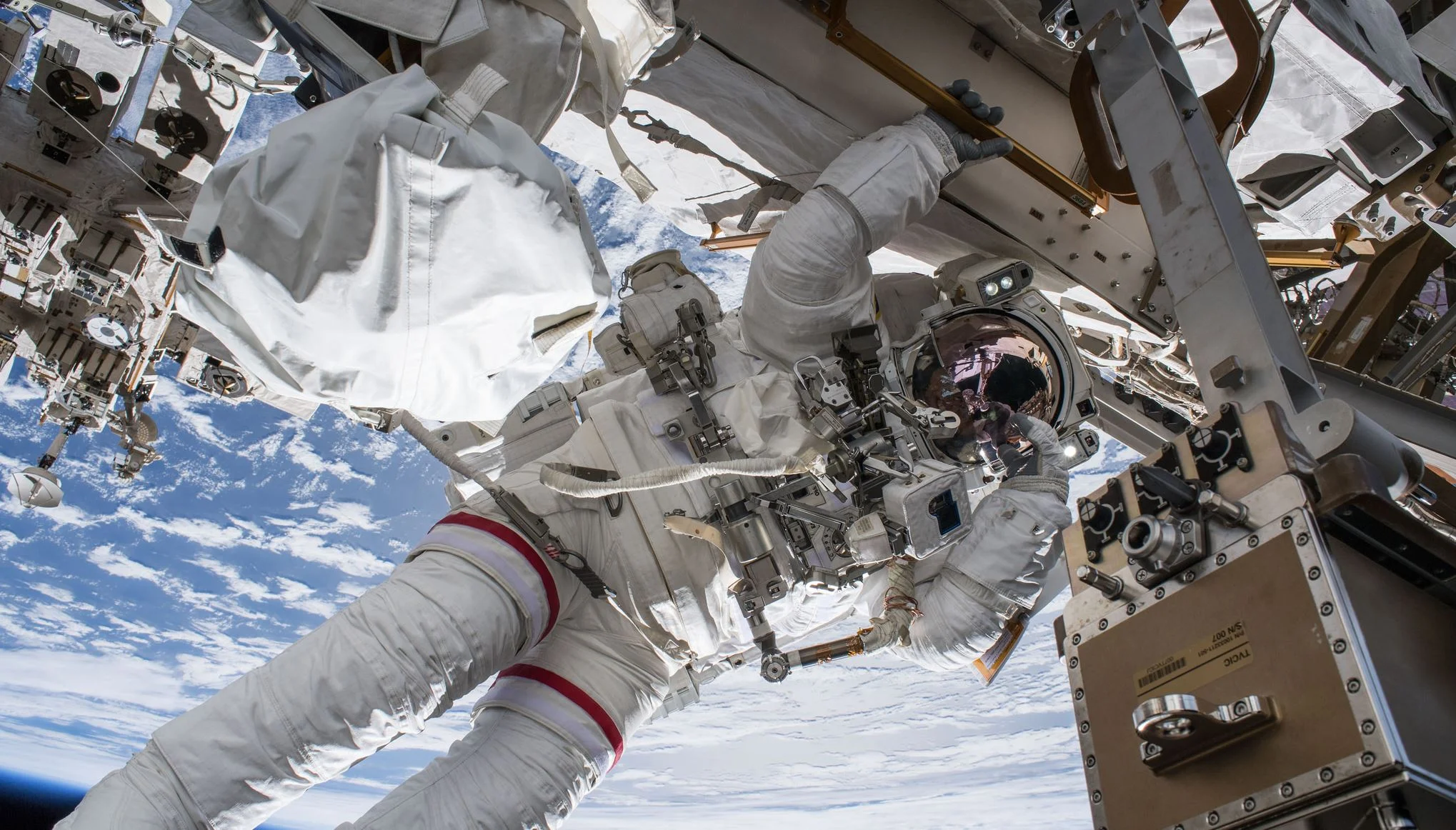
The milestones just keep coming for SpaceX. After the recent successful test flight of the Crew Dragon capsule, another of SpaceX’s ventures is about to meet its own milestone. The SpaceX Starhopper could have its first test flight as soon as this week.
