After almost seventy years of spaceflight, space debris has become a rather serious problem. This junk, which floats around in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), consists of the spent first rocket stages and non-functioning satellites and poses a major threat to long-term missions like the International Space Station and future space launches. And according to numbers released by the Space Debris Office at the European Space Operations Center (ESOC), the problem is only getting worse.
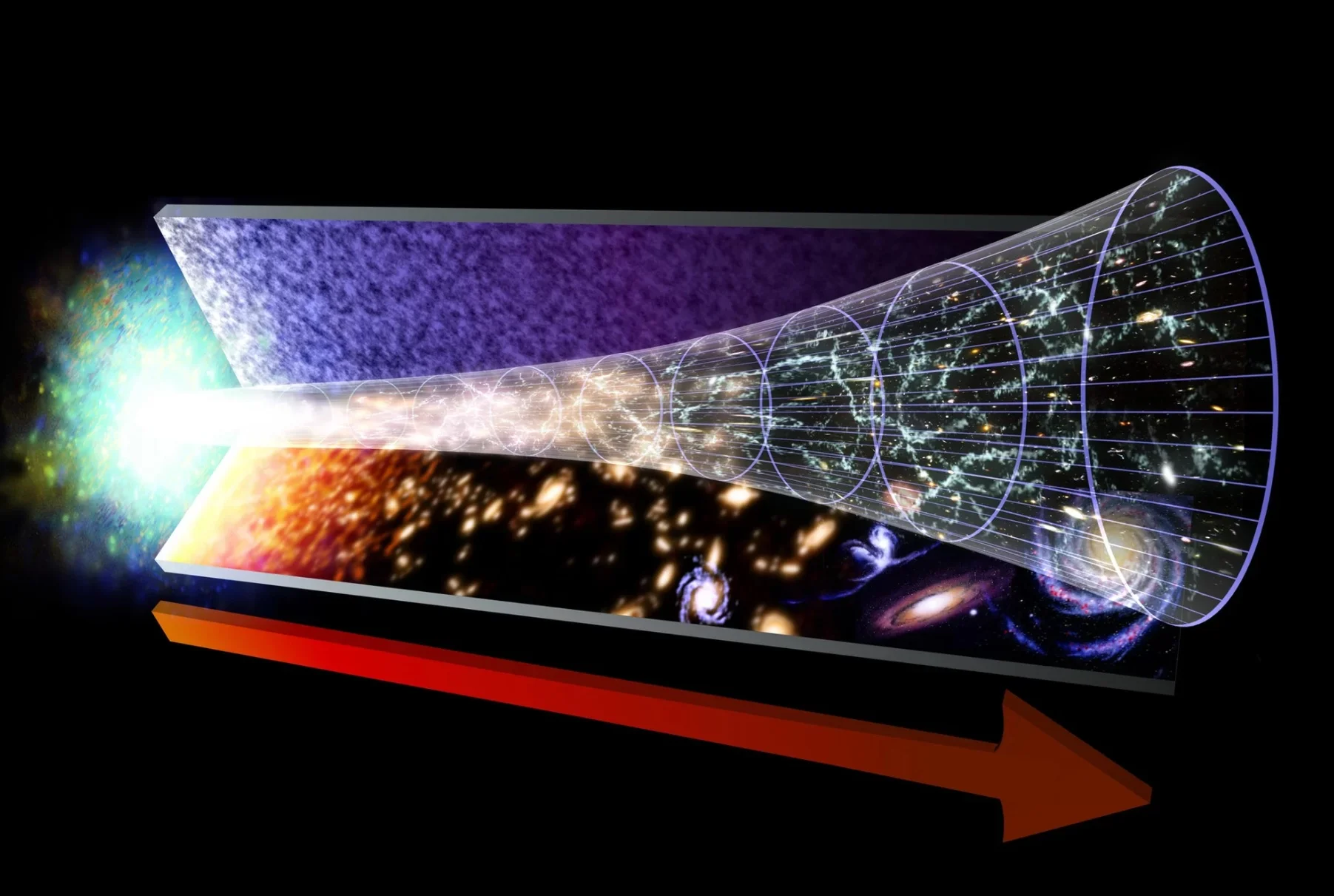
How we proved Einstein right on a galactic scale – and what it means for dark energy and dark matter
Chasing 'Oumuamua
There’s sand on titan, where does it come from?
