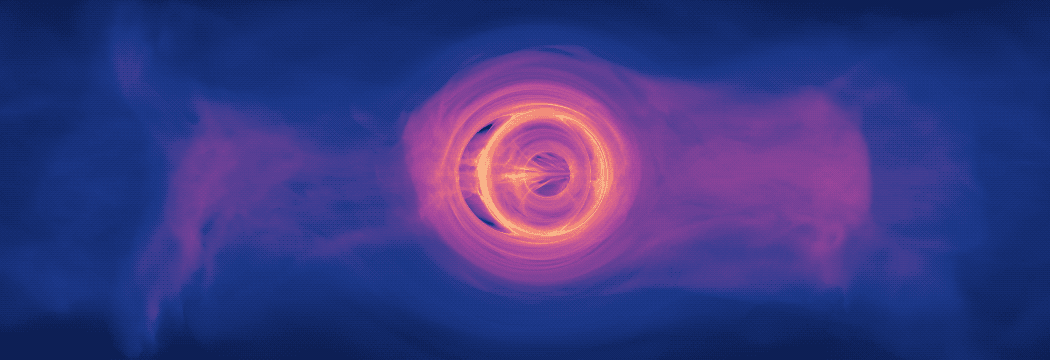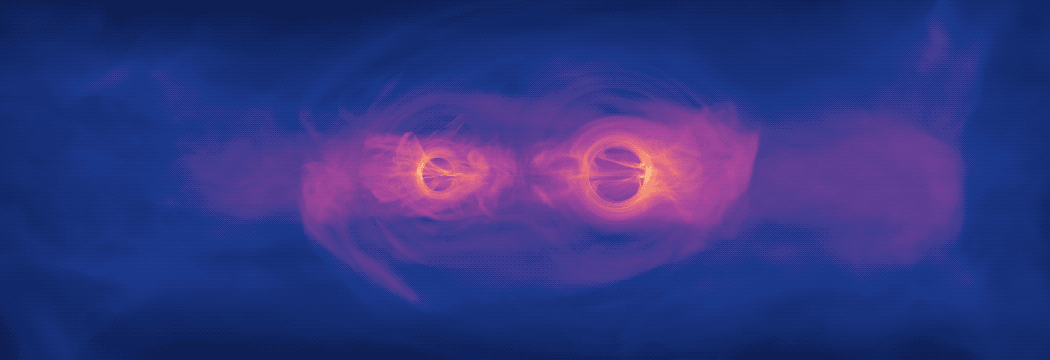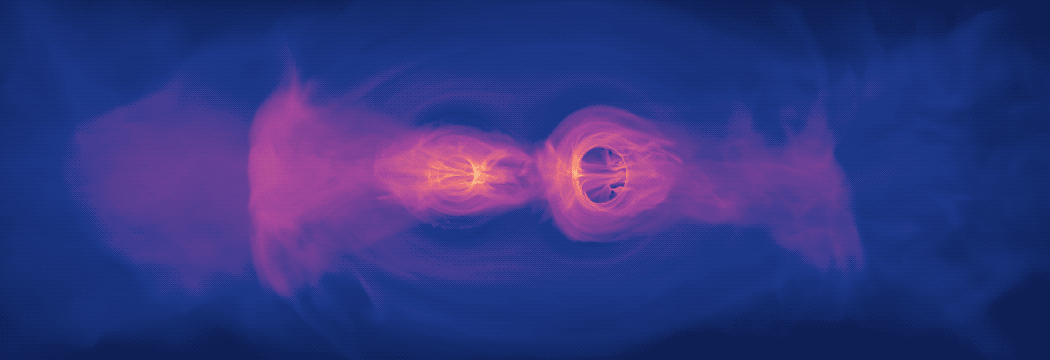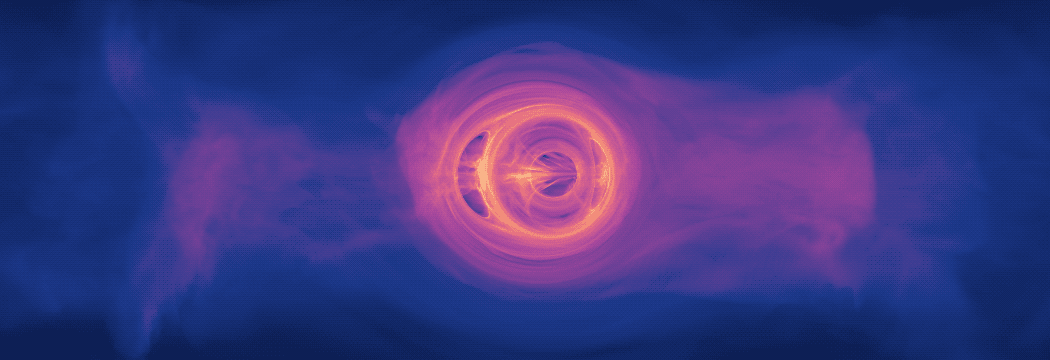
New Simulation Sheds Light on Spiraling Supermassive Black Holes
A new model is bringing scientists a step closer to understanding the kinds of light signals produced when two supermassive black holes, which are millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun, spiral toward a collision. For the first time, a new computer simulation that fully incorporates the physical effects of Einstein’s general theory of relativity shows that gas in such systems will glow predominantly in ultraviolet and X-ray light.
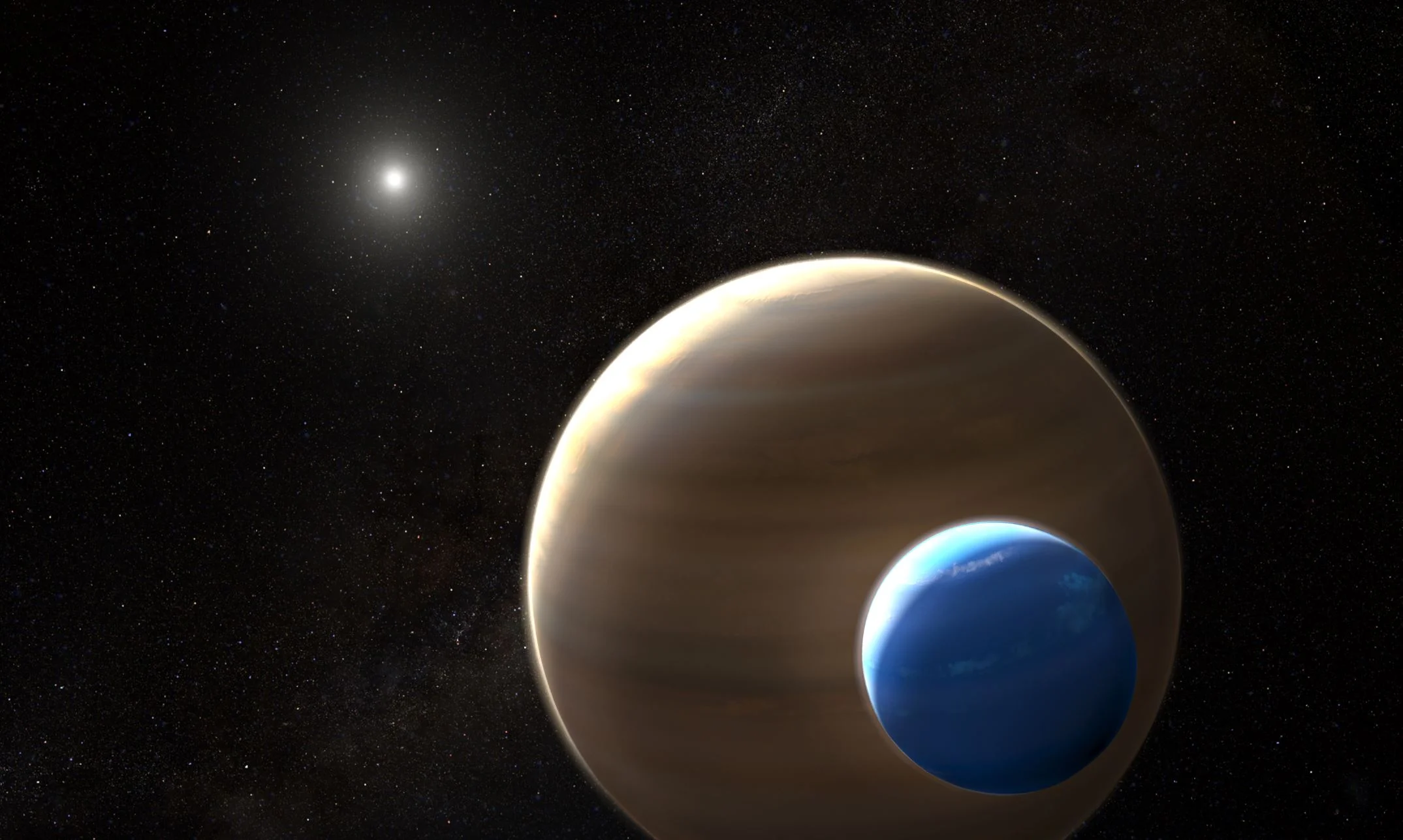
Astronomers Find First Evidence of Possible Moon Outside Our Solar System!