NASA Mission Reveals Asteroid Has Big Surprises
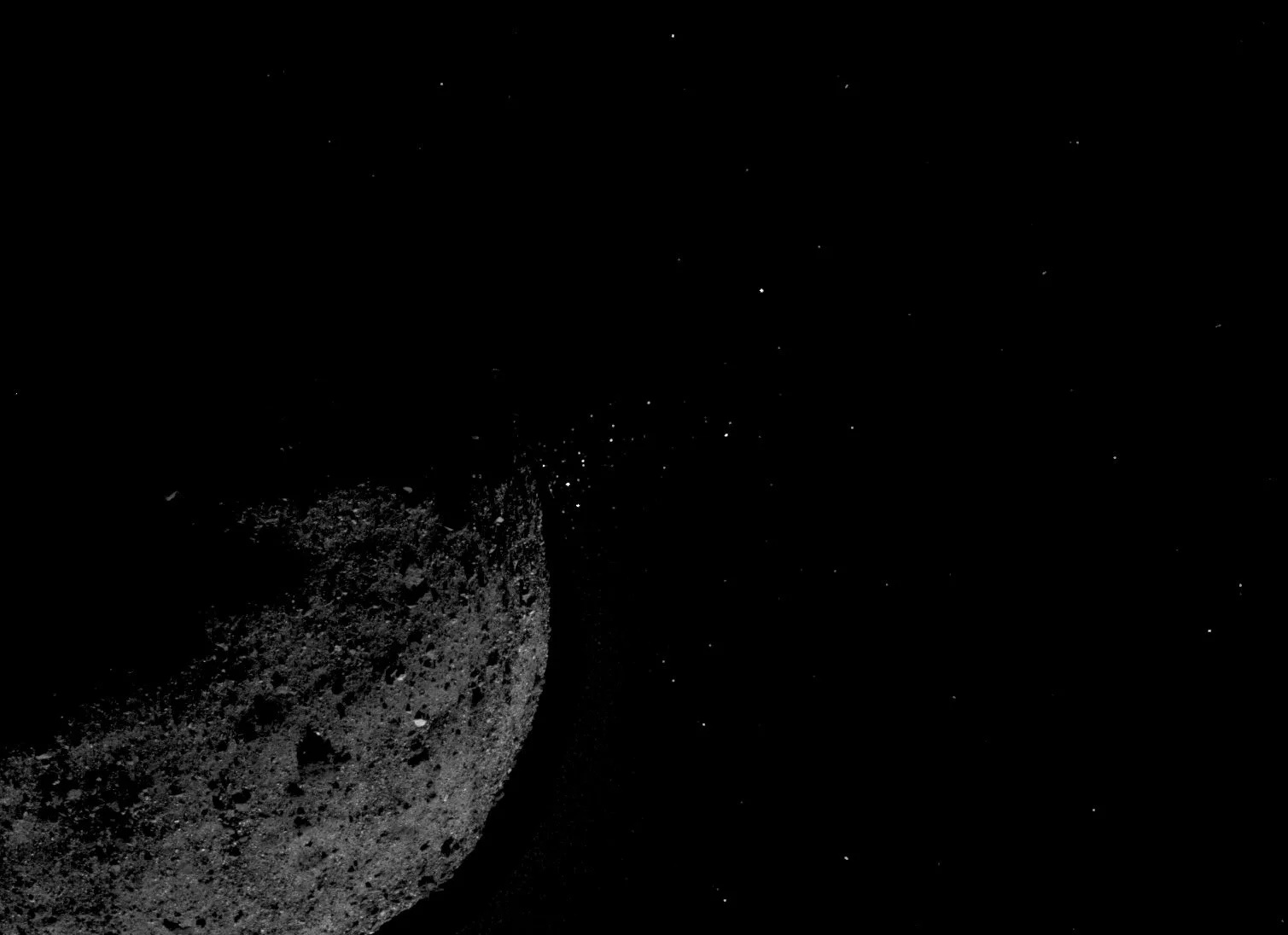
A NASA spacecraft that will return a sample of a near-Earth asteroid named Bennu to Earth in 2023 made the first-ever close-up observations of particle plumes erupting from an asteroid’s surface. Bennu also revealed itself to be more rugged than expected, challenging the mission team to alter its flight and sample collection plans, due to the rough terrain.