Even though the Cassini orbiter ended its mission on of September 15th, 2017, the data it gathered on Saturn and its largest moon, Titan, continues to astound and amaze. During the thirteen years that it spent orbiting Saturn and conducting flybys of its moons, the probe gathered a wealth of data on Titan’s atmosphere, surface, methane lakes, and rich organic environment that scientists continue to pore over.
Will We Know Life When We See It? NASA-led Group Takes Stock of the Science
In the last decade we have discovered thousands of planets outside our solar system and have learned that rocky, temperate worlds are numerous in our galaxy. The next step will involve asking even bigger questions. Could some of these planets host life? And if so, will we be able to recognize life elsewhere if we see it?
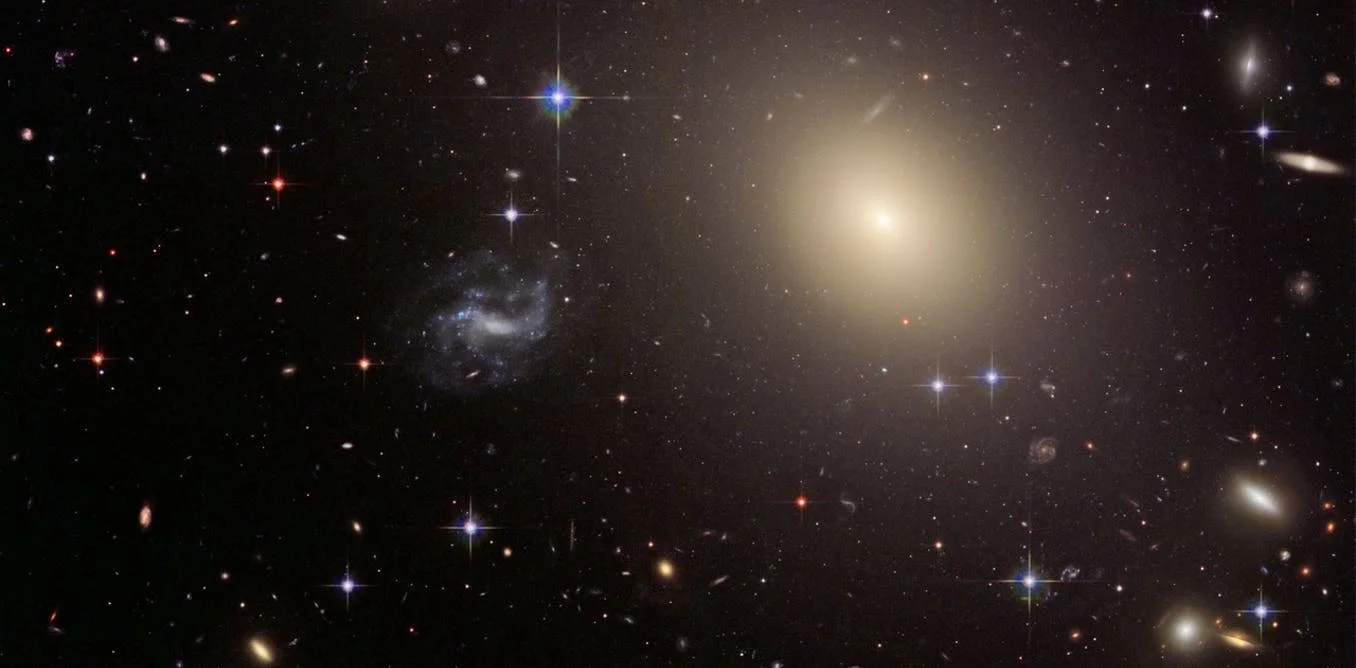
Red Nuggets’ Are Galactic Gold for Astronomers
About a decade ago, astronomers discovered a population of small, but massive galaxies called “red nuggets.” A new study using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory indicates that black holes have squelched star formation in these galaxies and may have used some of the untapped stellar fuel to grow to unusually massive proportions.