In Star Wars VI we first meet the Ewoks living on the Forest Moon of Endor. The planet Endor itself is a gas giant, but the Forest Moon is a habitable world, peopled by small furry sentient creatures. While we may not be living in the Star Wars universe, astronomers have now found the first evidence for a moon orbiting a gas giant planet in a star system other than our own.
A Universe Aglow - MUSE spectrograph reveals that nearly the entire sky in the early Universe is glowing with Lyman-alpha emission
Deep observations made with the MUSE spectrograph on ESO’s Very Large Telescope have uncovered vast cosmic reservoirs of atomic hydrogen surrounding distant galaxies. The exquisite sensitivity of MUSE allowed for direct observations of dim clouds of hydrogen glowing with Lyman-alpha emission in the early Universe — revealing that almost the whole night sky is invisibly aglow.
A decade of commercial space travel – what’s next?
Technosignatures are NASA’s New Target for Detecting Other Civilizations in Space. Wait. What’s a Technosignature?
Plant-rich diets may help prevent depression – new evidence
Being depressed can negatively affect your appetite and what you eat, but can bad eating habits bring your mood down? Our latest study, a systematic review of the best available evidence, found a clear link between the quality of a person’s diet and their risk of depression. And it goes beyond the effect of diet on body size or other aspects of health that can affect mental health.
Optical Rocket Boosts Electrons to Nearly the Speed of Light
A team of researchers from the University of Nebraska–Lincoln recently conducted an experiment where they were able to accelerate plasma electrons to close to the speed of light. This “optical rocket”, which pushed electrons at a force a trillion-trillion times greater than that generated by a conventional rocket, could have serious implications for everything from space travel to computing and nanotechnology.
Titan First-Ever Detected Dust Storms Proves the Moon to be More Earth-like than Ever
Ever since the Cassini orbiter entered the Saturn system in July of 2004, scientists and the general public have been treated to a steady stream of data about this ringed giant and its many fascinating moons. In particular, a great deal of attention was focused on Saturn’s largest moon Titan, which has many surprising Earth-like characteristics.
