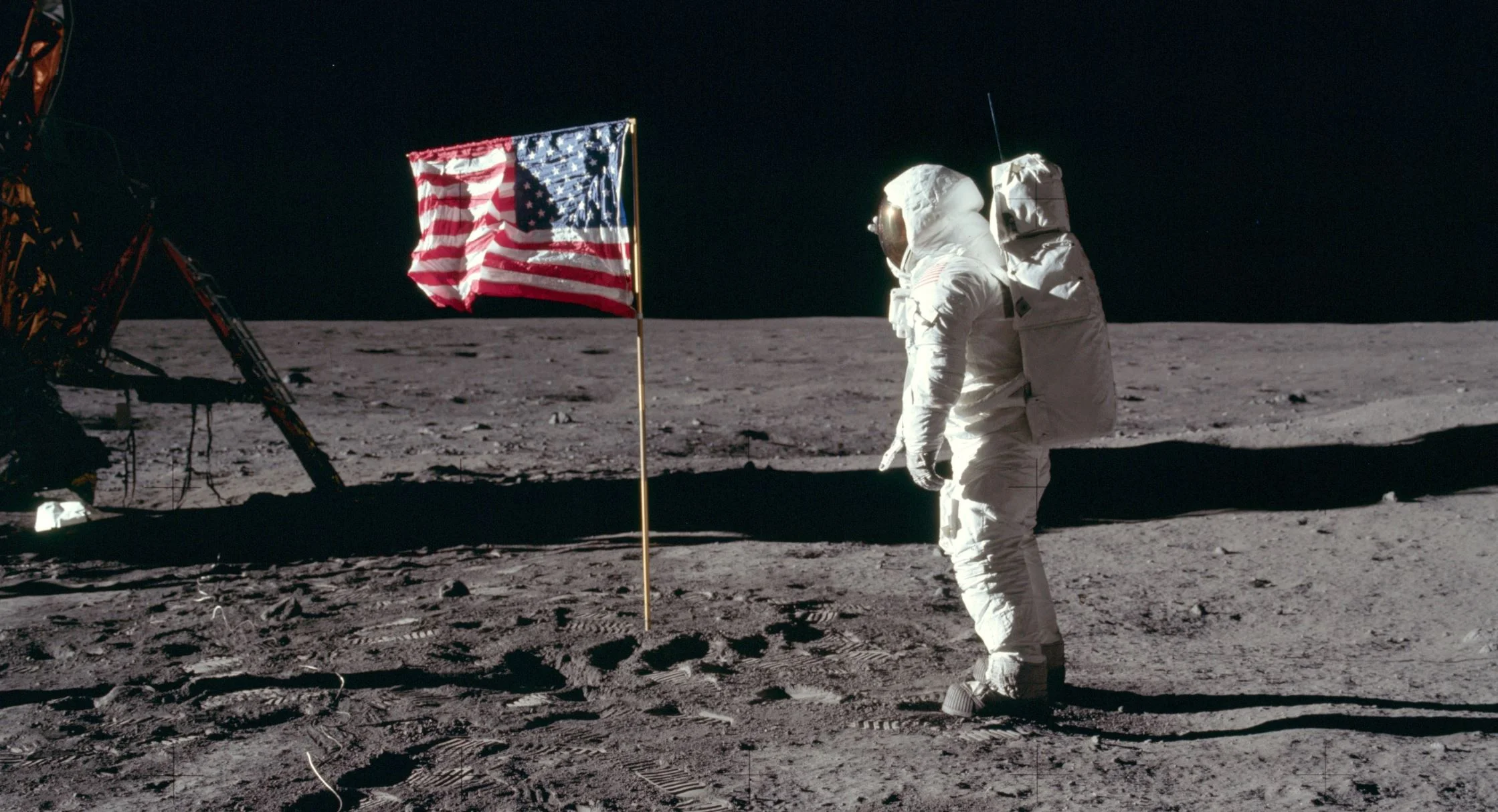
Many people who are old enough to have experienced the first moon landing will vividly remember what it was like watching Neil Armstrong utter his famous quote: “That’s one small step for a man, one giant leap for mankind.”. Half a century later, the event is still one of the top achievements of humankind. Despite the rapid technological advances since then, astronauts haven’t actually been back to the moon since 1972.
