In February of 2016, scientists at the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO) made history by announcing the first-ever detection of gravitational waves (GWs). These ripples in the very fabric of the Universe, which are caused by black hole mergers or white dwarfs colliding, were first predicted by Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity roughly a century ago.
The Incredible Challenge of Landing Heavy Payloads On Mars!
CERN: Study sheds light on one of physics’ biggest mysteries – why there’s more matter than antimatter
All those hours you 'wasted' on gaming as a kid might have been useful after all
Always had the idea that the hours you spent behind your Nintendo, Xbox, PC or Playstation must have been good for something? You can now provide that vague notion with a scientific basis. A recently published study in the Journal of Communication shows that a certain type of intelligence increases through gaming.
NASA’s Fermi Satellite Clocks ‘Cannonball’ Pulsar Speeding Through Space
Astronomers found a pulsar hurtling through space at nearly 2.5 million miles an hour — so fast it could travel the distance between Earth and the Moon in just 6 minutes. The discovery was made using NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope and the National Science Foundation's Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA).
We did a breakthrough ‘speed test’ in quantum tunnelling, and here’s why that’s exciting
New evidence suggests we should eat fewer eggs
Algorithms have already taken over human decision making
I can still recall my surprise when a book by evolutionary biologist Peter Lawrence entitled “The making of a fly” came to be priced on Amazon at $23,698,655.93 (plus $3.99 shipping). While my colleagues around the world must have become rather depressed that an academic book could achieve such a feat, the steep price was actually the result of algorithms feeding off each other and spiraling out of control. It turns out, it wasn’t just sales staff being creative: algorithms were calling the shots.
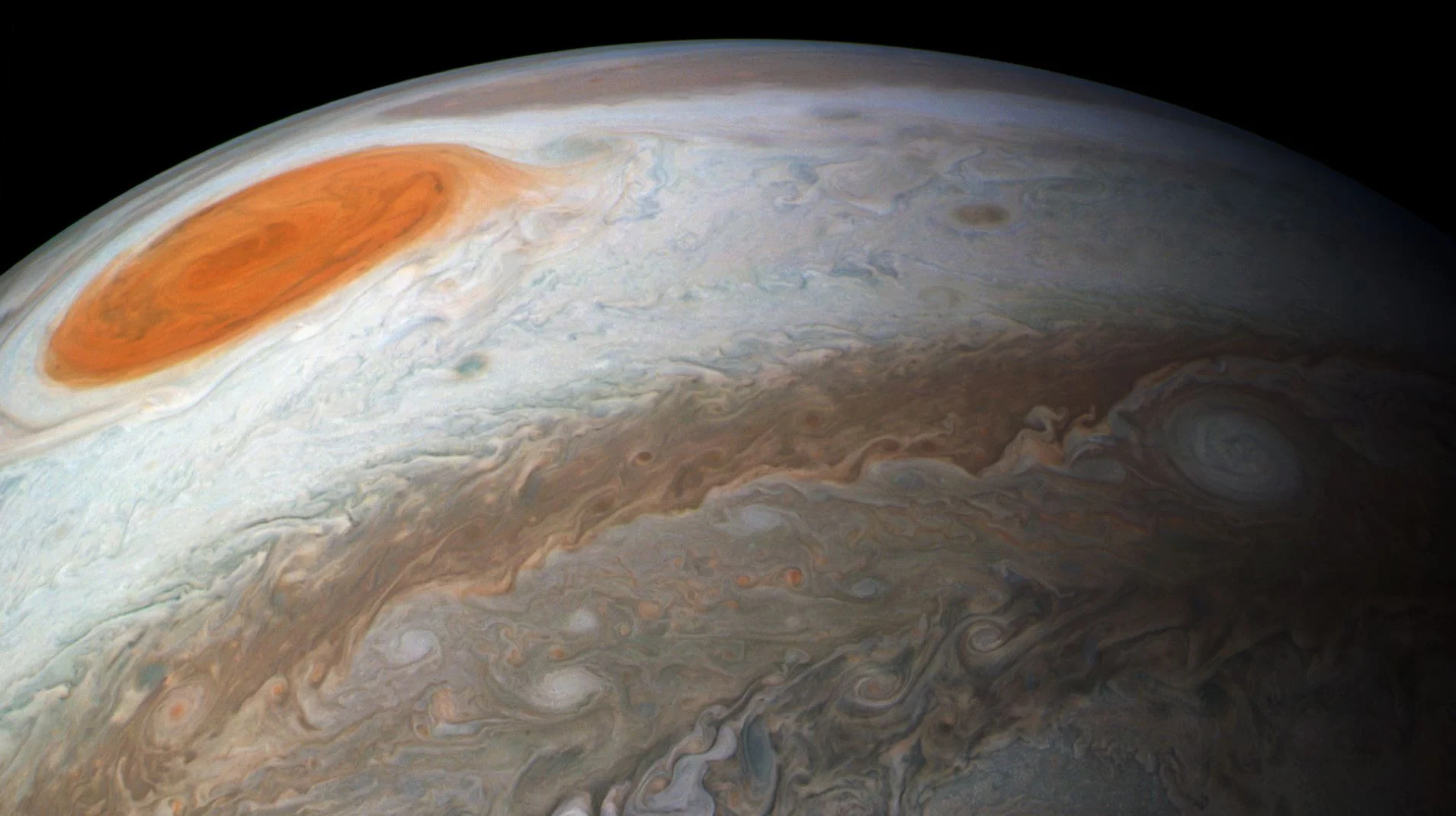
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot: A 300-year-old cyclone persists but is shrinking