Why alcohol after sport and exercise is a bad idea
How we proved Einstein right on galactic scales – and what it means for dark energy and dark matter
How an advanced civilization could stop dark energy from preventing their future exploration
During the 1930s, astronomers came to realize that the Universe is in a state of expansion. By the 1990s, they realized that the rate at which it is expansion is accelerating, giving rise to the theory of “Dark Energy”. Because of this, it is estimated that in the next 100 billion years, all stars within the Local Group – the part of the Universe that includes a total of 54 galaxies, including the Milky Way – will expand beyond the cosmic horizon.
Could cyanobacteria help to terraform mars?
Billions of years ago, Earth’s atmosphere was much different than it is today. Whereas our current atmosphere is a delicate balance of nitrogen gas, oxygen and trace gases, the primordial atmosphere was the result of volcanic outgassing – composed primarily of carbon dioxide, methane, ammonia, and other harsh chemicals. In this respect, our planet’s ancient atmosphere has something in common with Mars’ current atmosphere.
Once in a Blue Dune
What is the summer solstice? An astronomer explains
The summer solstice marks the official start of summer. It brings the longest day and shortest night of the year for the 88 percent of Earth’s people who live in the Northern Hemisphere. People around the world observe the change of seasons with bonfires and festivals and Fête de la Musique celebrations.
You’re eating microplastics in ways you don’t even realize
We’re increasingly aware of how plastic is polluting our environment. Much recent attention has focused on how microplastics – tiny pieces ranging from 5 millimetres down to 100 nanometres in diameter – are filling the seas and working their way into the creatures that live in them. That means these ocean microplastics are entering the food chain and, ultimately, our bodies.