The Most Efficient Way to Explore the Entire Milky Way, Star by Star
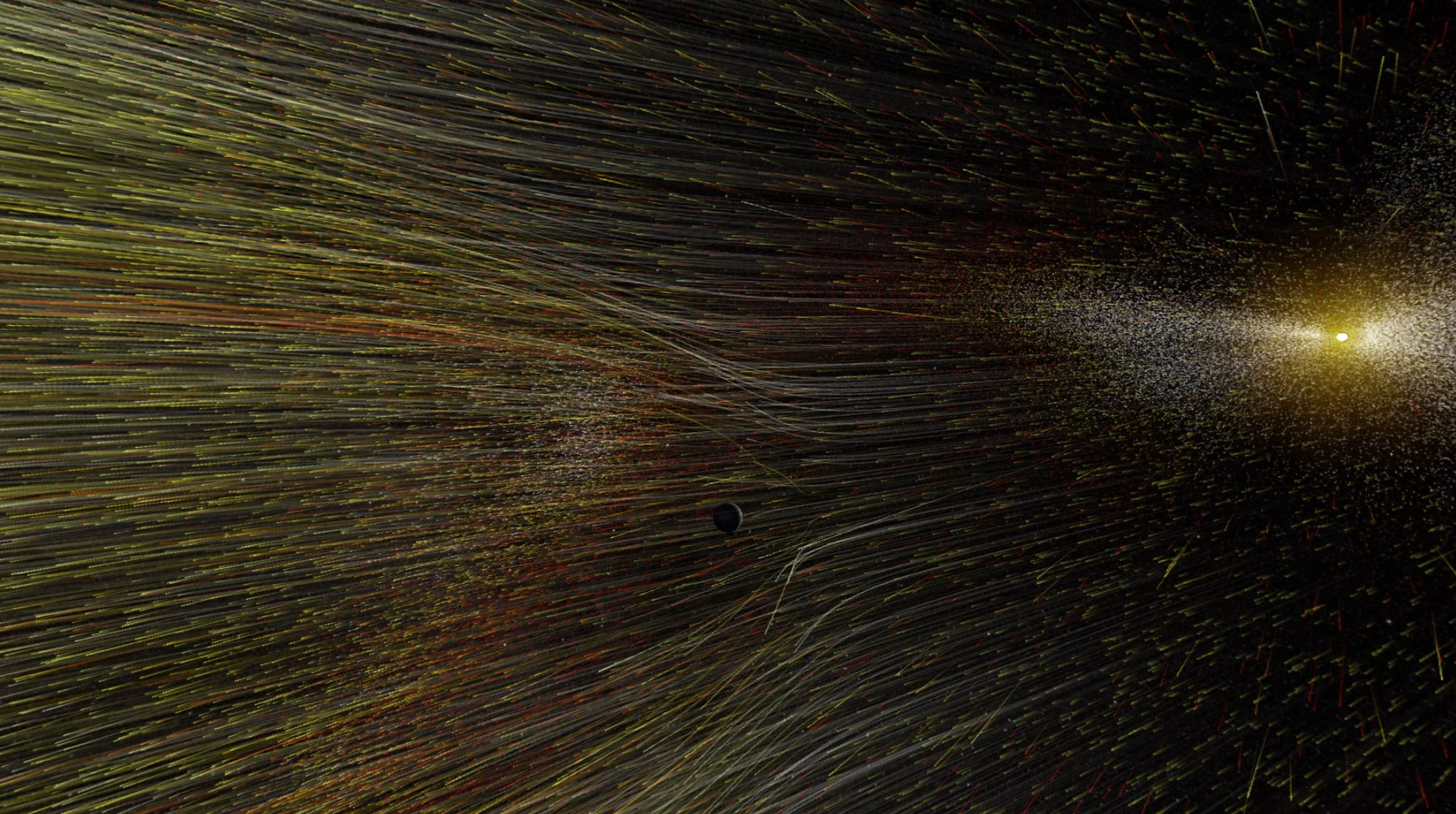
It seems like the stuff of dreams, the idea that humanity will one day venture beyond the Solar System and become an interstellar species. Who knows? Given enough time and the right technology (and assuming there’s not some serious competition), we might even be able to colonize the entire Milky Way galaxy someday. And while this seems like a far-off prospect at best, it makes sense to contemplate what a process like this would entail.
Four surprising technological innovations that came out of the Apollo moon landings
NASA’s Apollo program was one of the most challenging technological achievements in the 20th century. Beyond the space race and exploration, it contributed to several inventions and innovations that are still having an impact on our lives. But at the same time, there are several myths regarding what technologies actually came out of it.