Gravity influences how we make decisions – new research
Using Black Holes to Conquer Space: The Halo Drive!
The idea of one day traveling to another star system and seeing what is there has been the fevered dream of people long before the first rockets and astronauts were sent to space. But despite all the progress we have made since the beginning of the Space Age, interstellar travel remains just that – a fevered dream. While theoretical concepts have been proposed, the issues of cost, travel time and fuel remain highly problematic.
Cooking up Alien Atmospheres on Earth
Researchers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, are cooking up an alien atmosphere right here on Earth. In a new study, JPL scientists used a high-temperature "oven" to heat a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide to more than 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit (1,100 Celsius), about the temperature of molten lava. The aim was to simulate conditions that might be found in the atmospheres of a special class of exoplanets (planets outside our solar system) called "hot Jupiters."
Chances for life expand when passing stars push binaries together
Planetary systems can be harsh environments in their early history. The young worlds orbit suns in stellar nurseries, clusters of stars where violent encounters are commonplace. None of this makes it easy for life to get going, but now astronomers at the University of Sheffield find one positive of this tumultuous period. A model developed by undergraduate student Bethany Wootton and Royal Society Dorothy Hodgkin Fellow Dr Richard Parker looks at how the habitable zone – the region around a star where the temperature allows liquid water to exist – changes around pairs of stars, so-called binary systems.
This is What It’ll Look Like When the Milky Way and Andromeda Galaxies Collide Billions of Years from Now
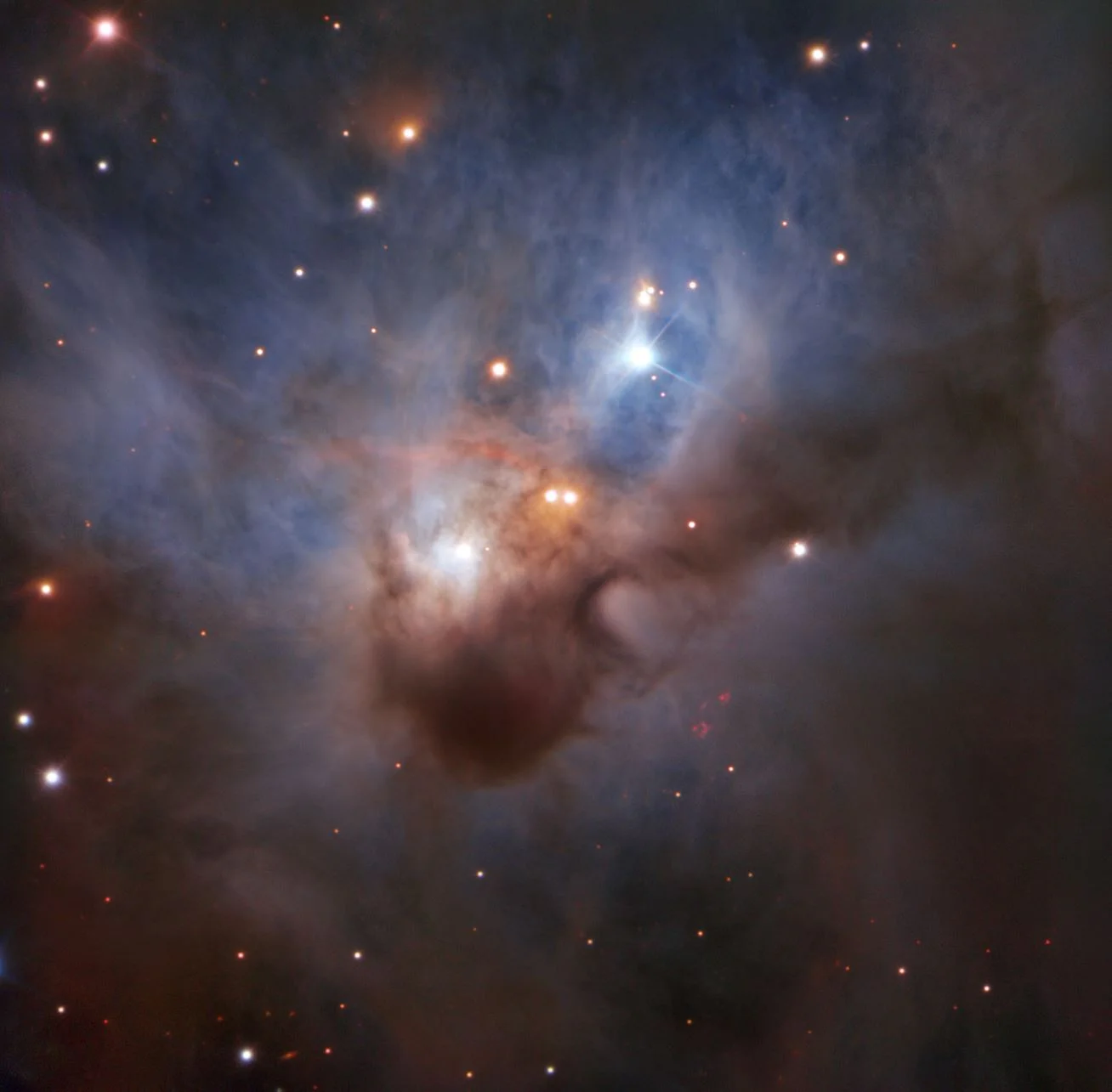
A Cosmic Bat in Flight - ESO’s Cosmic Gems Programme captures the Cosmic Bat’s dusty clouds
Hidden in one of the darkest corners of the Orion constellation, this Cosmic Bat is spreading its hazy wings through interstellar space two thousand light-years away. It is illuminated by the young stars nestled in its core — despite being shrouded by opaque clouds of dust, their bright rays still illuminate the nebula. Too dim to be discerned by the naked eye, NGC 1788 reveals its soft colours to ESO's Very Large Telescope in this image — the most detailed to date.
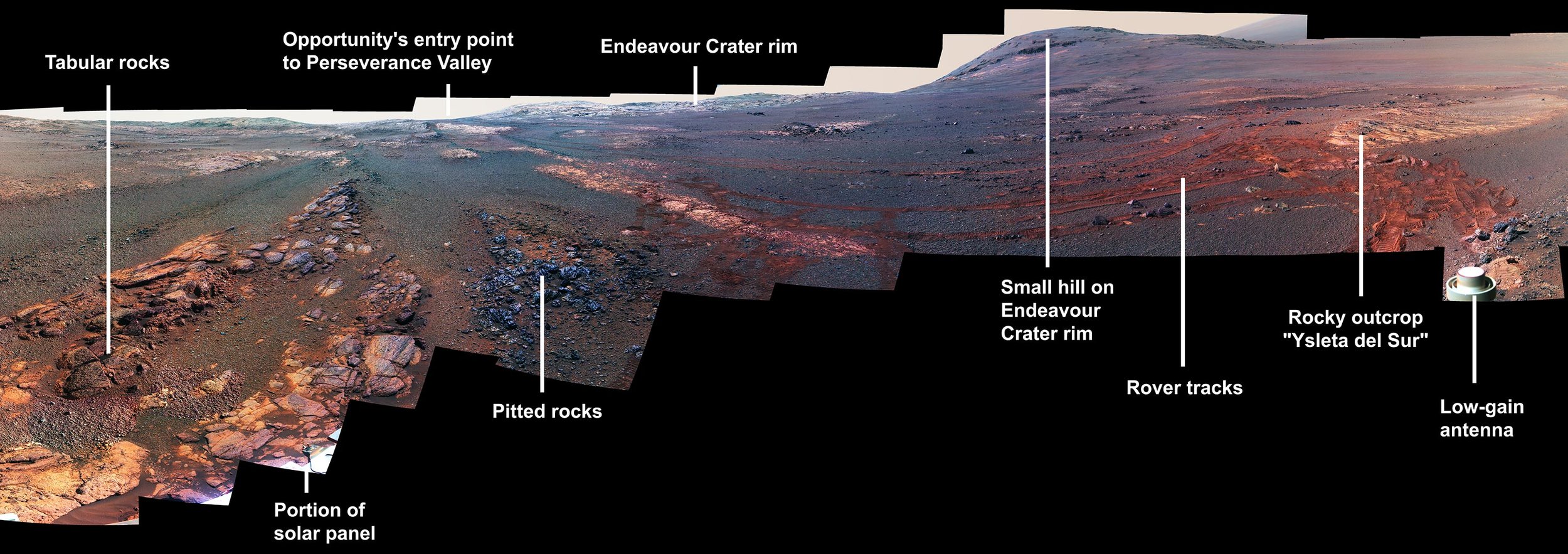