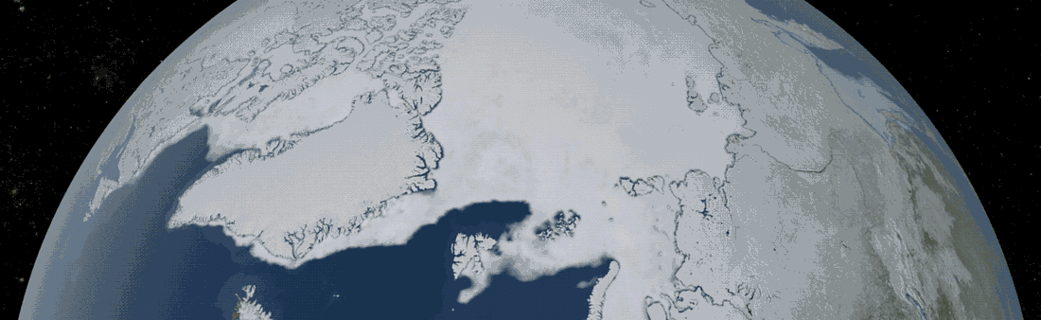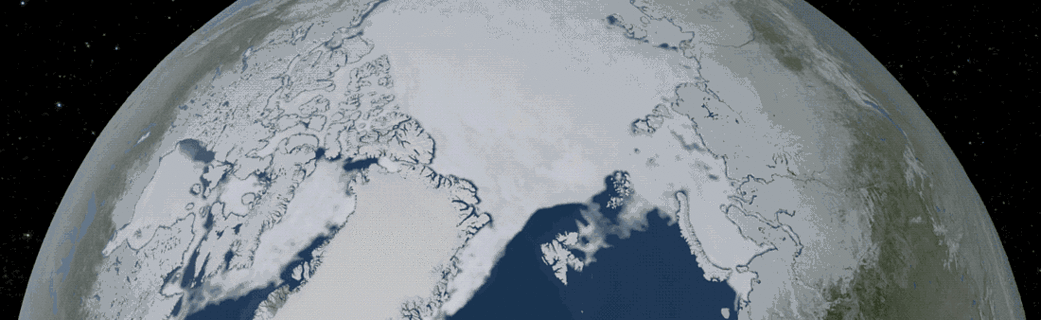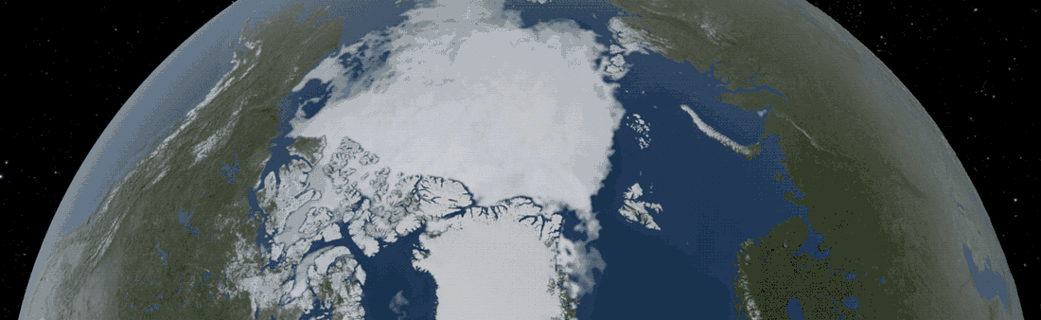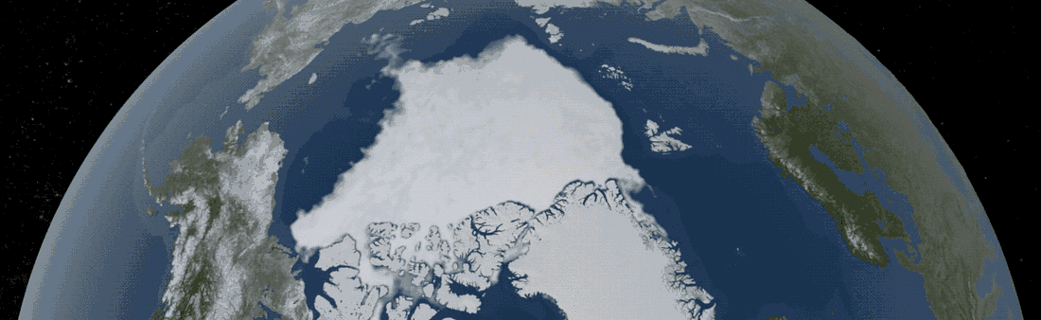
2018 Arctic Summertime Sea Ice Minimum Extent Tied for Sixth Lowest on Record
Arctic sea ice likely reached its 2018 lowest extent on Sept. 19 and again on Sept. 23, according to NASA and the NASA-supported National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) at the University of Colorado Boulder. Analysis of satellite data by NSIDC and NASA showed that, at 1.77 million square miles (4.59 million square kilometers), 2018 effectively tied with 2008 and 2010 for the sixth lowest summertime minimum extent in the satellite record.