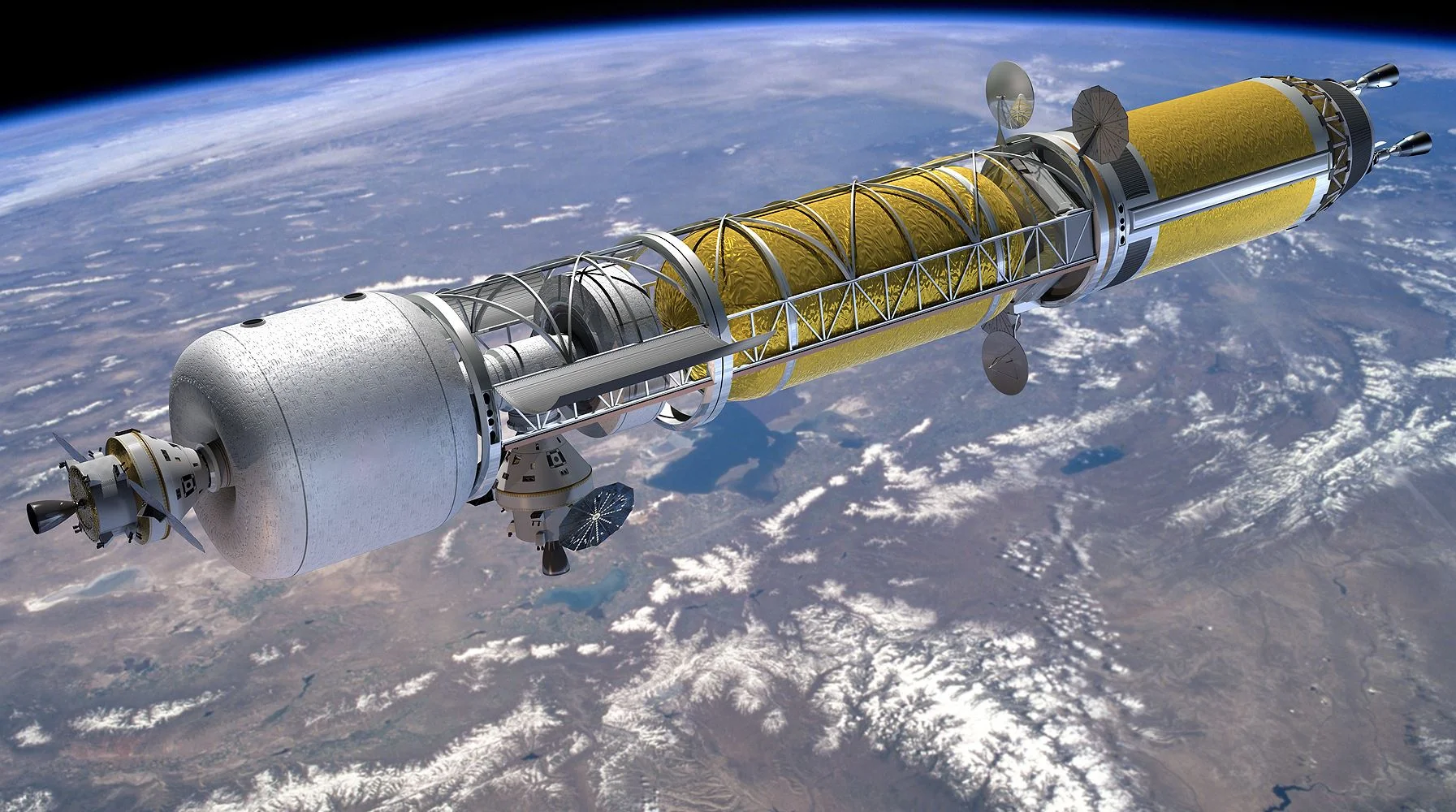
Earth To Mars In 100 Days? The Power Of Nuclear Rockets
Meet the Comet Interceptor. It’ll Wait Patiently In Space for a Comet, Then Pounce On It
Who Wants to be a Trillionaire? Mission to Psyche Could Uncover Tons of Precious Metals!
It has been said that within the next quarter century, the world’s first trillionaires will emerge. It is also predicted that much of their wealth will stem from asteroid mining, a burgeoning space industry where minerals and volatile compounds will be harvested from Near-Earth Asteroids. This industry promises to flood the market with ample supplies of precious metals like gold, silver and platinum.
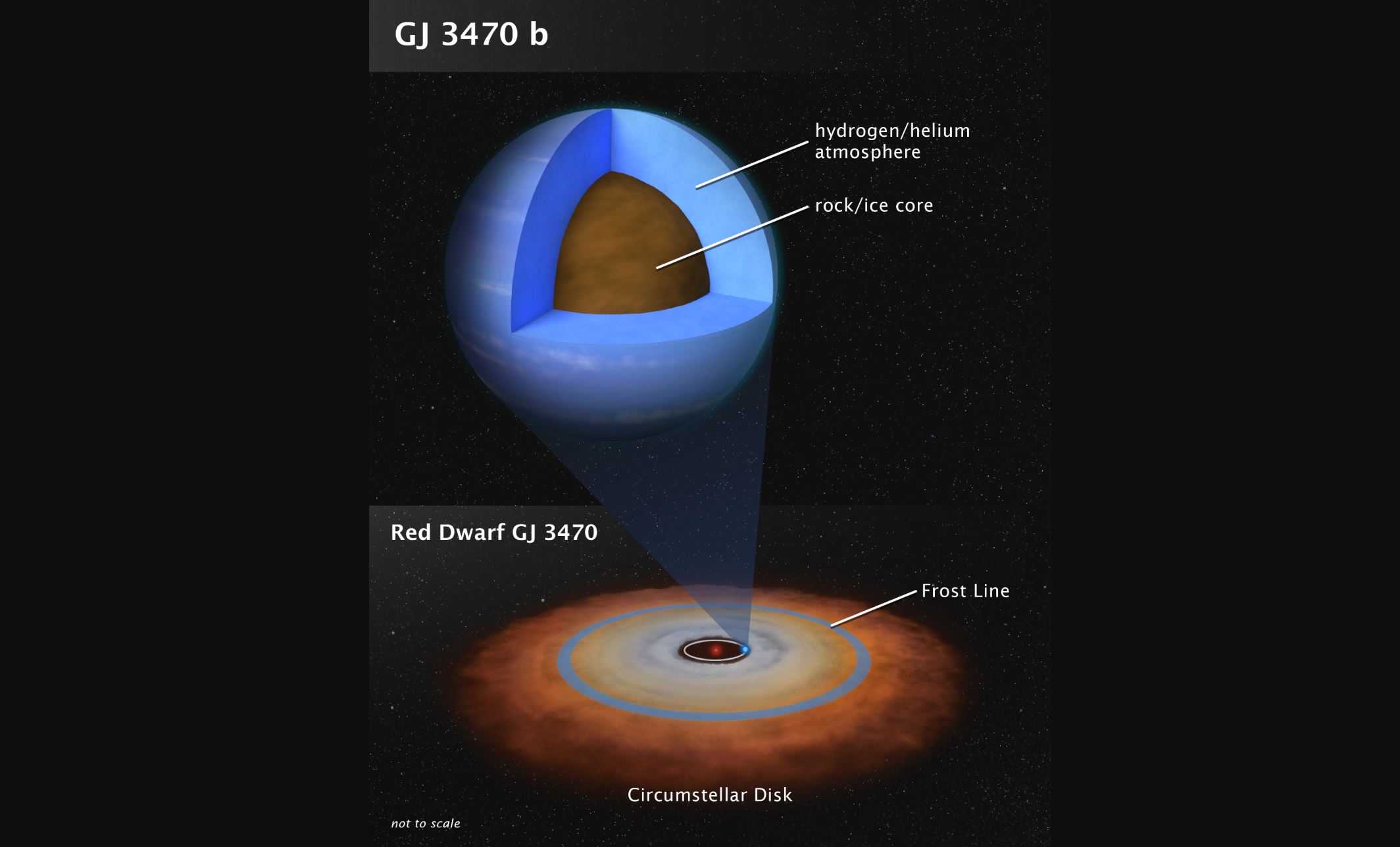
Atmosphere of Midsize Planet Revealed by Hubble, Spitzer!