Opportunity's Parting Shot Was a Beautiful Panorama
Over 29 days last spring, NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity documented this 360-degree panorama from multiple images taken at what would become its final resting spot in Perseverance Valley. Located on the inner slope of the western rim of Endeavour Crater, Perseverance Valley is a system of shallow troughs descending eastward about the length of two football fields from the crest of Endeavour's rim to its floor.
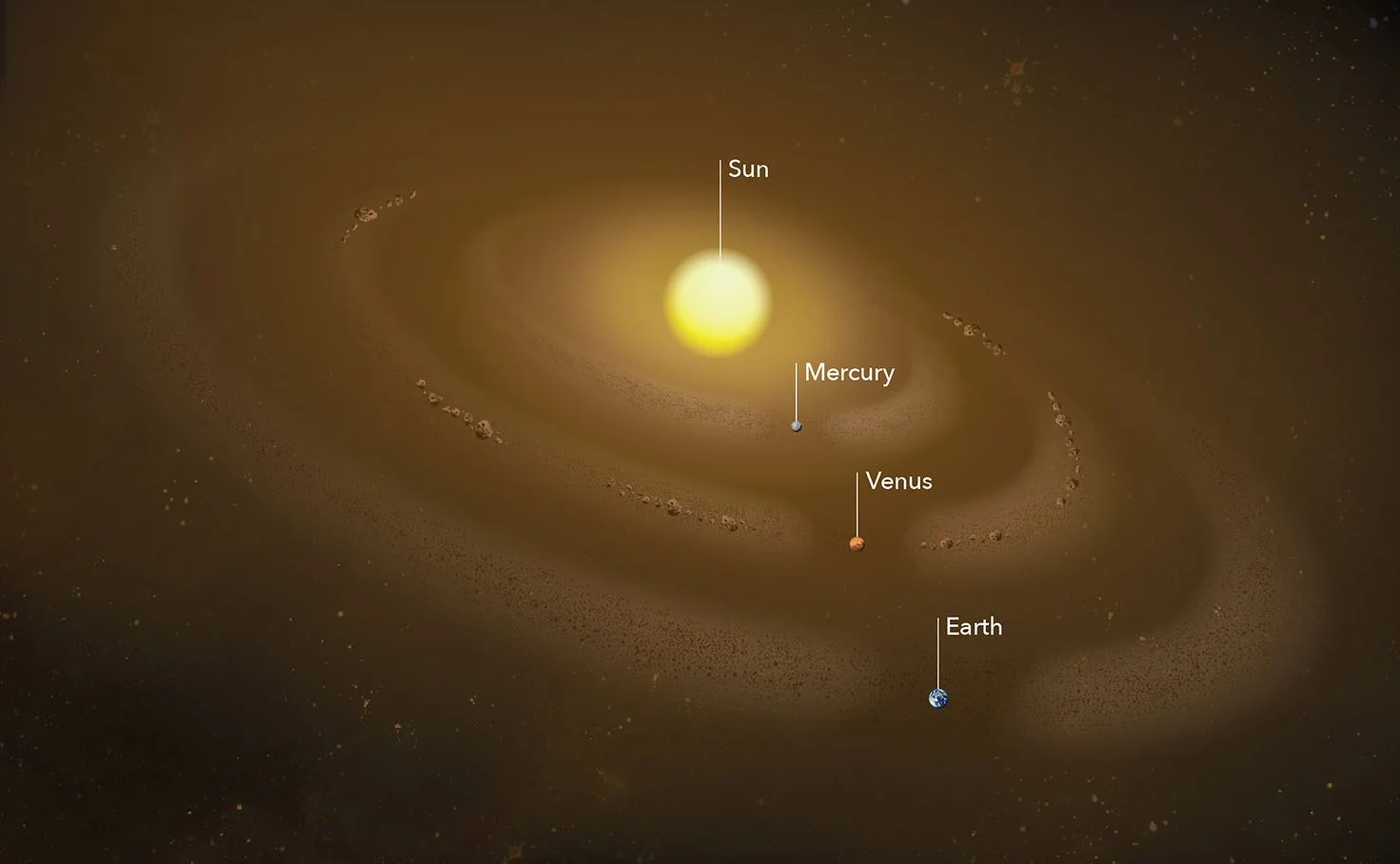
What Scientists Found After Sifting Through Dust in the Solar System
Just as dust gathers in corners and along bookshelves in our homes, dust piles up in space too. But when the dust settles in the solar system, it’s often in rings. Several dust rings circle the Sun. The rings trace the orbits of planets, whose gravity tugs dust into place around the Sun, as it drifts by on its way to the center of the solar system.
Do cosmic rays come from galactic bubbles?
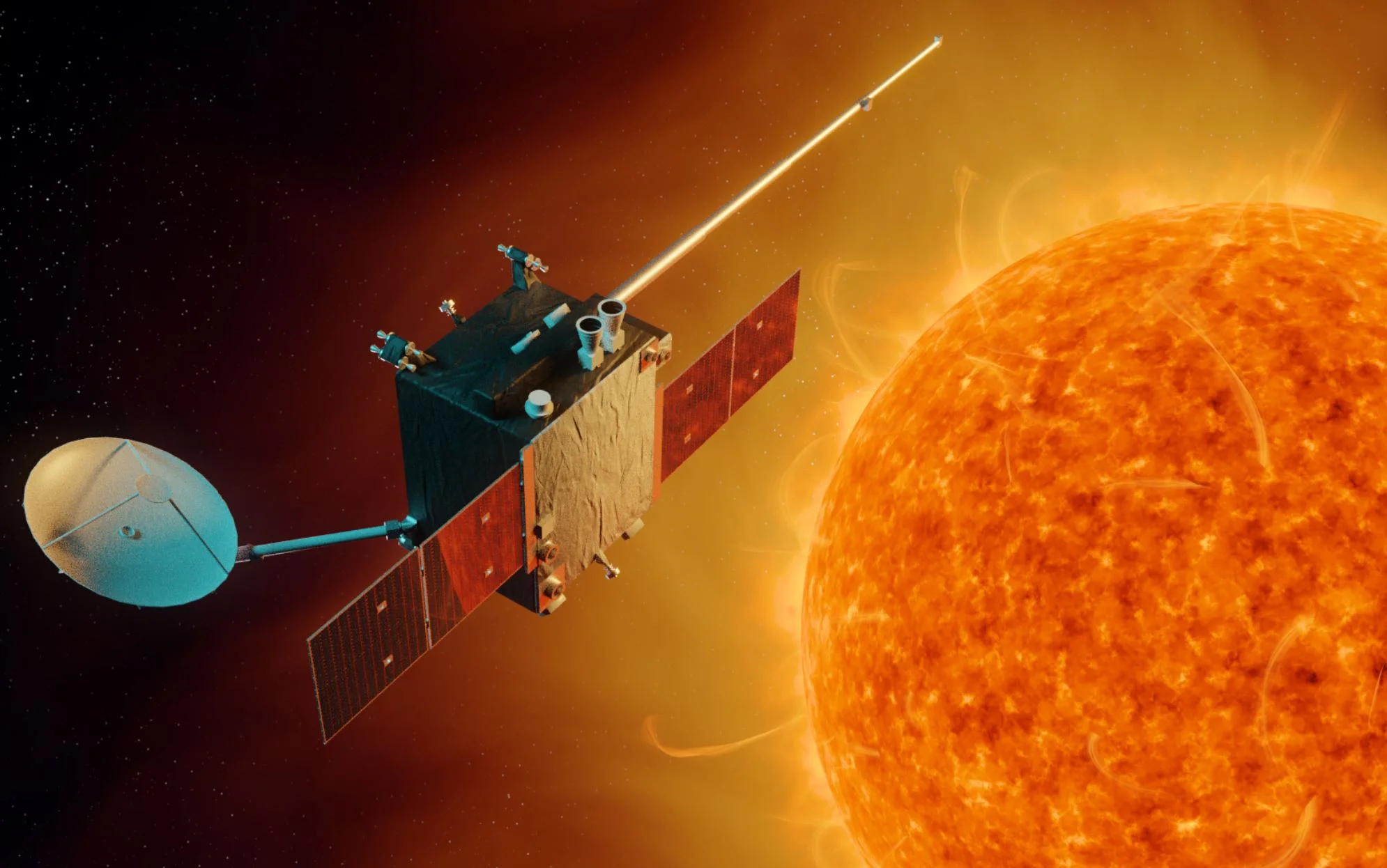
Our space weather mission will venture deeper into space than any other – here’s what it could achieve