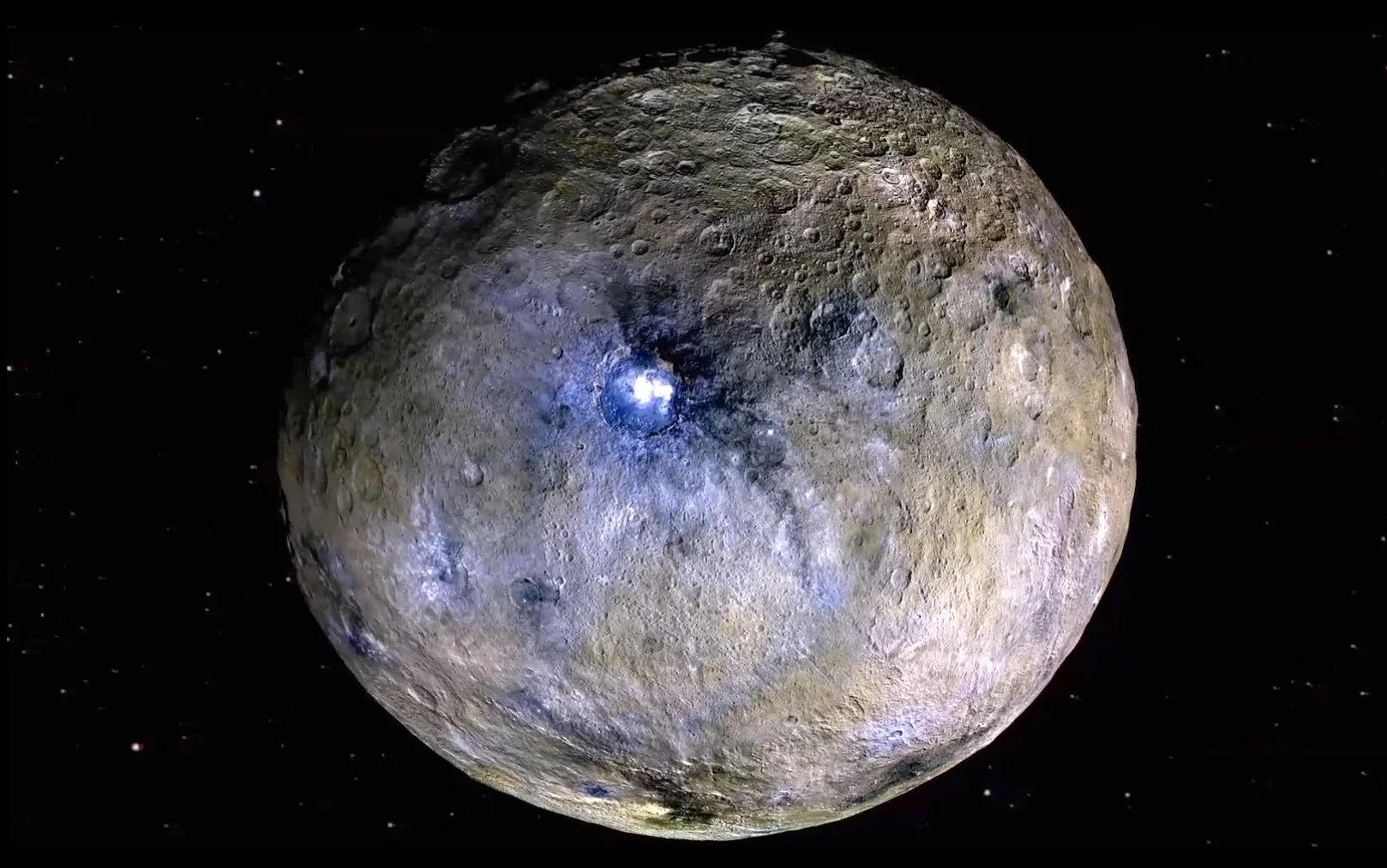
Ceres has even more organic molecules on it than previously thought!
In March of 2015, NASA’s Dawn mission became the first spacecraft to visit the protoplanet Ceres, the largest body in the Main Asteroid Belt. It was also the first spacecraft to visit a dwarf planet, having arrived a few months before the New Horizons mission made its historic flyby of Pluto. Since that time, Dawn has revealed much about Ceres, which in turn is helping scientists to understand the early history of the Solar System.
Getting hot and sweaty: how heat and spice might affect our appetite
New way to find baby gas giants is way more accurate
Wollemi pines are dinosaur trees
To avoid humans, more wildlife now work the night shift
For their first 100 million years on planet Earth, our mammal ancestors relied on the cover of darkness to escape their dinosaur predators and competitors. Only after the meteor-induced mass extinction of dinosaurs66 million years ago could these nocturnal mammals explore the many wondrous opportunities available in the light of day.
The secret information hidden in your hair
Your hair can say a lot about you. It doesn’t just give people clues about your personality or your taste in music. It can also record evidence of how much you drink, whether you smoke or take drugs, and perhaps even how stressed you are. My colleagues and I research how hair can be used to provide more accurate testing for these attributes. And a recent court case shows how far the technology has come.
A powerful dust storm has darkened the skies over opportunity on mars
NASA’s Opportunity mission can rightly be called the rover that just won’t quit. Originally, this robotic rover was only meant to operate on Mars for 90 Martian days (or sols), which works out to a little over 90 Earth days. However, since it made its landing on January 25th, 2004, it has remained in operation for 14 years, 4 months, and 18 days – exceeding its operating plan by a factor of 50!