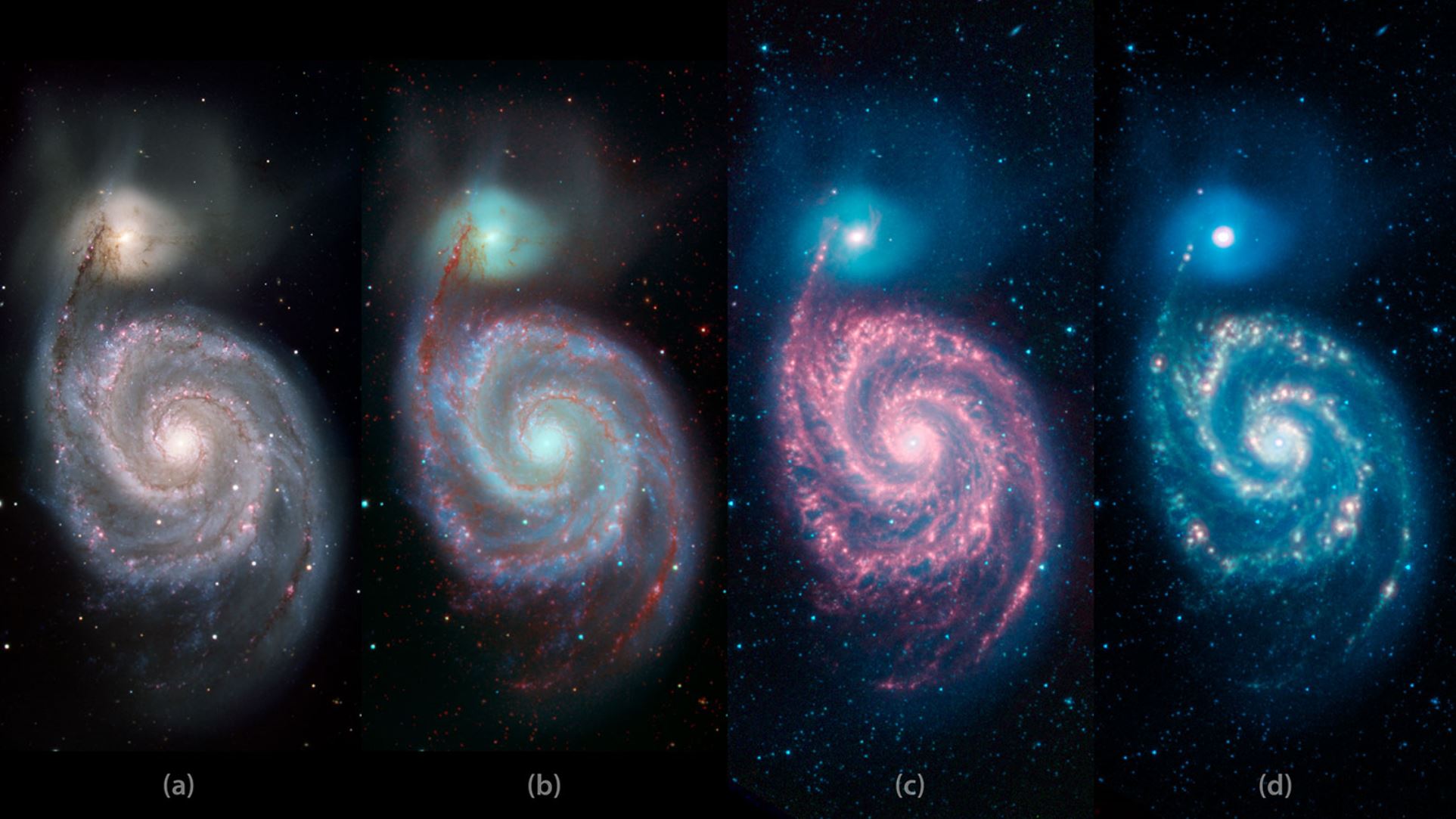
A Whirlpool 'Warhol' from NASA's Spitzer Telescope
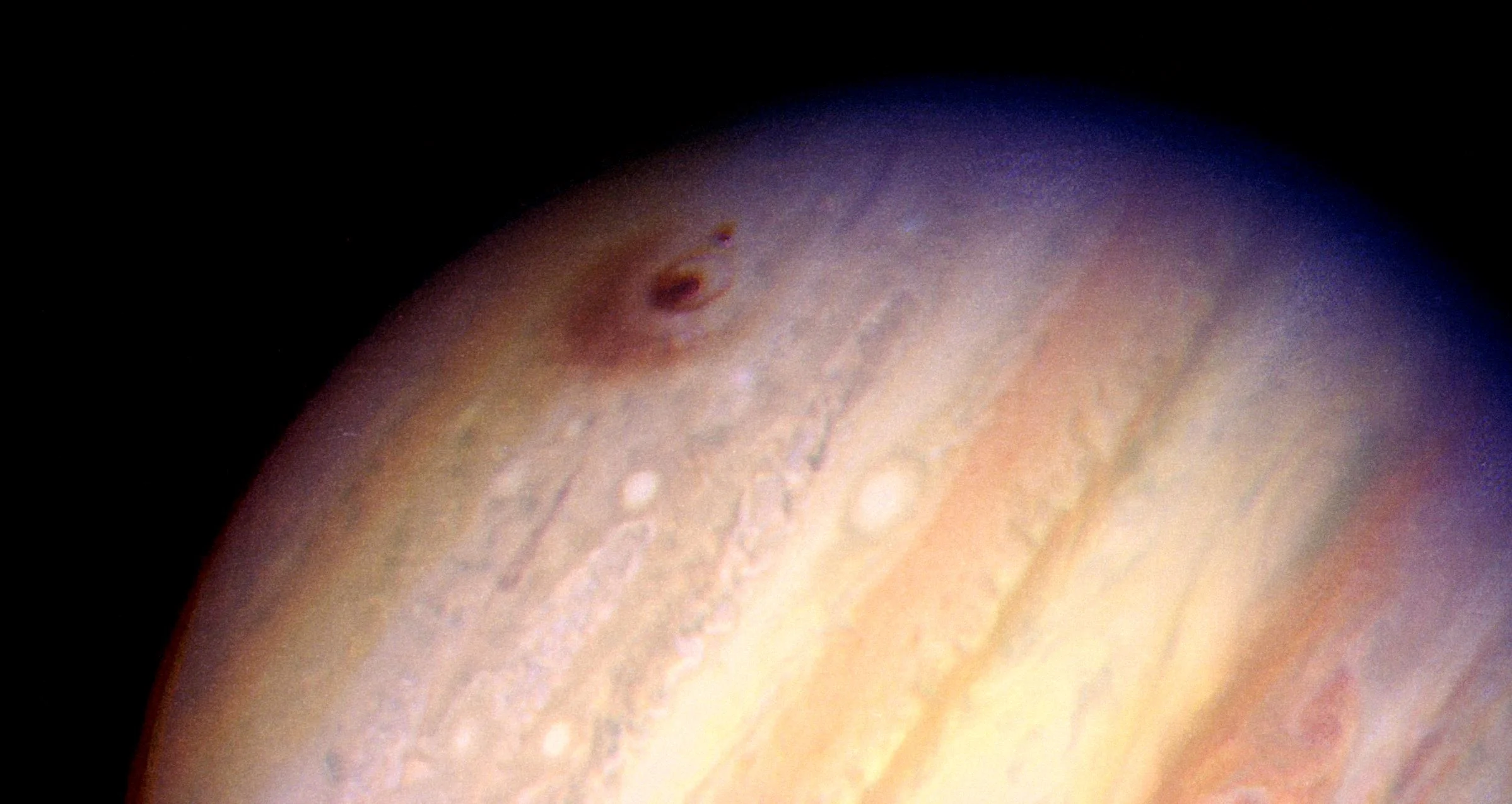
How A Historic Jupiter Comet Impact Led to Planetary Defense
Twenty-five years ago, humanity first witnessed a collision between a comet and a planet. From July 16 to 22, 1994, enormous pieces of the comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 (SL9), discovered just a year prior, crashed into Jupiter over several days, creating huge, dark scars in the planet’s atmosphere and lofting superheated plumes into its stratosphere.