You may have noticed that some weather forecasts have started mentioning the chances of seeing an aurora, also known as northern lights. Just as the atmosphere of the Earth gives us terrestrial weather, the nearby, vast atmosphere of the sun gives rise to space weather – triggering events such as auroras. Many weather institutes around the world now provide forecasts of the weather in space because of the hazard it poses to services we rely on, such as satellite positioning services, power distribution and communications.
Hydrogen fuels rockets, but what about power for daily life? We’re getting close
Gamma Ray Telescopes could Detect Starships Powered by Black Hole
In the course of looking for possible signs of Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence (ETI), scientists have had to do some really outside-of-the-box thinking. Since it is a foregone conclusion that many ETIs would be older and more technologically advanced than humanity, those engaged in the Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence (SETI) have to consider what a more advanced species would be doing.
SpaceX Dragon 2 pulled off nail-biting landing – here’s the rocket science
A fiery Dragon lit up the sky over the Atlantic before cooling off with a watery splashdown on March 8. The SpaceX Dragon 2 capsule is of enormous significance for spaceflight as it has just become the first commercial vehicle to automatically dock with the International Space Station (ISS) and return to Earth. The spacecraft will now aim to carry astronauts to the ISS in a few months.
“Goldilocks” Stars May Be “Just Right” for Finding Habitable Worlds
Discovery Alert! Kepler's First Planet Candidate Confirmed, 10 Years Later
Moon mining could help meet future energy needs
If you were transported to the Moon this very instant, you would surely and rapidly die. That’s because there’s no atmosphere, the surface temperature varies from a roasting 130 degrees Celsius (266 F) to a bone-chilling minus 170 C (minus 274 F). If the lack of air or horrific heat or cold don’t kill you then micrometeorite bombardment or solar radiation will. By all accounts, the Moon is not a hospitable place to be.
Hayabusa2 Left a Dark Spot Where it Touched Down on Ryugu. Engineers Aren’t Sure Why
On June 27th, 2018, the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency‘s (JAXA) Hayabusa2 spacecraft rendezvoused with the asteroid 162173 Ryugu. Carrying on in the same tradition as its predecessor, Hayabusa2 recently conducted landing operations on the asteroid’s surface as part of the agency’s second sample-return mission from an asteroid.