The Great Red Spot, a storm larger than the Earth and powerful enough to tear apart smaller storms that get drawn into it, is one of the most recognizable features in Jupiter’s atmosphere and the entire solar system. The counterclockwise-moving storm, an anticyclone, boasts wind speeds as high as 300 miles per hour. This prominent feature, observed since 1830, and possibly as far back as the 1660s, has long been a source of great fascination and scientific study.
SpaceX Tests the Starship’s Hexagonal Heatshield. Starhopper Tests Could Come as Early as This Week!
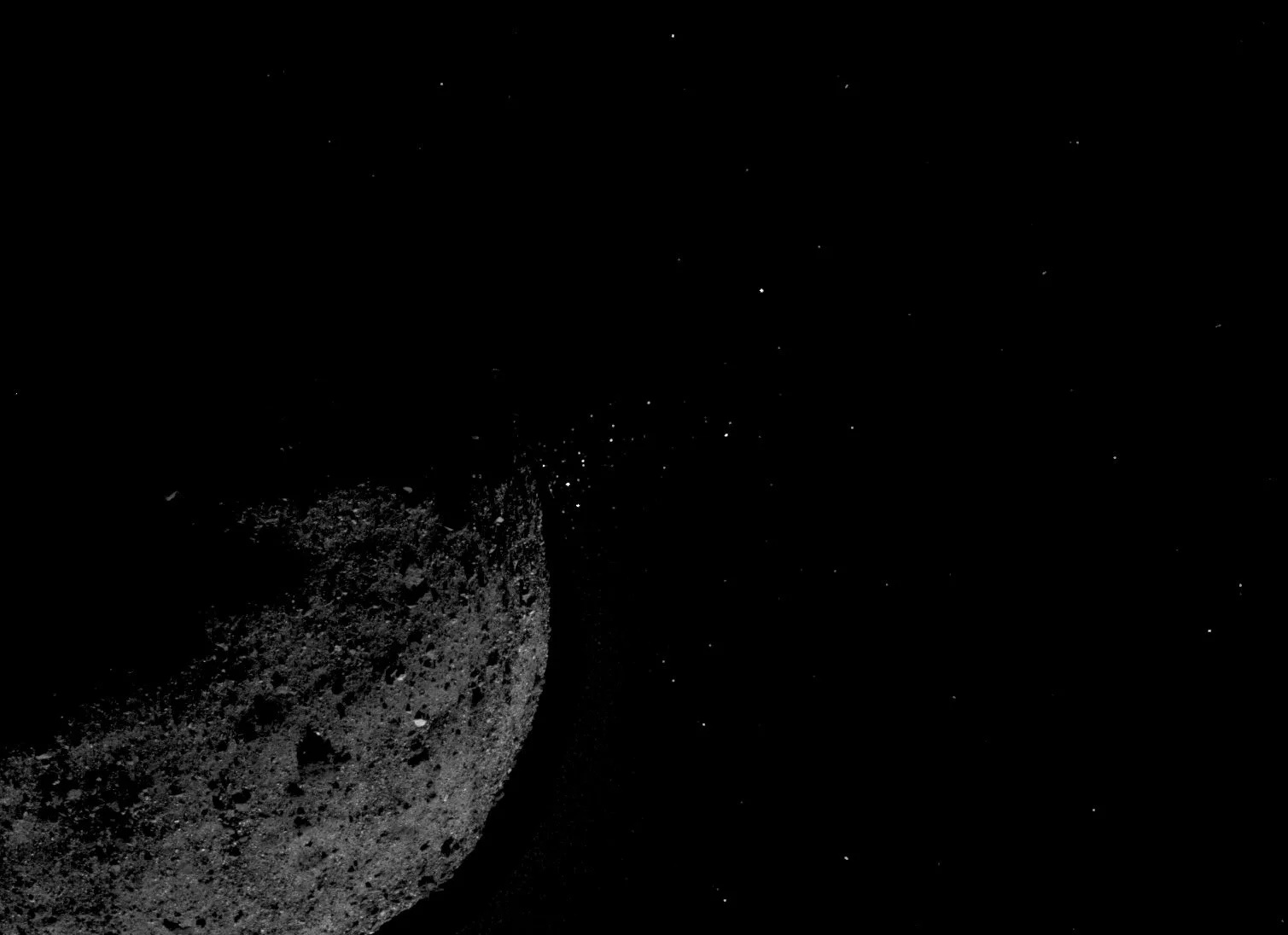
NASA Mission Reveals Asteroid Has Big Surprises
A NASA spacecraft that will return a sample of a near-Earth asteroid named Bennu to Earth in 2023 made the first-ever close-up observations of particle plumes erupting from an asteroid’s surface. Bennu also revealed itself to be more rugged than expected, challenging the mission team to alter its flight and sample collection plans, due to the rough terrain.
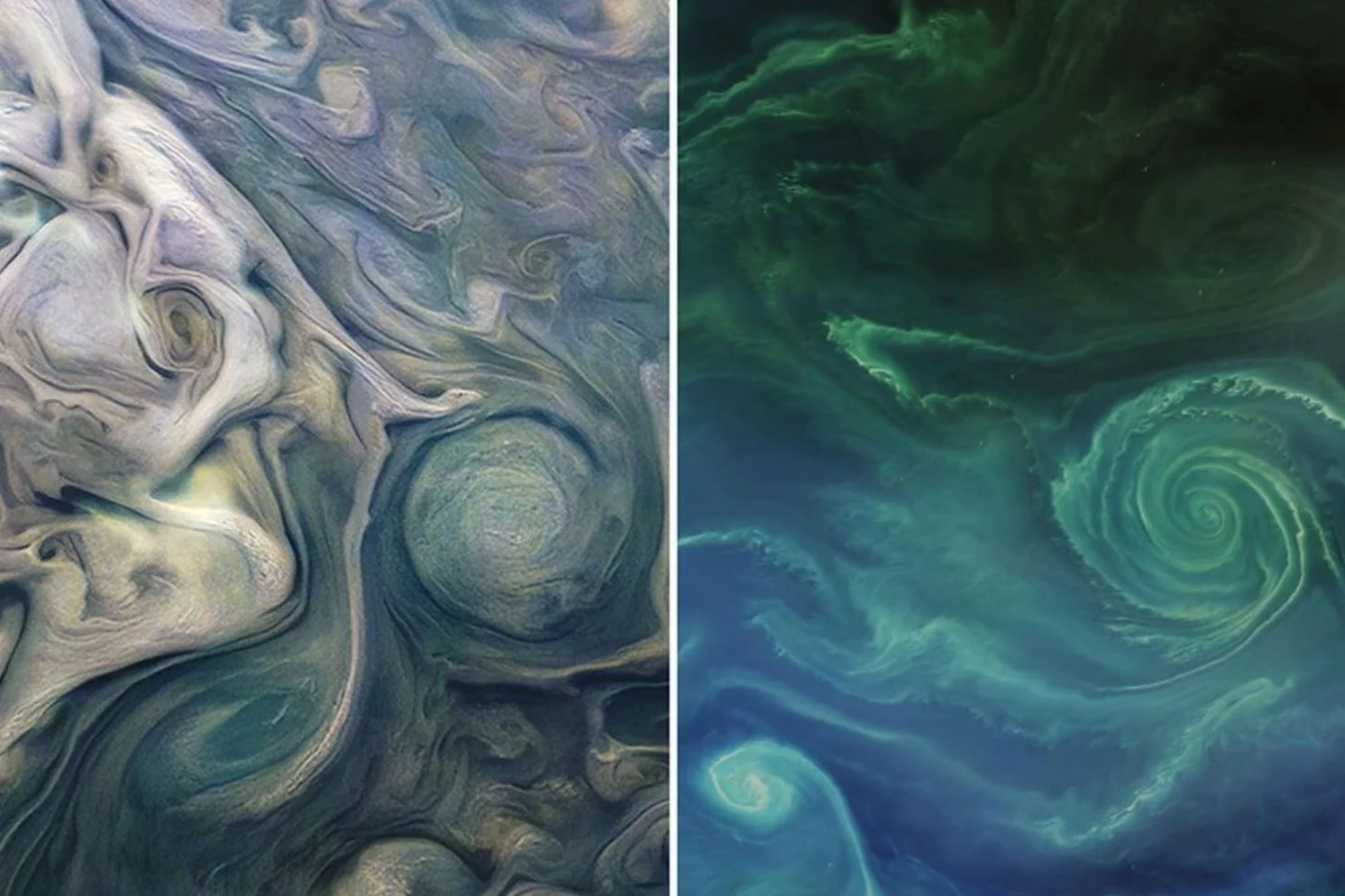
Jupiter or Earth? Which One’s Which, and Why Do They Look so Similar?
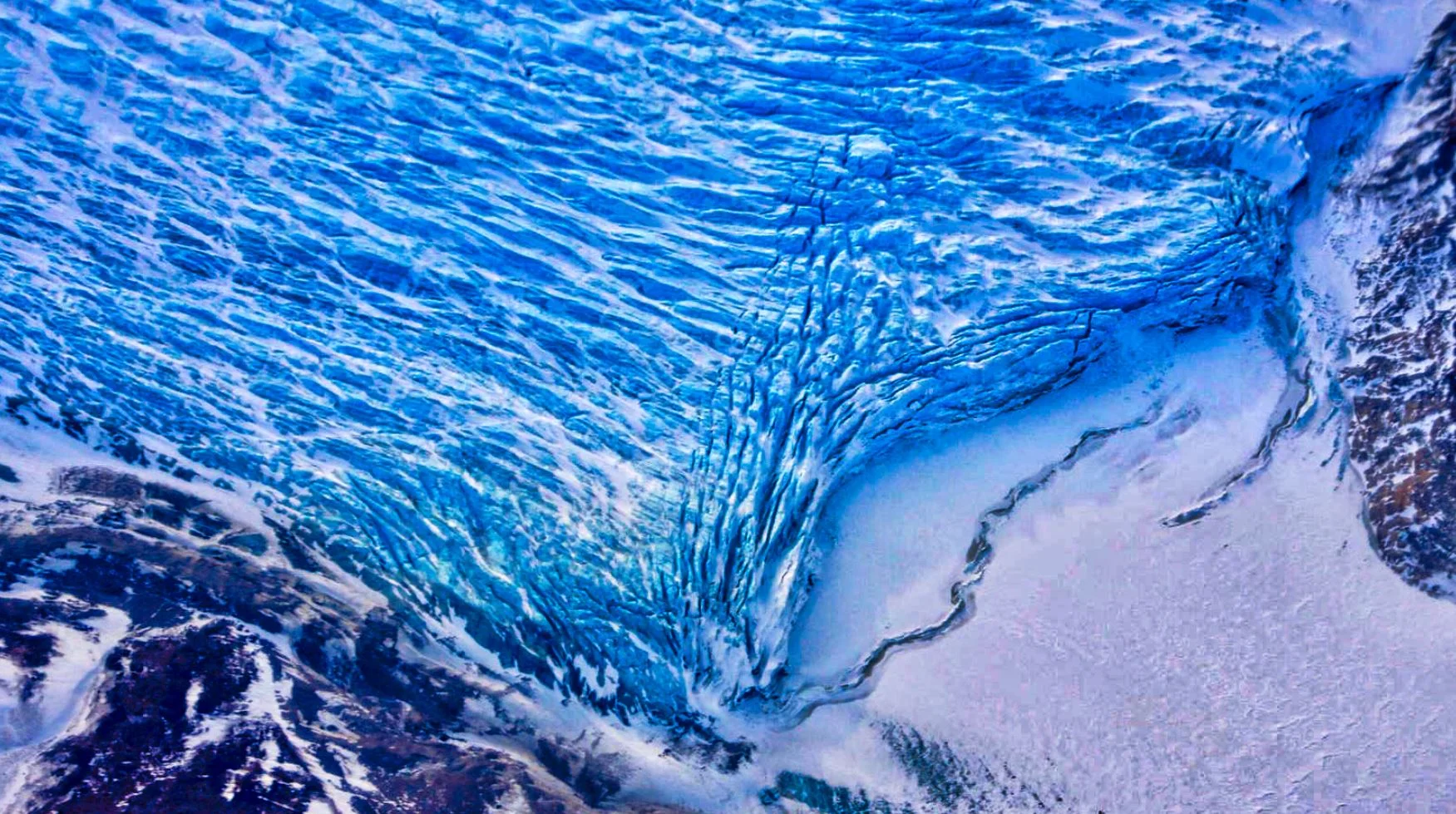