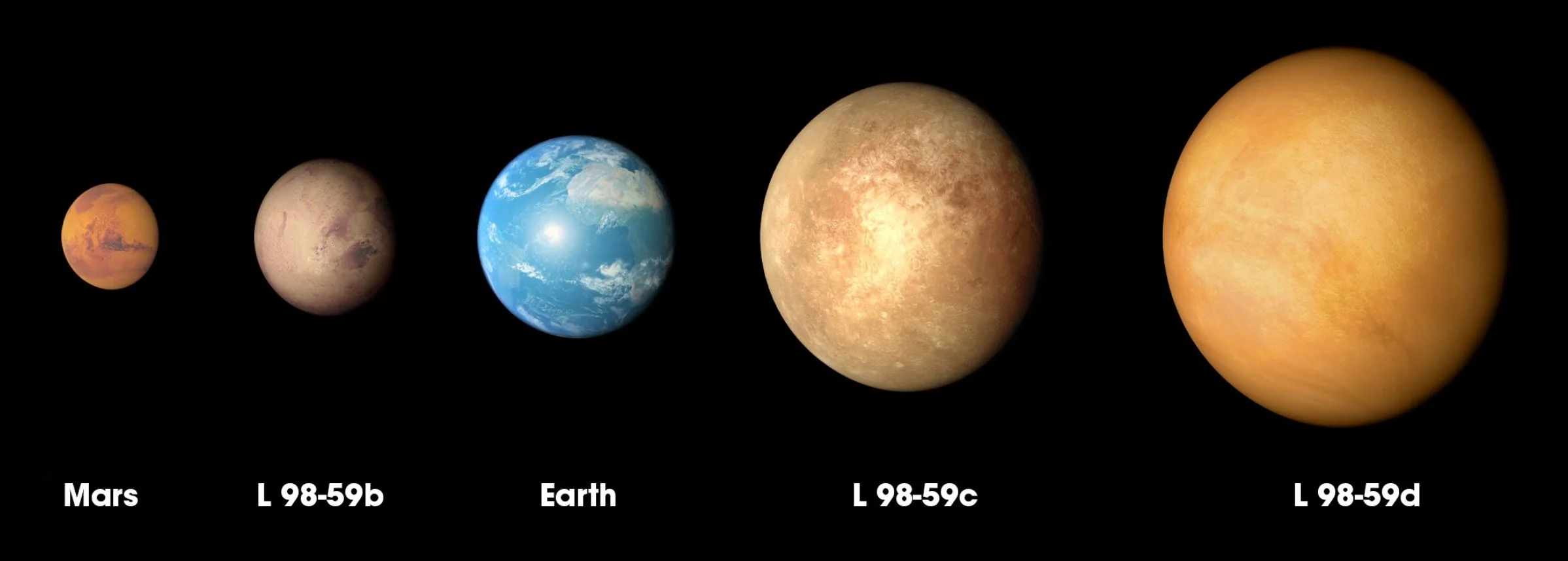
Amazing discovery of smallest exoplanet ever!
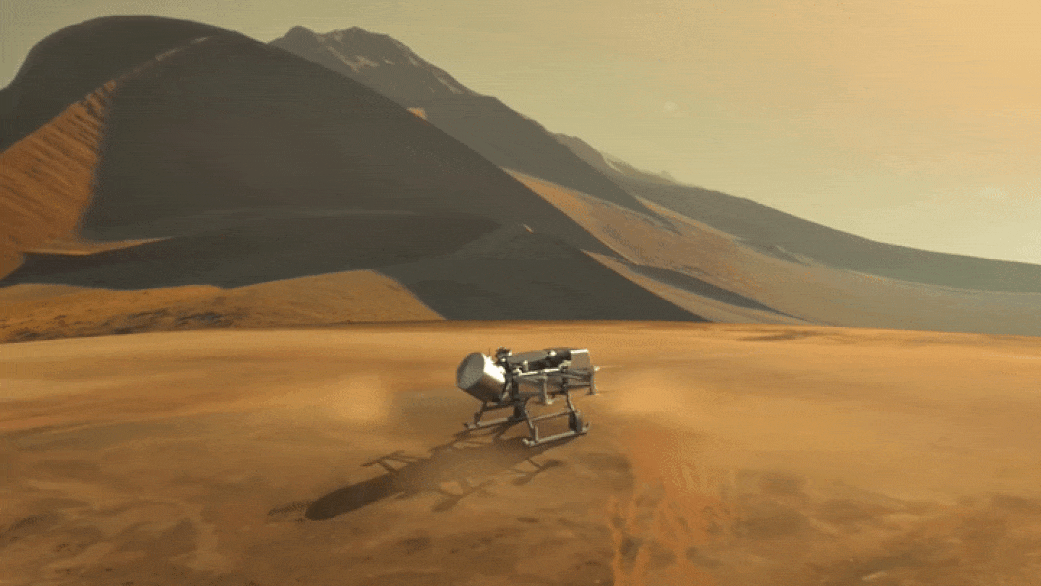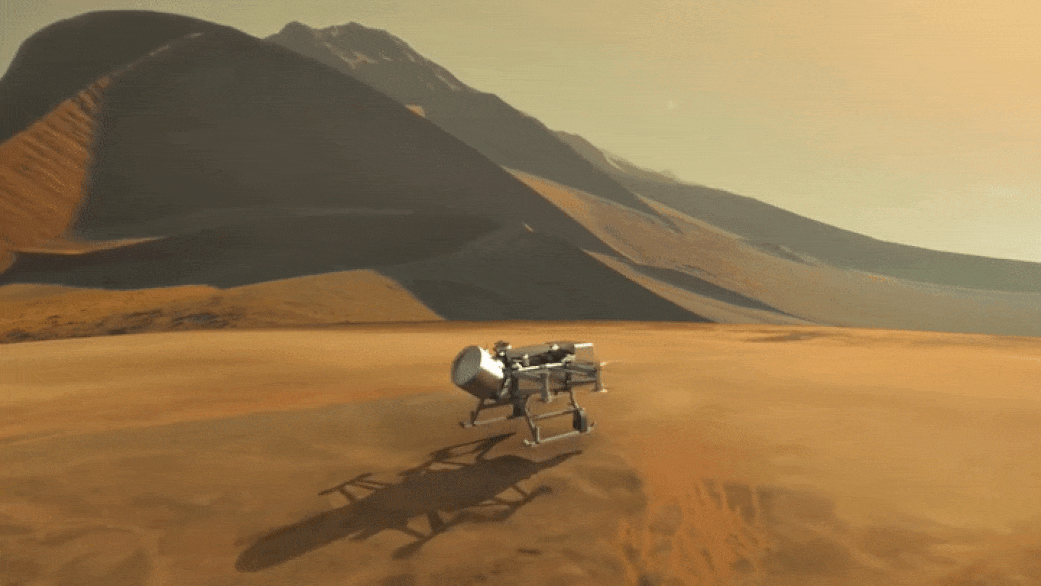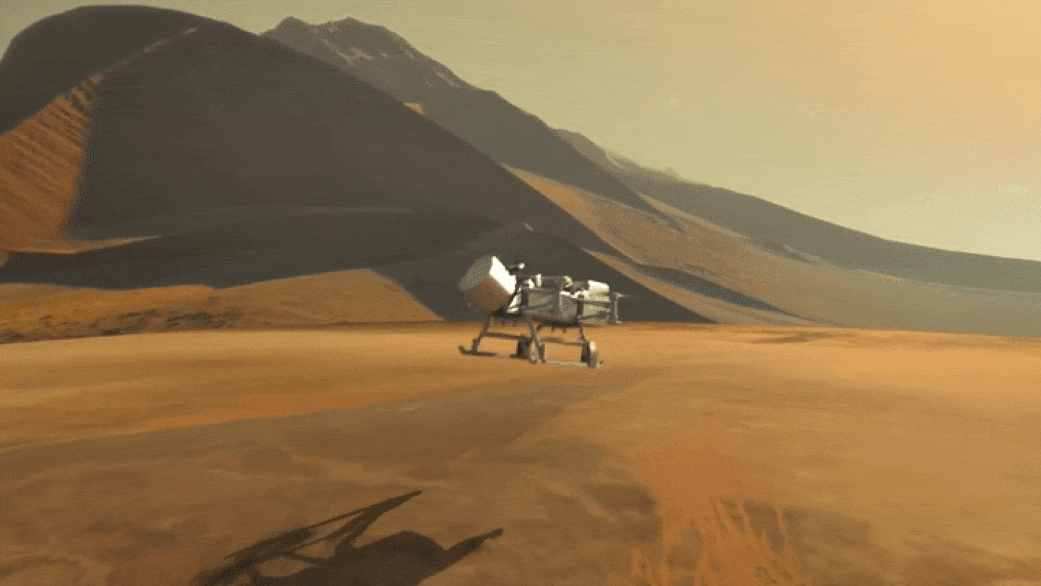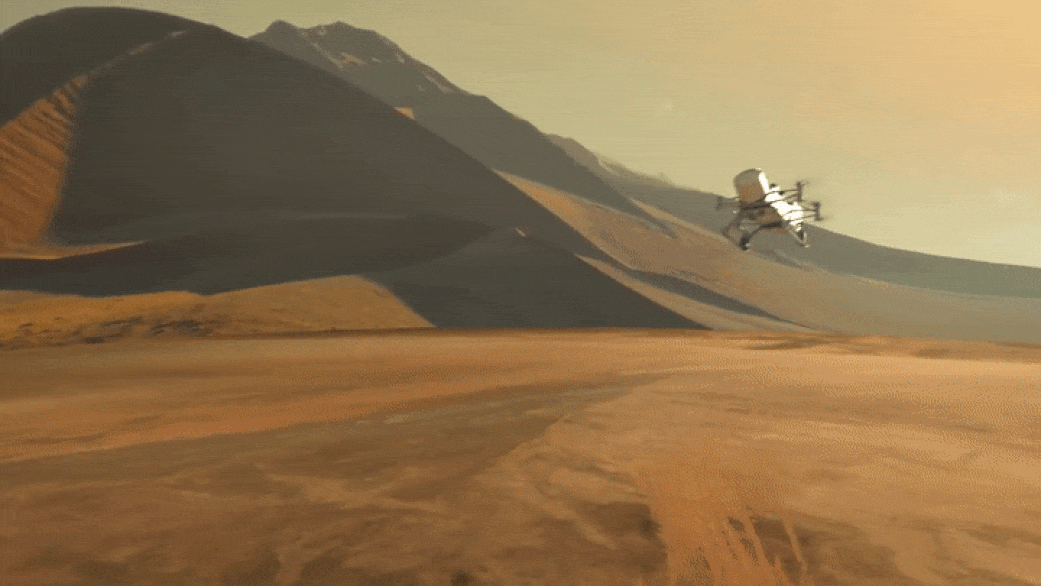
NASA's Revolutionary Dragonfly Will Fly Around Titan Looking for Origins, Signs of Life!
Accelerating exoplanet discovery using chemical fingerprints of stars
Stars are born when huge clouds of dust and gas collapse in on themselves and ignite. These clouds are made up of raw elements, like oxygen and titanium, and each cloud has a unique composition that imprints on the star. And within the stellar afterbirth – from the material that didn’t find its way into the star – planets are formed.