NASA's Greenland Mission Still Surprises in Year Four
Only seven months after NASA's Oceans Melting Greenland (OMG) mission wrapped its last field campaign on the world's largest island, an OMG crew is back in Greenland to collect more data. With two or three field projects a year since 2016, no wonder OMG has made the most comprehensive measurements yet of how ocean water lapping at the undersides of Greenland's melting glaciers affects them. All that data has answered a lot of existing questions — and it's raised plenty of new ones.
How H2 becomes ‘molecule that made the universe’
New evidence for a human magnetic sense that lets your brain detect the Earth’s magnetic field
Gravity influences how we make decisions – new research
Brain wave stimulation may improve Alzheimer’s symptoms
Using Black Holes to Conquer Space: The Halo Drive!
The idea of one day traveling to another star system and seeing what is there has been the fevered dream of people long before the first rockets and astronauts were sent to space. But despite all the progress we have made since the beginning of the Space Age, interstellar travel remains just that – a fevered dream. While theoretical concepts have been proposed, the issues of cost, travel time and fuel remain highly problematic.
Researchers reverse the flow of time on IBM’s quantum computer
Quantum simulation gives a sneak peek into the possibilities of time reversal. An international team of scientists led by Argonne explored the concept of reversing time in a first-of-its-kind experiment, managing to return a computer briefly to the past. The results present new possibilities for quantum computer program testing and error correction.
Cooking up Alien Atmospheres on Earth
Researchers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, are cooking up an alien atmosphere right here on Earth. In a new study, JPL scientists used a high-temperature "oven" to heat a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide to more than 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit (1,100 Celsius), about the temperature of molten lava. The aim was to simulate conditions that might be found in the atmospheres of a special class of exoplanets (planets outside our solar system) called "hot Jupiters."