Lakes on Titan Might Have Exotic Crystals Encrusted Around Their Shores
Titan is a mysterious, strange place for human eyes. It’s a frigid world, with seas of liquid hydrocarbons, and a structure made up of layers of water, different kinds of ice, and a core of hydrous silicates. It may even have cryovolcanoes. Adding to the odd nature of Saturn’s largest moon is the presence of exotic crystals on the shores of its hydrocarbon lakes.
From miniature satellites to giant sun shields – the extreme technology transforming space engineering
This year marks the 50th anniversary of the first Apollo moon landing. This was possible thanks to an extraordinary acceleration of space technology. Within a remarkably short period of time leading up to the event, engineers had mastered rocket propulsion, on-board computing and space operations, partially thanks to an essentially unlimited budget.
Hubble is the Ultimate Multitasker: Discovering Asteroids While it’s Doing Other Observations
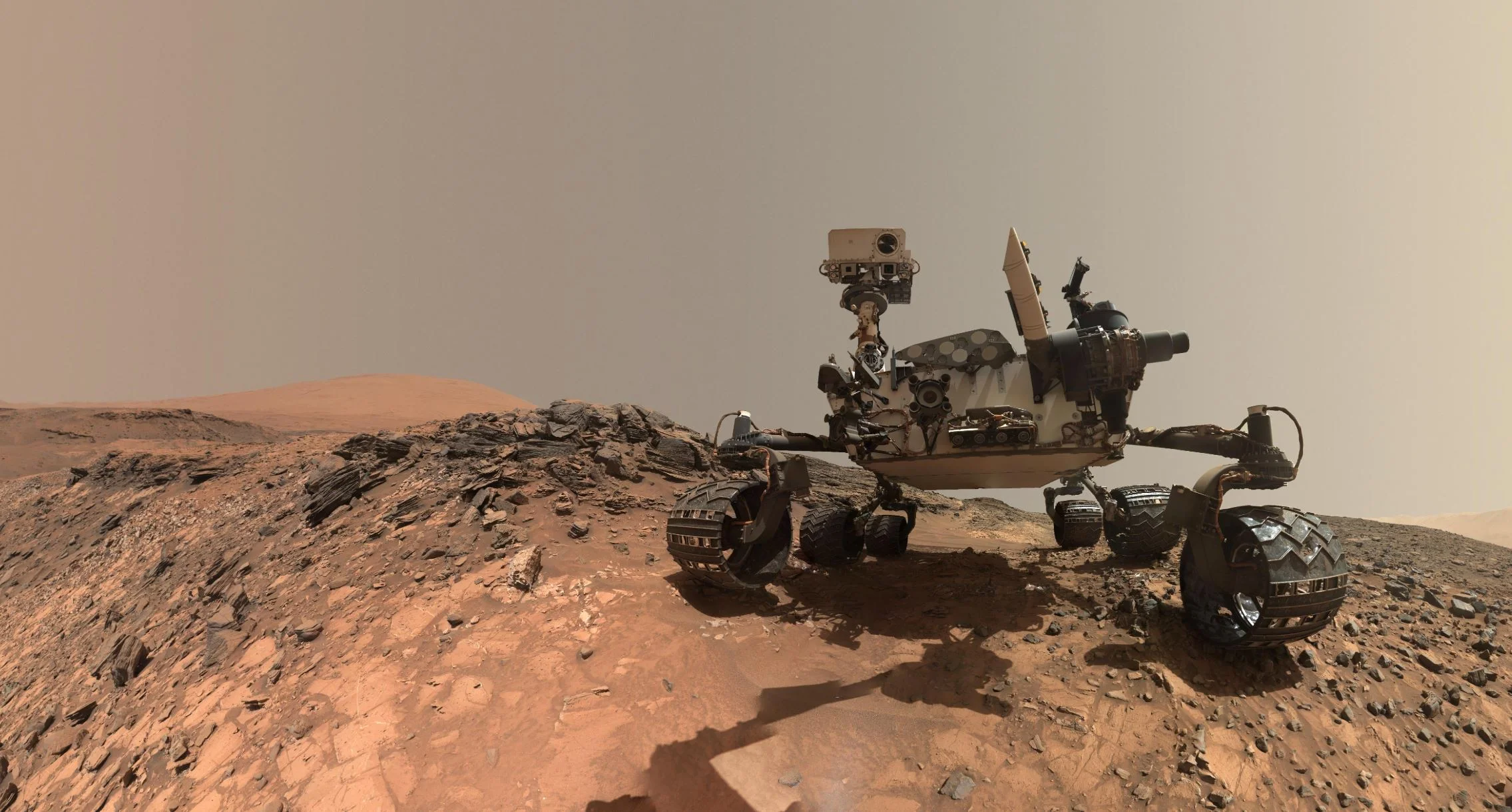
Curiosity Sniffs a Spike in Methane. Could it be a Sign of Life?
Since it landed on Mars in 2012, one of the main scientific objectives of the Curiosity rover has been finding evidence of past (or even present) life on the Red Planet. In 2014, the rover may have accomplished this very thing when it detected a tenfold increase in atmospheric methane in its vicinity and found traces of complex organic molecules in drill samples while poking around in the Gale Crater.